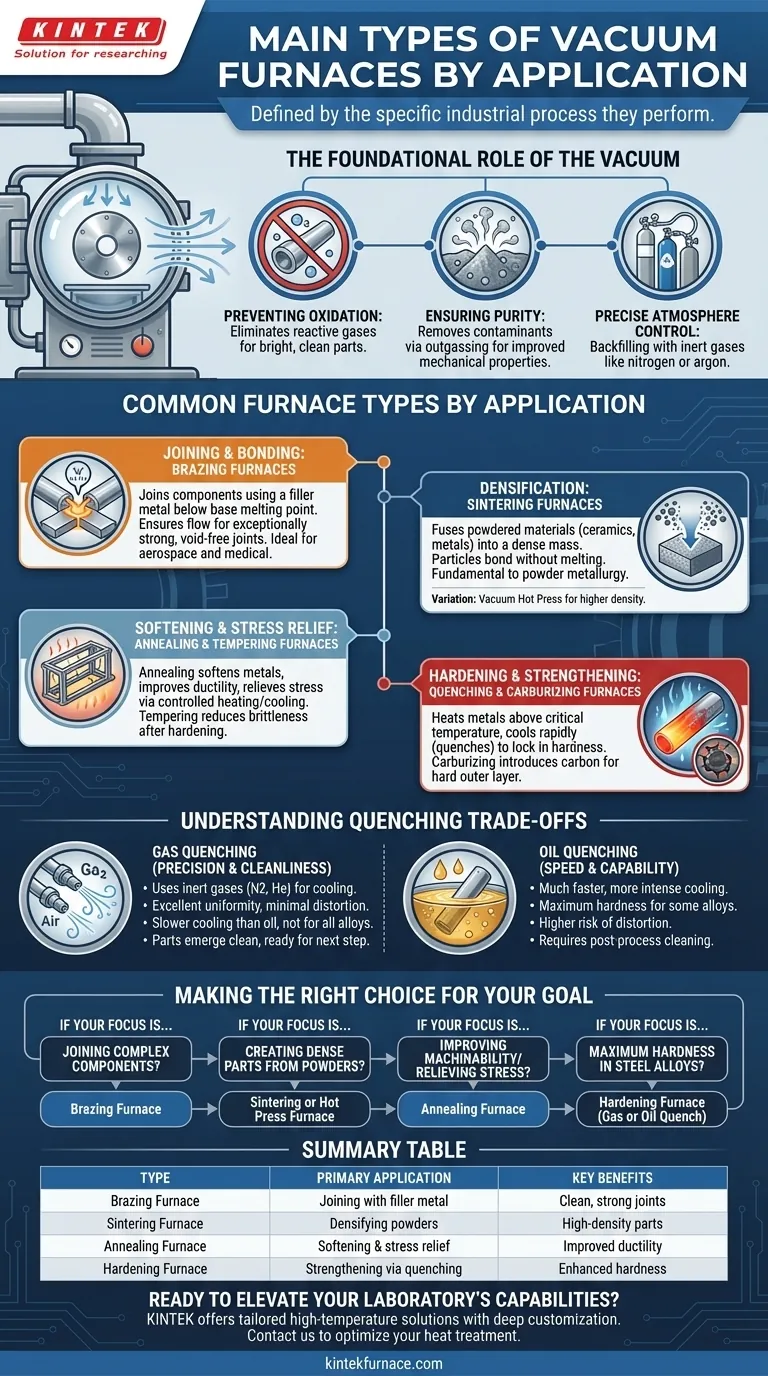
The primary types of vacuum furnaces are best understood by their specific industrial application. While all operate by removing air to create a controlled environment, each type is engineered for a distinct heat treatment process. The most common categories include vacuum brazing, sintering, annealing, and hardening furnaces (which encompass gas and oil quenching), each designed to achieve a unique metallurgical outcome.
A vacuum furnace is not a single tool, but a category of highly specialized equipment. The key is to recognize that the "type" of furnace is defined by the process it's built to perform—whether it's joining, hardening, or softening materials in an oxygen-free environment.

