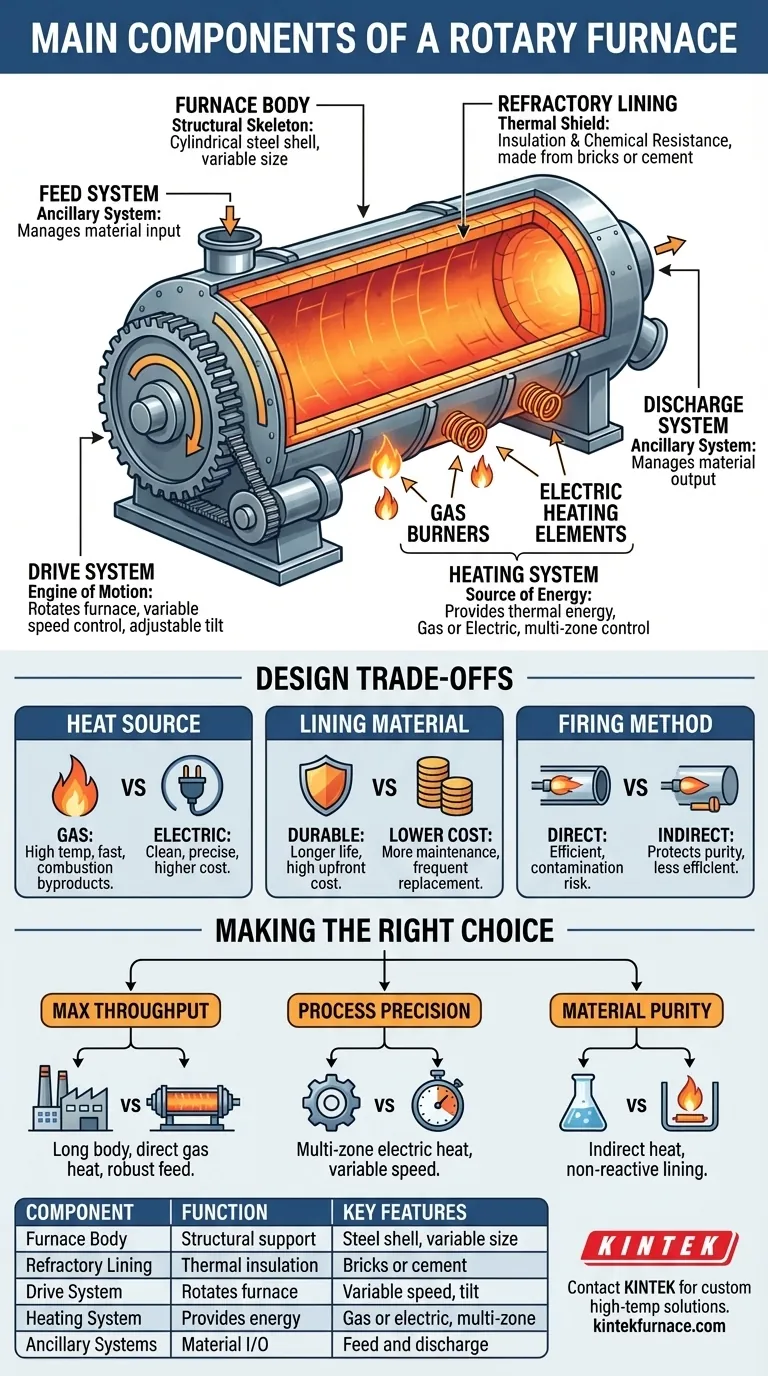
At its core, a rotary furnace is not a single object but a dynamic system designed for continuous material processing at high temperatures. Its primary components are the furnace body, the internal refractory lining, the drive system that facilitates rotation, and the heating system that provides the necessary thermal energy. These parts work in concert to mix, heat, and transform materials as they travel through the furnace.
Understanding the components of a rotary furnace is about recognizing how structure, insulation, motion, and heat are integrated. The genius of the design lies in using rotation to ensure uniform heat exposure and consistent processing, a principle achieved through the specific function of each core part.

