At its core, an IGBT induction melting furnace is characterized by its use of modern solid-state electronics to achieve exceptional efficiency, precise control, and high reliability. Its key operational features include constant power output for faster melting, minimal electrical interference with the power grid, advanced digital controls for automation, and robust self-protection mechanisms.
The defining advantage of an IGBT furnace is not just one feature, but how its integrated digital system delivers consistent high performance. Unlike older technologies, it maintains full power throughout the entire melting cycle, dramatically increasing speed and energy efficiency while reducing operational complexity.

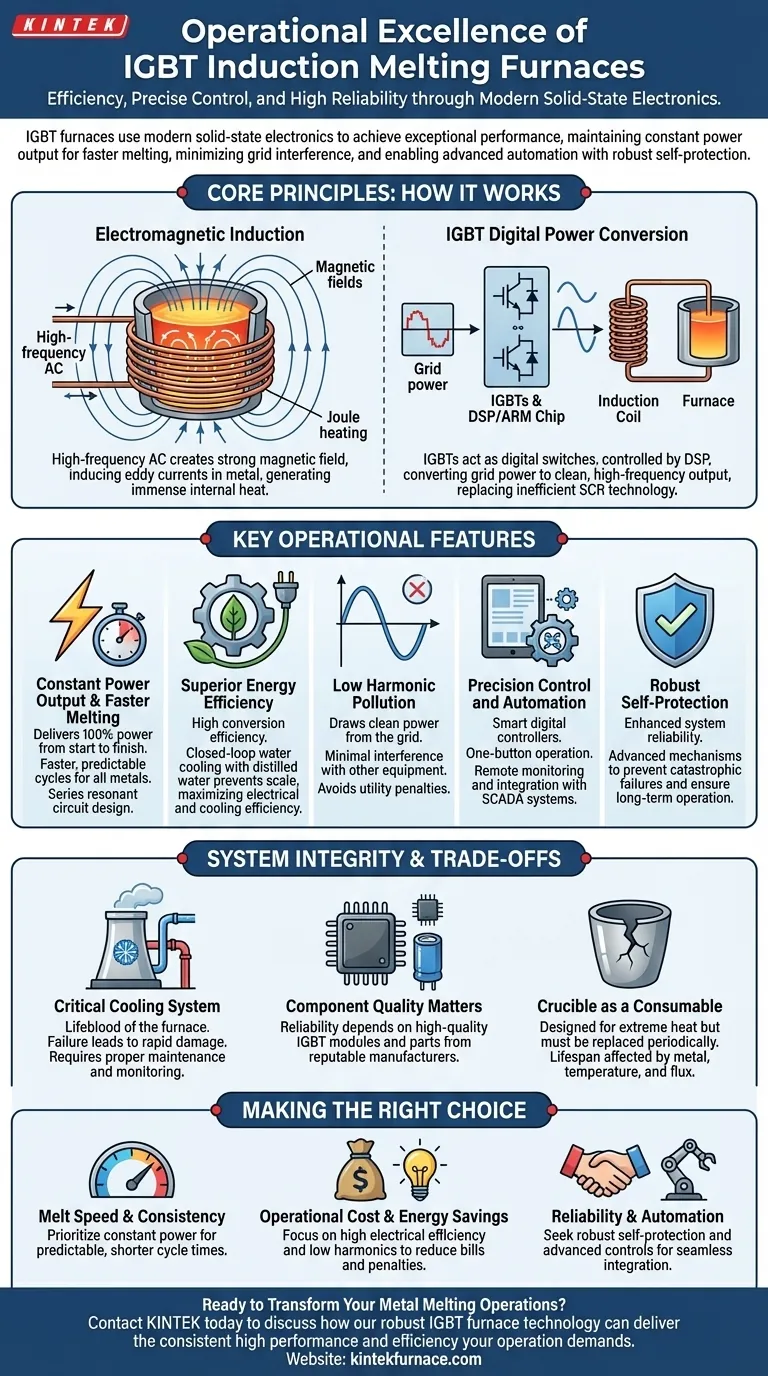
How an IGBT Furnace Works: The Core Principles
An IGBT furnace modernizes the century-old principle of induction heating by replacing legacy power components with advanced digital technology. This shift is the source of its primary operational benefits.
The Foundation: Electromagnetic Induction
The fundamental process remains the same as in all induction furnaces. A high-frequency alternating current is passed through a water-cooled copper coil.
This current generates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field inside the coil. When conductive material like steel or copper is placed within this field, the field induces strong internal electrical currents, known as eddy currents.
The material's natural electrical resistance fights against these eddy currents, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating, which quickly melts the metal from the inside out.
