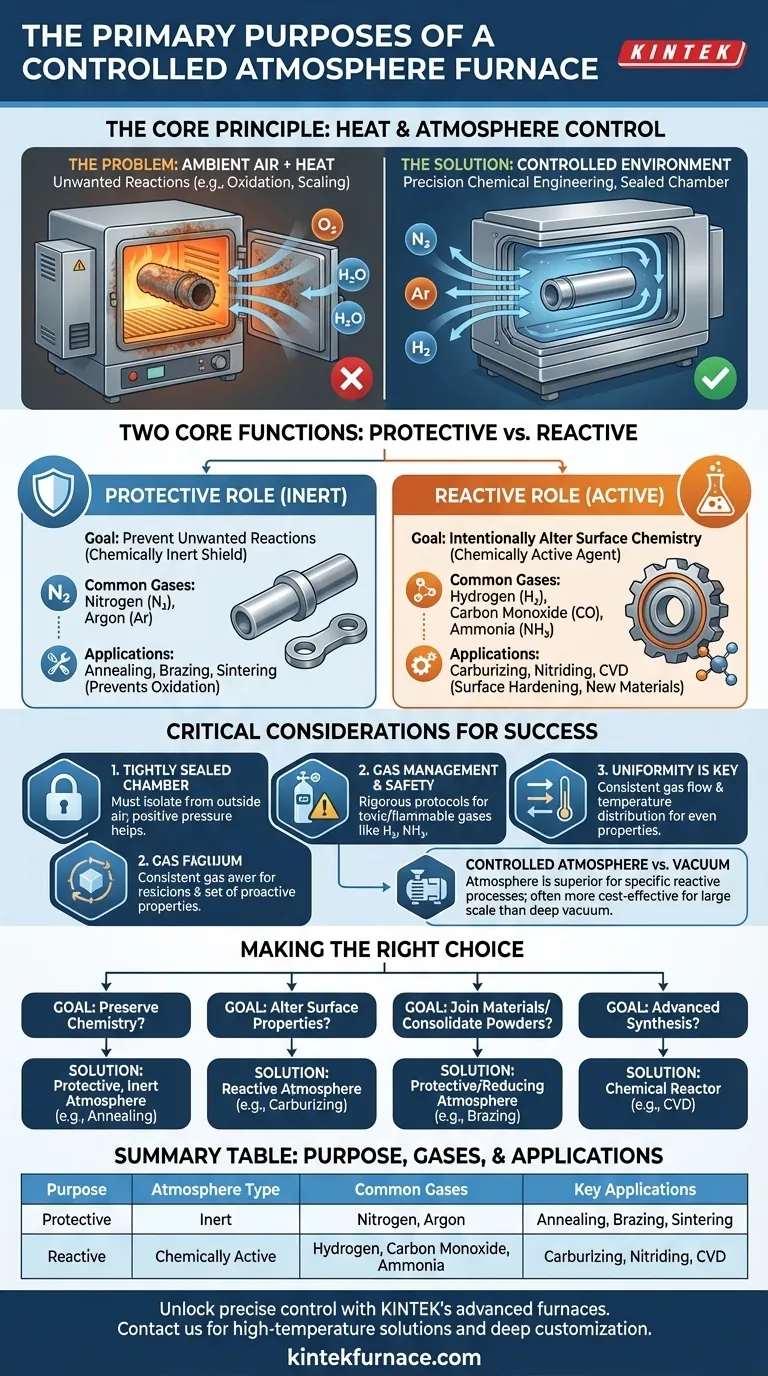
At its core, a controlled atmosphere furnace serves two opposite but equally critical purposes. It either creates a chemically inert environment to protect a material from unwanted reactions like oxidation during high-temperature processing, or it establishes a chemically active environment to intentionally change the material's surface properties.
A controlled atmosphere furnace is not just a heating device; it is a precision tool for chemical engineering. By replacing ambient air with a specific gas mixture, it gives you direct control over the chemical reactions that occur on a material's surface at high temperatures, which is essential for achieving desired final properties.

The Fundamental Principle: Why Control the Atmosphere?
The Problem with Heat and Air
When materials are heated to high temperatures, their atoms become highly energized and reactive.
