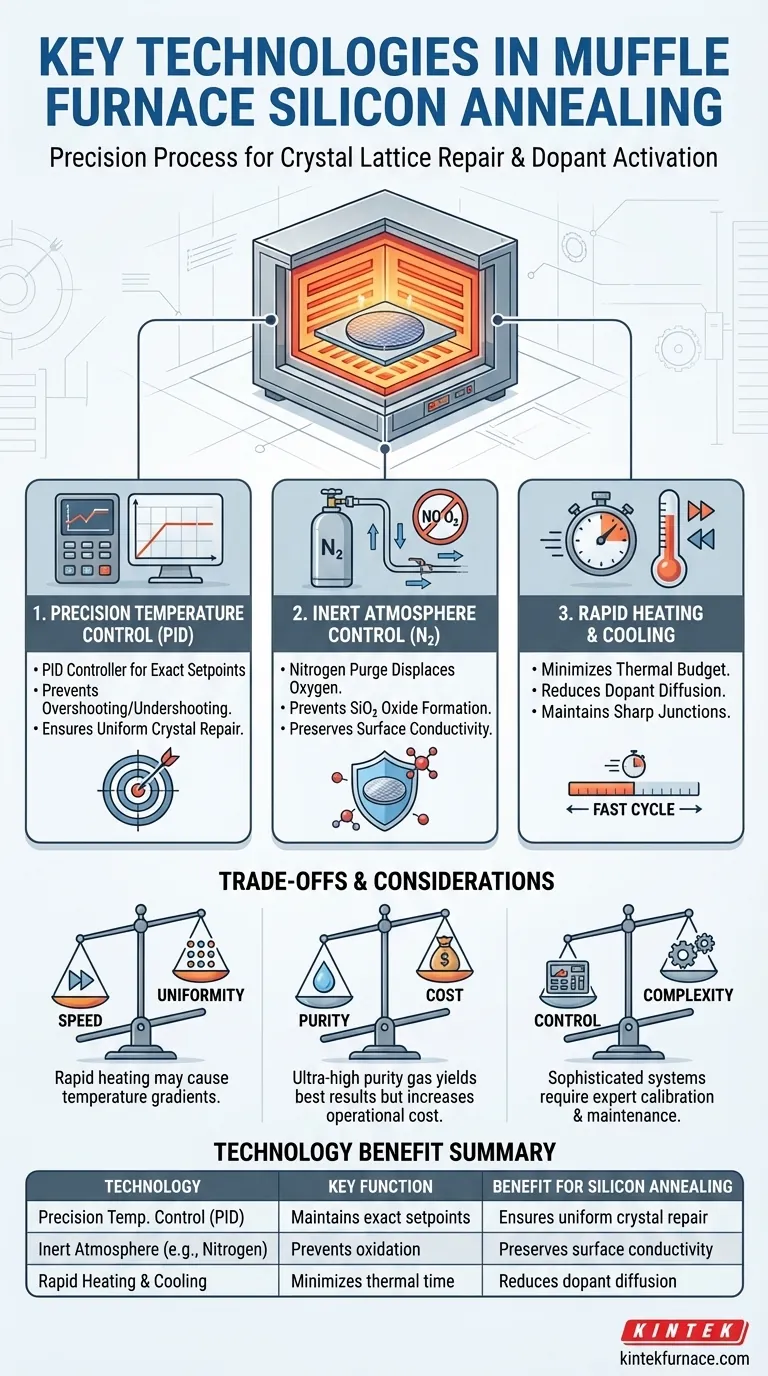
For annealing silicon-based materials, a muffle furnace relies on three core technologies working in concert. These are a precision temperature control system (typically PID), an inert atmosphere control system using gases like nitrogen, and a rapid heating and cooling mechanism. Together, these technologies enable the controlled modification of the silicon's crystal structure to achieve desired electrical properties.
The goal of annealing silicon is not simply to heat it. It is a precise thermal process designed to repair crystal lattice damage and activate dopants, and success hinges on a synergistic control of temperature, atmosphere, and the rate of thermal change.

The Core Challenge: Modifying the Silicon Crystal Structure
Annealing is a critical step in semiconductor fabrication. After processes like ion implantation, the silicon's crystal lattice is damaged, and implanted dopant atoms are not yet in electrically active positions.
The purpose of the anneal is twofold: to repair this lattice damage and to move dopant atoms into the correct sites within the crystal. This process "activates" the material, fundamentally altering its conductivity.
The Three Pillars of Silicon Annealing Technology
Achieving a successful anneal requires precise management of the furnace environment. Three technologies are non-negotiable for this task.
Pillar 1: Precision Temperature Control
The heart of the system is its ability to hit and hold a specific temperature without deviation. This is managed by a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller.
A PID controller continuously calculates the difference between the desired temperature setpoint and the actual measured temperature. It then precisely adjusts the power to the heating elements to minimize this error, preventing overshooting or undershooting that could ruin the material.
Pillar 2: Inert Atmosphere Control
At the high temperatures required for annealing, silicon reacts readily with oxygen in the air, forming an insulating layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This is highly undesirable as it compromises the material's surface conductivity.
To prevent this, the furnace chamber is purged with an inert gas, most commonly nitrogen (N₂). This process displaces all the oxygen, creating a non-reactive environment and ensuring the silicon surface remains pure and conductive.
Pillar 3: Rapid Heating and Cooling
The duration of the high-temperature exposure, known as the "thermal budget," is critical. While heat is needed to repair the lattice, prolonged exposure can cause unwanted diffusion of dopant atoms, blurring the meticulously defined junctions in a semiconductor device.
A rapid heating and cooling system allows the material to reach its target temperature quickly, hold for a precise duration, and cool down fast. This minimizes the total thermal budget, achieving the necessary crystal repair while preserving the integrity of the device's structure.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
While these technologies are powerful, they come with operational complexities and trade-offs that must be managed.
Speed vs. Uniformity
Extremely rapid heating rates can sometimes create temperature gradients across the silicon wafer. The center may heat faster than the edges, leading to non-uniform annealing and inconsistent electrical properties across the device.
Purity vs. Cost
The effectiveness of the inert atmosphere depends directly on the purity of the nitrogen gas used. While ultra-high purity gas yields the best results by eliminating virtually all oxygen, it significantly increases operational costs compared to standard industrial-grade nitrogen.
Control vs. Complexity
A sophisticated furnace with fine-tuned PID algorithms, mass flow controllers for gas, and rapid thermal cycling capability offers superior control. However, this complexity demands expert calibration, regular maintenance, and a deeper understanding from the operator to diagnose and prevent process deviations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The emphasis you place on each technology depends on the specific outcome you need to achieve for your silicon material.
- If your primary focus is maximizing conductivity: Pay closest attention to the nitrogen atmosphere control to prevent the formation of any insulating oxide layers.
- If your primary focus is preserving sharp dopant profiles: The rapid heating and cooling system is your most critical tool for minimizing the thermal budget.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and yield: Meticulous calibration and tuning of the PID temperature controller is paramount for repeatability.
Ultimately, mastering the annealing process is about understanding how these three core technologies interact to precisely shape the final properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Key Function | Benefit for Silicon Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control (PID) | Maintains exact temperature setpoints | Ensures uniform crystal repair and dopant activation |
| Inert Atmosphere Control (e.g., Nitrogen) | Prevents oxidation by displacing oxygen | Preserves surface conductivity and material purity |
| Rapid Heating and Cooling | Minimizes thermal exposure time | Reduces dopant diffusion and maintains sharp junctions |
Enhance your semiconductor annealing process with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored options like Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum Furnaces, along with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to achieve superior material properties and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















