The primary advantages of a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace are its ability to produce exceptionally high-purity metals and alloys while offering precise control over the entire melting process. By performing the melting inside a vacuum, it prevents oxidation and removes dissolved gas impurities. The use of induction heating ensures rapid, uniform, and clean temperature control, making it a cornerstone technology for creating advanced materials.
A VIM furnace is more than just a tool for melting metal; it is a highly controlled refining environment. Its core value lies in its unique ability to combine a vacuum atmosphere with induction heating to eliminate contamination and achieve a level of chemical and thermal precision that is impossible with conventional air-melting techniques.

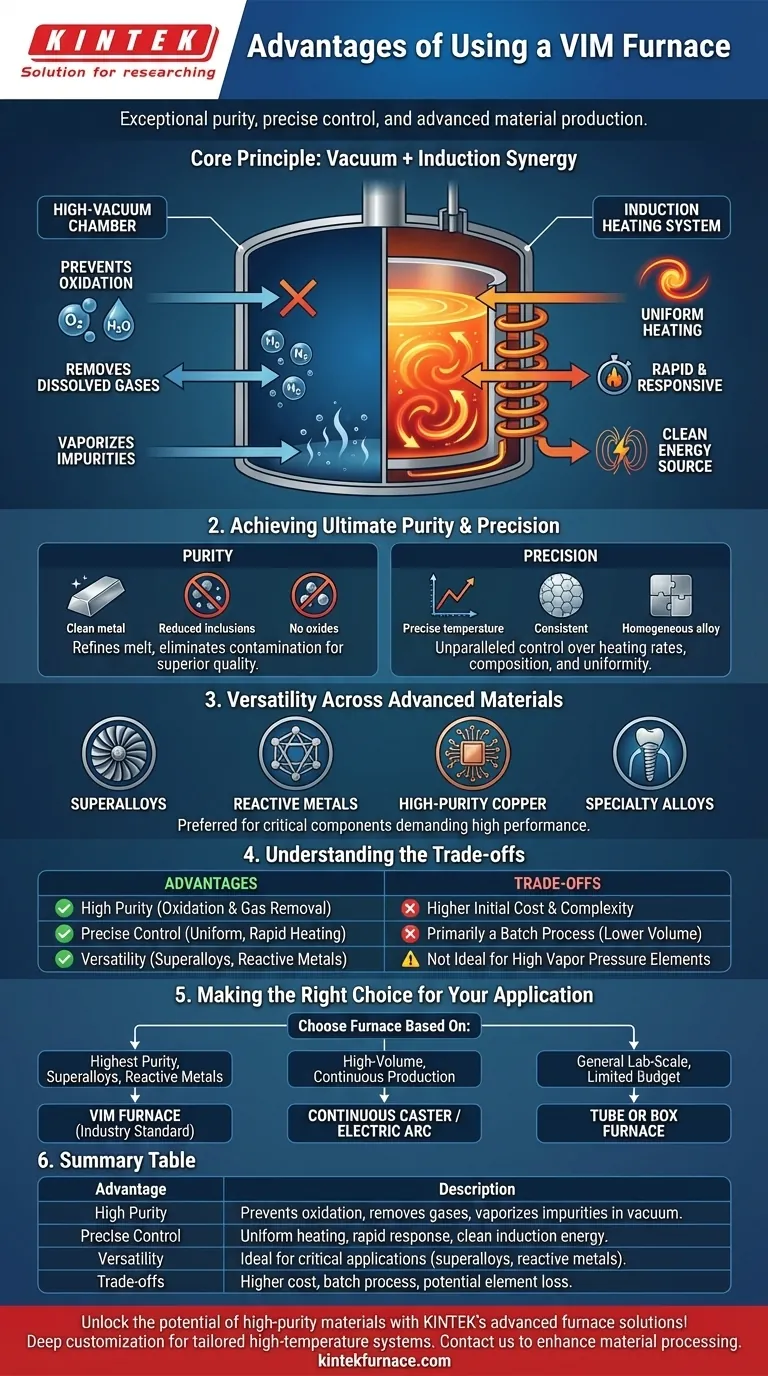
The Core Principle: Combining Vacuum and Induction
A VIM furnace's advantages stem from the powerful synergy between its two defining technologies: a high-vacuum chamber and an induction heating system. Understanding how these two elements work together is key to appreciating its capabilities.