The Core Anatomy of a Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace's effectiveness is a direct result of how its main components are designed and integrated. Each part serves a distinct and critical purpose in creating a controlled, high-temperature processing environment.
The Furnace Body: The Structural Skeleton
The furnace body is the external, cylindrical shell that provides the primary structure. It is typically constructed from welded steel plate to ensure durability and contain the entire process.
The length and diameter of this body are highly variable, ranging from a few meters to over 200 meters, depending entirely on the specific application and required throughput.
The Refractory Lining: The Thermal Shield
Inside the steel body is the refractory lining, a critical layer that serves two essential functions. It is the furnace's primary insulator, protecting the steel shell from extreme internal temperatures.
This lining also provides a barrier against chemical corrosion and abrasion from the materials being processed. It is made from specialized materials like refractory bricks, castable cement, or moldable substances chosen specifically for the process temperature and chemical environment.
The Drive System: The Engine of Motion
The drive system, consisting of a large drive gear or driven rollers, is responsible for rotating the entire furnace body. This motion is fundamental to the furnace's operation, as it constantly tumbles and mixes the material inside.
Most modern drive systems offer variable speed control. This feature is crucial for precisely managing the material's residence time inside the furnace and controlling the rate of heat transfer, allowing operators to fine-tune the process. Some designs also allow for adjusting the tilt, which influences how quickly material moves through the cylinder.
The Heating System: The Source of Energy
The heating system generates the high temperatures required for processing. This is typically achieved through one of two methods: gas burners or electric heating elements.
Heat is transferred to the material via conduction, convection, and radiation. Advanced furnaces often feature multi-zone heating control, allowing for different temperature profiles along the length of the furnace, which is essential for complex chemical reactions or phase changes.
Ancillary Systems: Input and Output
While not part of the core furnace chamber itself, the feed and discharge systems are essential for continuous operation. These mechanisms manage the controlled input of raw materials into one end of the furnace and the removal of the finished product from the other.
Understanding the Design Trade-offs
The choice and design of each component involve critical trade-offs that directly impact the furnace's performance, operating cost, and suitability for a specific task.
Heat Source: Gas vs. Electric
A gas-fired system can often achieve very high temperatures quickly and may have lower operational costs. However, it introduces combustion byproducts into the furnace atmosphere, which can be undesirable for sensitive materials.
An electric heating system provides exceptionally clean heat and highly precise temperature control. This makes it ideal for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere or exact temperature profiles, though it can be more expensive to operate.
Lining Material: Durability vs. Cost
The selection of refractory material is a balance between performance and budget. Highly durable, chemically resistant materials that can withstand extreme temperatures have a longer service life but come at a significant upfront cost.
Less expensive materials may be suitable for lower-temperature or less corrosive applications but will require more frequent maintenance and replacement, leading to increased downtime.
Firing Method: Direct vs. Indirect
In a directly heated furnace, the burners or heating elements are located inside the main chamber, in direct contact with the process material. This is thermally efficient but risks contaminating the material.
In an indirectly heated furnace (often called a rotary tube furnace), the rotating process tube is heated from the outside. This method protects the material from any byproducts of combustion, ensuring high purity, but it is less energy-efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific process requirements will determine the ideal configuration of these components.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: A long furnace body with a high-capacity, direct-fired gas heating system and robust feed/discharge systems is crucial.
- If your primary focus is process precision: Prioritize a multi-zone electric heating system and a variable-speed drive for fine-tuned control over temperature and residence time.
- If your primary focus is material purity: An indirectly heated furnace with a specialized, non-reactive refractory lining is necessary to prevent any contamination.
By understanding how each component contributes to the whole, you can effectively specify or operate a rotary furnace to meet your exact technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Body | Structural support and containment | Cylindrical steel shell, variable size |
| Refractory Lining | Thermal insulation and chemical resistance | Made from bricks or cement, protects shell |
| Drive System | Rotates furnace for mixing and movement | Variable speed control, adjustable tilt |
| Heating System | Provides thermal energy for processing | Gas or electric, multi-zone control |
| Ancillary Systems | Manages material input and output | Feed and discharge mechanisms |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a custom rotary furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your material processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