The IGBT Advantage: Digital Power Conversion
The key innovation is how the furnace creates the high-frequency current. IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) are high-power, fast-switching electronic components.
These transistors act as digital switches, chopping up the standard grid electricity and re-forming it into a clean, high-frequency output. They are controlled by a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) or ARM chip, which allows for precise management of power and frequency.
This digital approach is a significant upgrade over older SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) technology, which was less efficient, harder to control, and created significant electrical noise.
Key Operational Features Explained
The use of IGBT technology translates directly into tangible benefits on the factory floor. These features are not isolated; they work together to create a more efficient and reliable melting system.
Constant Power Output & Faster Melting
Perhaps the most significant operational benefit is the furnace's ability to maintain constant power output.
Because of its series resonant circuit design, the system's power delivery is not affected by changes in the electrical load or the thickness of the furnace lining. It delivers 100% power from the start of the melt to the very end.
This results in measurably faster melting times and predictable cycle durations, a critical advantage for production planning, especially when melting stainless steel, copper, or aluminum.
Superior Energy Efficiency
The system is engineered for efficiency at every level. The IGBT power supply itself has a very high conversion efficiency, minimizing wasted energy.
Furthermore, the closed-loop water cooling system often uses distilled water and heat exchangers. This prevents the buildup of scale and mineral deposits inside the critical copper coils, ensuring maximum cooling and electrical efficiency are maintained over the long term.
Low Harmonic Pollution
Older SCR-based furnaces were notorious for creating harmonic pollution—a form of electrical noise that distorts the power grid's sine wave. This can interfere with other sensitive electronic equipment in the factory and lead to penalties from the utility provider.
IGBT furnaces produce exceptionally low harmonics. This means they draw clean power from the grid, ensuring they operate without disrupting other factory equipment and avoiding power quality issues.
Precision Control and Automation
Modern IGBT furnaces are managed by smart, all-digital controllers. This enables features like one-button operation for simplified startup and shutdown sequences.
These systems also include rich communication interfaces, allowing for remote monitoring, control, and integration into larger factory automation or SCADA systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and System Integrity
While highly advanced, the performance of an IGBT furnace is dependent on the integrity of its core systems. Understanding these dependencies is key to ensuring reliability.
The Critical Role of the Cooling System
The furnace's high power density generates immense heat, not just in the metal but in the electronics and copper coil. The water cooling system is not an accessory; it is the lifeblood of the furnace.
A failure in the cooling loop—whether from a pump failure, a blockage, or a leak—can lead to a rapid and catastrophic failure of the power supply or the coil itself. Proper maintenance of the cooling circuit is non-negotiable.
The Importance of Component Quality
The reliability of an IGBT furnace is directly tied to the quality of its electronic components. The IGBT modules, capacitors, and control board are sophisticated and operate under high stress.
Systems built with components from reputable, top-tier manufacturers demonstrate significantly higher long-term reliability and are less prone to premature failure. Sourcing a furnace from a proven manufacturer is critical.
The Furnace Crucible as a Consumable
The crucible, typically made of graphite or a specialized ceramic, holds the molten metal. It is designed to withstand extreme temperatures but is ultimately a consumable item.
The lifespan of the crucible is affected by the type of metal being melted, the pouring temperature, and the chemical additives (flux) used. Its replacement represents a recurring operational cost that must be factored into financial planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the right melting technology depends on balancing your primary production goals with operational realities.
- If your primary focus is melt speed and consistency: The constant power output of an IGBT furnace is its defining advantage, delivering predictable and shorter cycle times compared to older technologies.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and energy savings: The combination of high electrical efficiency and low harmonic pollution directly reduces electricity bills and eliminates the risk of power factor penalties.
- If your primary focus is reliability and automation: Seek out systems with robust self-protection functions, documented use of high-quality electronic components, and advanced digital controls for seamless integration.
By understanding the principles behind its features, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|
| Constant Power Output | Faster, more predictable melting cycles from start to finish. |
| Superior Energy Efficiency | Lower electricity bills and minimal wasted energy. |
| Low Harmonic Pollution | Clean power draw, avoiding grid interference and penalties. |
| Advanced Digital Control | Simplified automation, remote monitoring, and precise management. |
| Robust Self-Protection | Enhanced system reliability and reduced risk of catastrophic failure. |
Ready to Transform Your Metal Melting Operations?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides foundries and metalworking facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including IGBT Induction Melting Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements—whether your focus is on maximizing melt speed, minimizing operational costs, or achieving full automation.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our robust IGBT furnace technology can deliver the consistent high performance and efficiency your operation demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















