In professional practice, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) is primarily produced through sintering. A secondary method, plasma spraying, is also employed to create dense monolithic forms and specialized composites.
The method chosen to produce molybdenum disilicide is not merely a manufacturing step; it is a critical decision that directly influences the material's final density, crystal structure, and ultimately, its performance in high-temperature, oxidative environments.
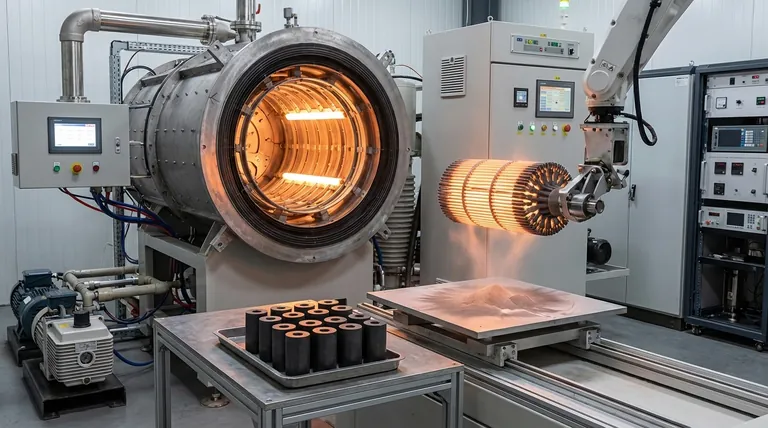

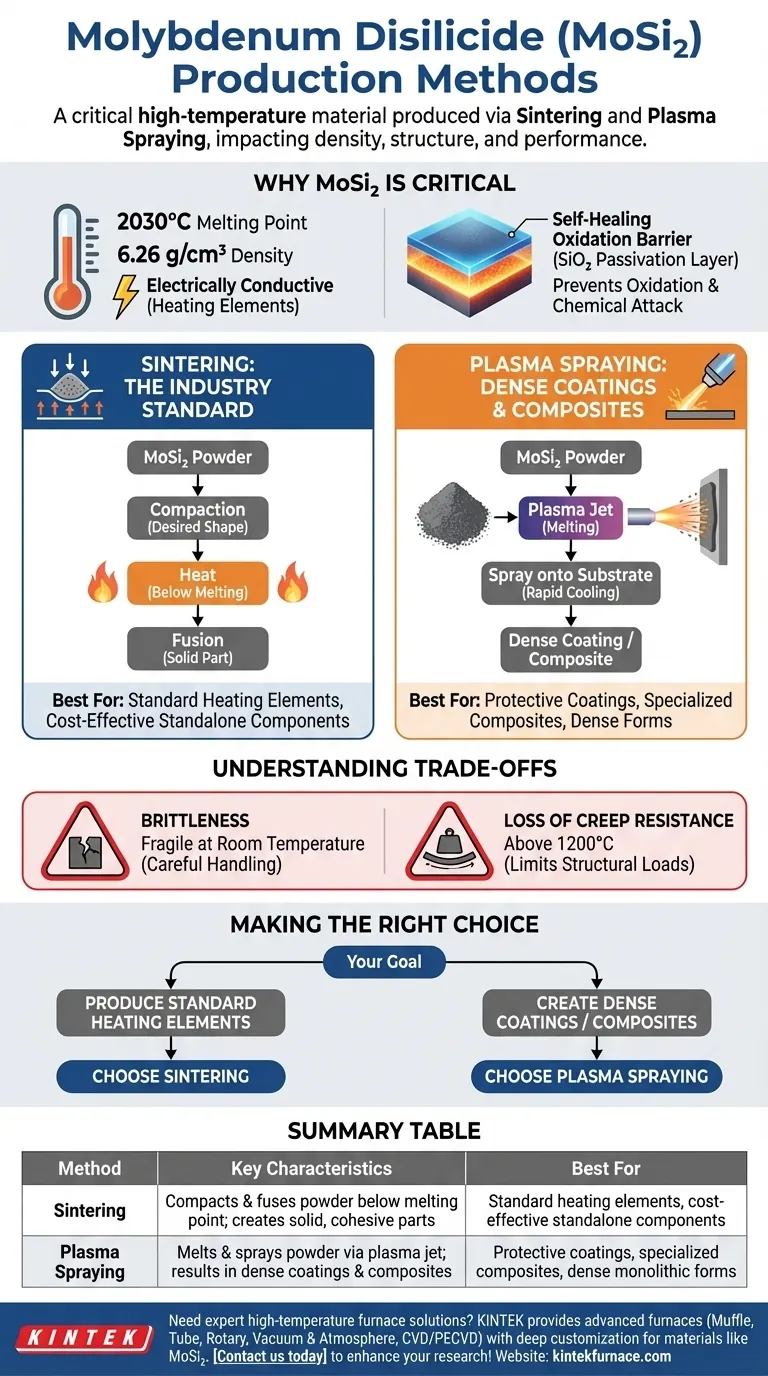
Why MoSi₂ is a Critical High-Temperature Material
To understand the production methods, we must first recognize the properties that make MoSi₂ so valuable. It is an intermetallic compound, a type of material that sits between a metal and a ceramic.
