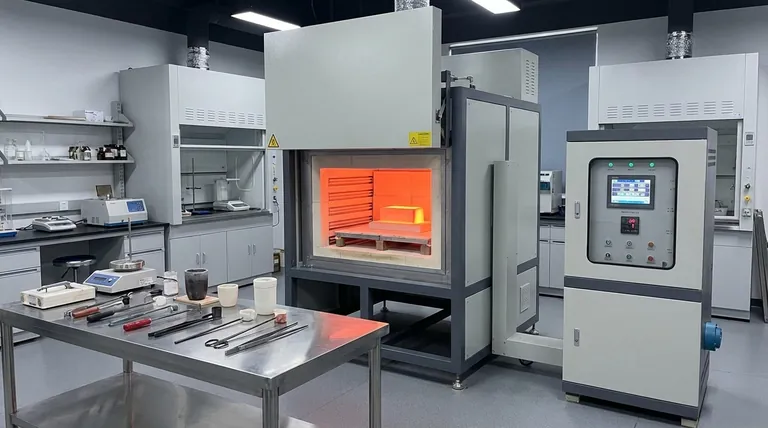
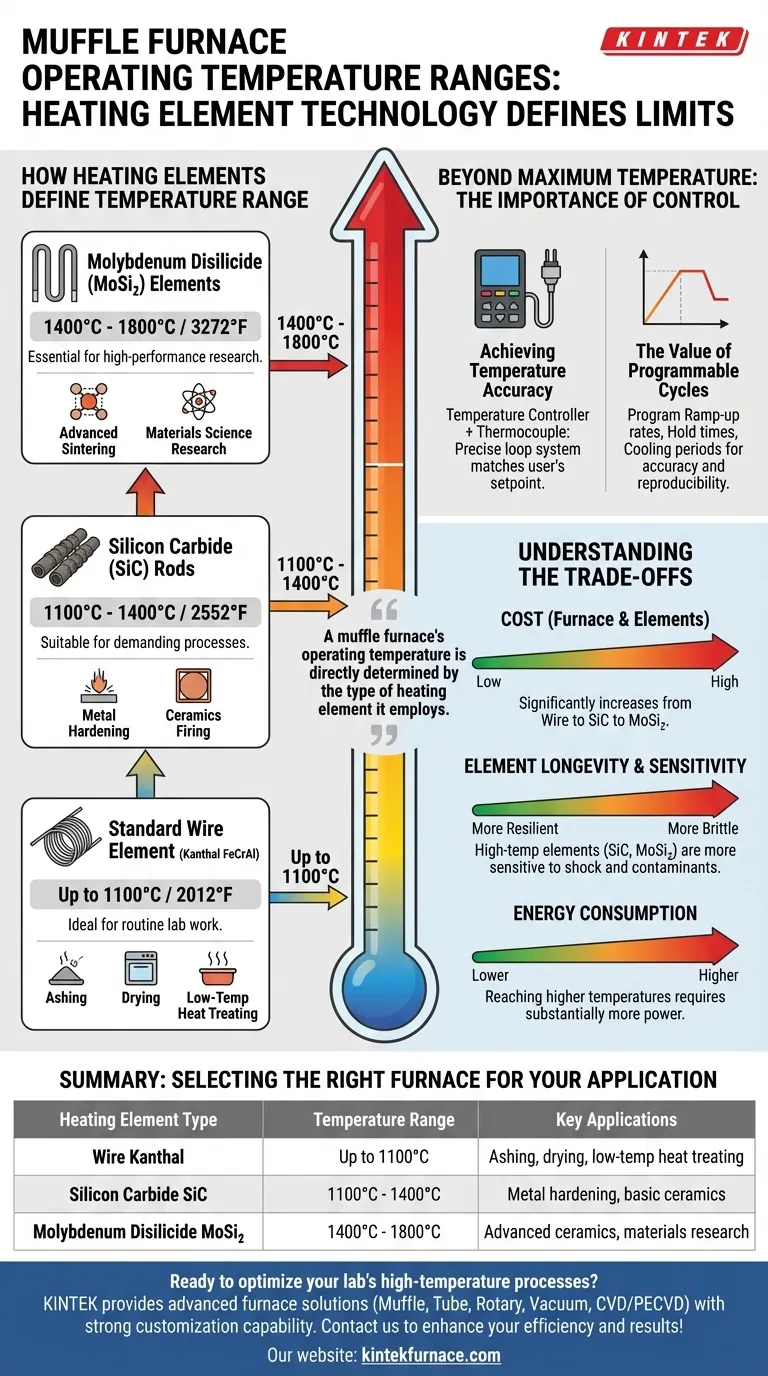
A muffle furnace's operating temperature is not a single specification but is directly determined by the type of heating element it employs. For general-purpose applications below 1100°C, furnaces typically use metallic wire elements. For higher temperatures up to 1400°C, they rely on silicon carbide rods, and for extreme heat up to 1800°C, they use silicon molybdenum elements.