Achieving Ultimate Purity
The vacuum environment is the primary reason for the superior quality of VIM-processed materials. It actively refines the melt by creating conditions that are hostile to impurities.
- Prevents Oxidation: By removing oxygen and water vapor, the vacuum completely prevents the formation of oxides, which are brittle inclusions that degrade the mechanical properties of metals.
- Removes Dissolved Gases: Elements like hydrogen and nitrogen, which become trapped in the metal during processing, are pulled out of the liquid melt by the vacuum. This process, known as degassing, is critical for preventing porosity and embrittlement.
- Vaporizes Impurities: The vacuum lowers the boiling point of certain volatile impurities, allowing them to be "boiled off" and removed from the melt, further cleansing the final product.
Precision Control Over Temperature and Composition
Induction heating provides a level of control that is simply not possible with fuel-fired or resistance furnaces. It uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the conductive material itself.
- Uniform Heating: The electromagnetic forces create a natural stirring action within the liquid metal. This ensures the temperature is extremely uniform throughout the batch, preventing hot spots and ensuring a consistent, homogeneous alloy.
- Rapid and Responsive: Heat is generated almost instantly, allowing for very precise control over heating and cooling rates. This is essential for achieving specific microstructures in complex alloys.
- Clean Energy Source: Since the heat is generated within the material, there is no contamination from combustion byproducts or degrading heating elements, preserving the purity established by the vacuum.
Versatility Across Advanced Materials
The combination of purity and control makes VIM technology suitable for a wide range of demanding applications. It is the preferred method for producing materials where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
This includes superalloys for jet engine turbine blades, reactive metals like titanium, high-purity copper for electronics, and specialty steels and alloys for medical implants and other critical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a VIM furnace is a specialized piece of equipment. Its advantages come with trade-offs that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
VIM systems are significantly more complex and expensive than simple air-melt or tube furnaces. The need for robust vacuum pumps, sophisticated power supplies, and intricate control systems results in a higher initial investment and requires more specialized operator training.
Primarily a Batch Process
VIM is inherently a batch process, meaning one discrete quantity of material is processed at a time. While ideal for producing high-value, customized alloys, it is not efficient for the continuous, high-volume production of common-grade metals, where other furnace types excel.
Not Ideal for All Materials
While versatile, the deep vacuum can be problematic for alloys containing essential elements with very high vapor pressures (e.g., manganese, zinc). These elements can be unintentionally boiled off and removed from the melt, altering the final alloy chemistry if not managed carefully.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your material, your quality requirements, and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is producing the highest purity superalloys, reactive metals, or medical-grade materials: The VIM furnace is the industry standard, offering unparalleled control over contamination and chemistry.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of standard commodity metals: A technology like a continuous caster fed by an electric arc or basic oxygen furnace is far more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is general lab-scale heat treatment or synthesis on a limited budget: A simpler and less expensive tube or box furnace provides excellent utility for a wide range of non-critical applications.
Ultimately, selecting a VIM furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize material integrity and performance above all other considerations.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Purity | Prevents oxidation, removes gases, and vaporizes impurities in a vacuum environment. |
| Precise Control | Ensures uniform heating, rapid temperature response, and clean energy via induction. |
| Versatility | Ideal for superalloys, reactive metals, and high-purity materials in critical applications. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost, batch processing, and potential for element loss in certain alloys. |
Unlock the potential of high-purity materials with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including VIM, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material processing and achieve your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