Core Physical and Electrical Properties
Molybdenum disilicide has a moderate density of 6.26 g/cm³ and an exceptionally high melting point of 2030°C (3686°F).
Crucially, it is electrically conductive, which allows it to function as a resistive heating element capable of operating at extreme temperatures.
The Self-Healing Oxidation Barrier
The most important characteristic of MoSi₂ is its behavior at high temperatures. When heated, it forms a protective, or passivation, layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
This thin glass-like layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying material from further oxidation and chemical attack, which is essential for components like heating elements and heat shields.
Primary Production Methods Explained
The production technique directly impacts the final component's integrity and performance characteristics. Each method is suited for different applications.
Sintering: The Industry Standard
Sintering is the most common method for manufacturing MoSi₂ components, particularly for heating elements.
The process involves compacting MoSi₂ powder into a desired shape and then heating it to a high temperature, but below its melting point. This fuses the powder particles together, creating a solid, cohesive part.
Plasma Spraying: For Dense Coatings and Composites
Plasma spraying is a thermal spray coating process used to produce very dense forms of MoSi₂. In this technique, MoSi₂ powder is injected into a high-temperature plasma jet, where it melts and is sprayed onto a substrate.
This method results in rapid cooling, which can produce a mix of crystal structures, including the beta-phase (β-MoSi₂). It is ideal for applying protective coatings or creating complex composite materials.
Understanding the Material's Trade-offs
While exceptional at high temperatures, MoSi₂ has significant limitations that any engineer or designer must consider. These trade-offs are inherent to the material's ceramic-like nature.
Brittleness at Lower Temperatures
Like many advanced ceramics, MoSi₂ is very brittle and fragile at room temperature. This requires careful handling during installation and can make it susceptible to mechanical shock.
Loss of Creep Resistance Above 1200°C
While it excels at resisting oxidation, the material begins to lose its creep resistance (its ability to resist deformation under a constant load) at temperatures above 1200°C. This limits its use in structural applications under load at its highest operating temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application will dictate the most appropriate production method. The goal is to leverage the material's strengths while mitigating its weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is producing standard heating elements: Sintering is the established, reliable, and cost-effective method for creating standalone components.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, protective coatings or specialized composites: Plasma spraying offers superior density and adhesion for surface protection or integration into other materials.
Ultimately, understanding the connection between production, properties, and performance is the key to successfully deploying molybdenum disilicide in any demanding application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Compacts and fuses MoSi₂ powder below melting point; creates solid, cohesive parts | Standard heating elements, cost-effective standalone components |
| Plasma Spraying | Melts and sprays MoSi₂ powder via plasma jet; results in dense coatings and composites | Protective coatings, specialized composites, dense monolithic forms |
Need expert high-temperature furnace solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for materials like molybdenum disilicide. Contact us today to enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