Exposing a hot workpiece to ambient air, which contains roughly 21% oxygen and traces of water vapor, almost guarantees unwanted chemical reactions. The most common of these is oxidation, which can create a layer of scale, degrade surface finish, and compromise the material's structural integrity.
The Solution: A Purpose-Built Environment
A controlled atmosphere furnace solves this problem by creating a hermetically sealed chamber. Before heating, the ambient air is purged and replaced with a carefully selected gas or gas mixture.
This engineered atmosphere allows the thermal process (like annealing or brazing) to occur without interference from oxygen or other contaminants, ensuring the material's properties are determined by the heat treatment alone, not by random, uncontrolled surface reactions.
Two Core Functions: Protective vs. Reactive Atmospheres
The specific purpose of the furnace dictates the type of atmosphere used. These fall into two main categories: protective or reactive.
The Protective Role: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The primary goal of a protective atmosphere is to be chemically inert. It serves as a shield, safeguarding the material's surface from changing during the heating and cooling cycles.
Common applications include annealing, brazing, and sintering. In these processes, preventing oxidation is critical. An oxide layer on parts being brazed would prevent the filler metal from properly wetting and bonding, resulting in a failed joint.
Typical protective gases are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar). They are stable and do not readily react with most materials, even at high temperatures.
The Reactive Role: Inducing Chemical Change
Conversely, a reactive atmosphere is chosen to intentionally alter the material's surface chemistry. The gas itself becomes a key ingredient in the process, diffusing into the material to change its properties.
This is the principle behind surface-hardening processes. In carburizing, a carbon-rich atmosphere (using gases like carbon monoxide) diffuses carbon into the surface of steel to make it harder. In nitriding, a nitrogen-rich atmosphere (often from dissociated ammonia) forms hard nitride compounds on the surface.
Common reactive gases include Hydrogen (H₂) for reducing oxides, Carbon Monoxide (CO) for carburizing, and Ammonia (NH₃) for nitriding.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Considerations
While powerful, controlled atmosphere furnaces introduce operational complexities that must be managed for successful and safe operation.
A Tightly Sealed Chamber is Non-Negotiable
The entire principle relies on isolating the internal atmosphere from the outside air. Even a small leak can introduce oxygen, compromising the entire process. These furnaces require robust seals and are often run at a slight positive pressure to ensure any leakage flows outward, not inward.
Gas Management and Safety
Using reactive, flammable, or toxic gases like hydrogen or ammonia demands rigorous safety protocols. This includes leak detection systems, ventilation, pressure-relief mechanisms, and sometimes explosion-proof designs. The cost and complexity of this gas handling infrastructure are a significant consideration.
Uniformity is Key
It's not enough to simply fill the chamber with the right gas. The furnace must be designed to ensure uniform atmosphere flow and temperature distribution. Inconsistent conditions can lead to variations in material properties across the workpiece, such as uneven hardening or incomplete brazing.
Controlled Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
A vacuum furnace also prevents oxidation by removing the atmosphere entirely. However, a controlled atmosphere is superior for reactive processes (like carburizing) that require a specific gas. It's also often more cost-effective for large-scale processes where achieving a deep vacuum is not essential but preventing oxidation is.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the type of atmosphere and process parameters you will need.
- If your primary focus is preserving a material's existing chemistry during heat treatment: You need a protective, inert atmosphere using gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is intentionally altering a material's surface properties for hardness: You require a precisely controlled reactive atmosphere for processes like carburizing or nitriding.
- If your primary focus is joining materials via brazing or consolidating powders via sintering: You need a protective or slightly reducing atmosphere to eliminate oxide layers and ensure clean, strong metallurgical bonds.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis like CVD or graphitization: You will use the furnace as a chemical reactor, where precursor gases react to form entirely new materials.
Ultimately, mastering atmospheric control is the key to unlocking precise, repeatable, and high-quality outcomes in modern materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Atmosphere Type | Common Gases | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective | Inert | Nitrogen, Argon | Annealing, Brazing, Sintering |
| Reactive | Chemically Active | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide, Ammonia | Carburizing, Nitriding, CVD |
Unlock precise control over your material processes with KINTEK's advanced controlled atmosphere furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