The Foundational Role of the Vacuum
Before examining specific types, it's critical to understand why a vacuum is used. Removing atmosphere from the heating chamber accomplishes three key objectives.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The primary goal is to eliminate oxygen and other reactive gases. This prevents the formation of oxides on the material's surface, resulting in bright, clean parts that require no post-process cleaning.
Ensuring Purity
The vacuum actively pulls contaminants and volatile substances out of the material itself, a process known as outgassing. This leads to a higher purity and improved mechanical properties in the final product.
Enabling Precise Atmosphere Control
Once a vacuum is established, the furnace can be backfilled with a specific inert gas, like nitrogen or argon, at a precise pressure. This provides an unparalleled level of control over the processing environment.
Common Furnace Types by Application
The most practical way to classify vacuum furnaces is by the job they are designed to do. Each type uses a unique heating and cooling profile to manipulate a material's properties.
For Joining and Bonding: Brazing Furnaces
A vacuum brazing furnace is used to join two or more components using a filler metal. The process takes place below the melting point of the base materials.
The clean vacuum environment ensures the filler metal flows evenly and creates an exceptionally strong, void-free joint, which is critical for aerospace and medical applications.
For Densification: Sintering Furnaces
Vacuum sintering furnaces are used to fuse powdered materials—such as ceramics or metals—into a solid, dense mass.
By heating the compacted powder in a vacuum, particles bond together without melting. This process is fundamental to powder metallurgy and the creation of specialized metal-matrix composites. A vacuum hot press furnace is a variation that applies high pressure simultaneously with heat to achieve even greater density.
For Softening and Stress Relief: Annealing & Tempering Furnaces
Vacuum annealing furnaces are used to soften metals, improve their ductility, and relieve internal stresses built up during manufacturing. The process involves heating the material to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly.
Tempering furnaces perform a similar, but lower-temperature, heat treatment. This is typically done after a hardening process to reduce brittleness and increase toughness.
For Hardening and Strengthening: Quenching & Carburizing Furnaces
Vacuum hardening furnaces heat metals like steel above their critical transformation temperature and then cool them rapidly to lock in a hard, strong microstructure. The method of cooling, or quenching, is a major differentiator.
A vacuum carburizing furnace is a specialized type that introduces a carbon-rich gas into the chamber. This allows carbon to diffuse into the surface of steel parts, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gas vs. Oil Quenching
For hardening processes, the choice between gas and oil quenching is a critical decision with significant trade-offs.
Gas Quenching: Precision and Cleanliness
High-pressure gas quenching (HPGQ) uses inert gases like nitrogen or helium to cool parts. This method offers excellent temperature uniformity, minimizing the risk of distortion or cracking, especially in complex geometries.
The primary advantage is that parts emerge from the furnace clean and ready for the next step. However, its cooling rate is slower than oil, making it unsuitable for some low-alloy steels that require a more aggressive quench.
Oil Quenching: Speed and Capability
Oil quenching provides a much faster and more intense cooling rate. This is necessary to achieve maximum hardness in certain steel alloys with lower hardenability.
The downside is a higher risk of part distortion due to less uniform cooling. Furthermore, parts require significant post-process cleaning to remove oil residue, adding an extra step and cost to the manufacturing cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is joining complex components: A vacuum brazing furnace provides clean, strong joints without distorting the base materials.
- If your primary focus is creating dense parts from powders: A sintering or hot press furnace is designed for consolidating materials like ceramics or powdered metals.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or relieving stress: An annealing furnace is the correct choice for controlled softening and stress removal.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness in steel alloys: A hardening furnace with either gas or oil quenching capabilities is required, depending on the alloy's specific needs.
Understanding these functional distinctions is the first step toward leveraging vacuum technology to achieve superior material properties.
Summary Table:
| Type of Vacuum Furnace | Primary Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Furnace | Joining components with filler metal | Clean, strong joints; ideal for aerospace and medical |
| Sintering Furnace | Densifying powdered materials | High-density parts; used in powder metallurgy |
| Annealing Furnace | Softening metals and stress relief | Improved ductility and reduced internal stresses |
| Hardening Furnace | Strengthening metals via quenching | Enhanced hardness; options for gas or oil quenching |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with advanced vacuum furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse labs with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