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is dictated by its heating element technology. Choosing the right furnace means matching the element type to your specific temperature requirements, as this decision impacts cost, performance, and application suitability.

How Heating Elements Define Temperature Range
The core of any muffle furnace is its heating element. The material used for this element is the primary factor limiting the furnace's maximum achievable temperature and its ideal operating range.
Standard Wire Element Furnaces (Up to 1100°C / 2012°F)
These are the most common and cost-effective muffle furnaces, often referred to as standard box furnaces.
They use metallic wire elements, typically a Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloy, which are wound around the ceramic muffle chamber. They are ideal for routine laboratory work like ashing, drying, and low-temperature heat treating.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Furnaces (1100°C - 1400°C / 2552°F)
To achieve temperatures beyond the limits of wire elements, furnaces employ silicon carbide (SiC) rods.
These robust ceramic elements can operate at significantly higher temperatures. This makes them suitable for more demanding processes, including some metal hardening applications and the firing of certain ceramics.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Furnaces (1400°C - 1800°C / 3272°F)
For high-performance and research applications, furnaces use molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements.
These specialized U-shaped elements can reach extreme temperatures, making them essential for sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, and conducting materials science research at the highest heat levels.
Beyond Maximum Temperature: The Importance of Control
Simply reaching a high temperature is not enough; precise and repeatable control is what ensures successful outcomes. Modern furnaces achieve this through sophisticated control systems.
Achieving Temperature Accuracy
A temperature controller is the brain of the furnace. It works in a closed loop with a sensor, typically a thermocouple, placed inside the chamber. This system constantly measures the internal temperature and adjusts power to the heating elements to precisely match the user's setpoint.
The Value of Programmable Cycles
Modern digital controllers allow you to program entire heating profiles. This includes setting specific ramp-up rates (how fast it heats up), hold times (how long it stays at a specific temperature), and cooling periods. This programmability is critical for processes that require controlled thermal treatment, ensuring accuracy and reproducibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing capability with practical constraints. A higher temperature rating always comes with trade-offs.
Cost vs. Capability
The primary trade-off is cost. As the maximum operating temperature increases from a wire element to SiC to MoSi₂, the price of the furnace, and its replacement elements, increases significantly.
Element Longevity
High-temperature elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are more brittle and can be more sensitive to thermal shock or atmospheric contaminants than standard wire elements. Proper use and care are essential to maximize their lifespan.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining higher temperatures requires substantially more electrical power. The energy cost of operating an 1800°C furnace is much greater than that of an 1100°C model.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choose a furnace whose maximum temperature comfortably exceeds your required process temperature, but avoid over-specifying, as it adds unnecessary cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, drying, tempering below 1100°C): A standard wire element furnace offers the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is metal heat treatment or basic ceramics (up to 1400°C): A silicon carbide (SiC) furnace provides the necessary higher temperature range.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or high-temp sintering (above 1400°C): A molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) furnace is essential for reaching the required temperatures up to 1800°C.
Ultimately, understanding the link between heating element technology and temperature range empowers you to invest in a tool that precisely meets your technical and budgetary needs.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Wire (Kanthal) | Up to 1100°C | Ashing, drying, low-temperature heat treating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1100°C - 1400°C | Metal hardening, basic ceramics firing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1400°C - 1800°C | Advanced ceramics sintering, materials research |
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















