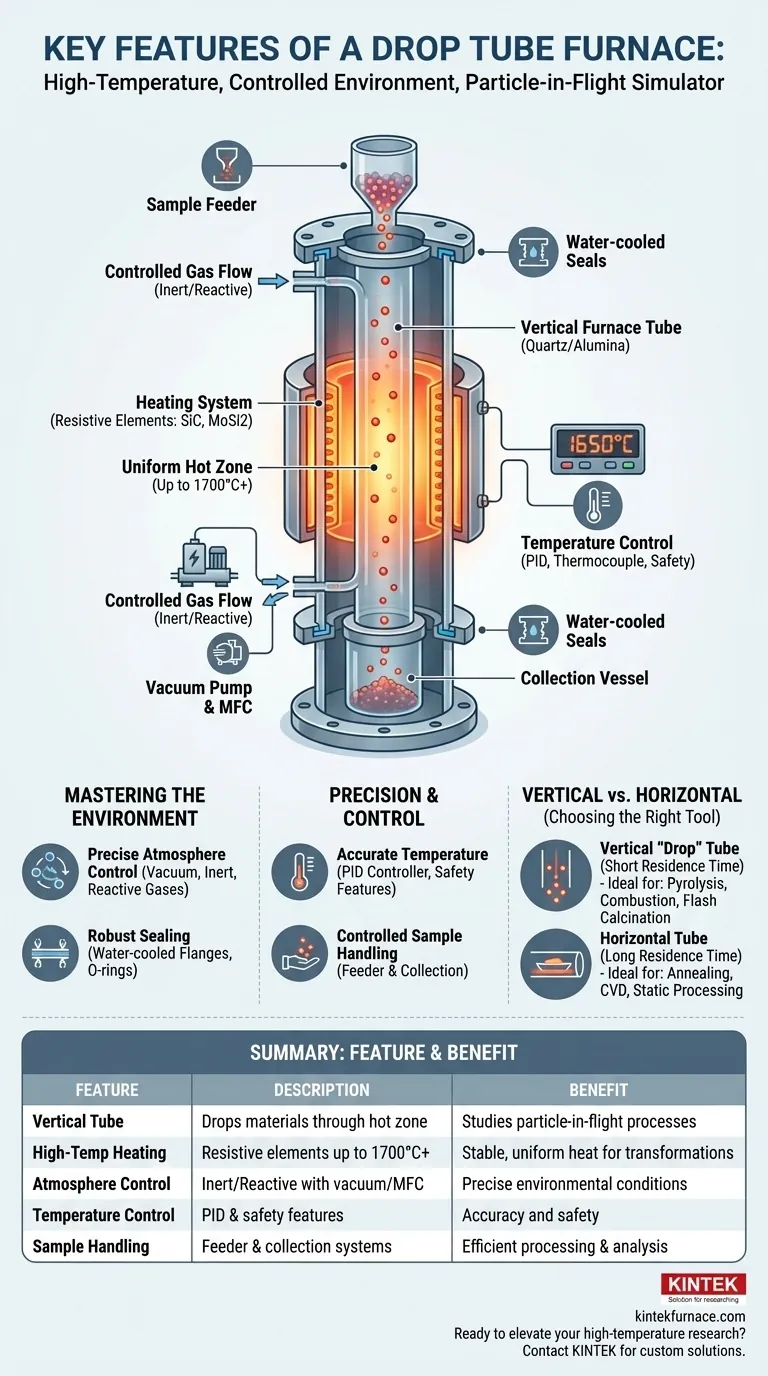
At its core, a drop tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for high-temperature material processing in a precisely controlled environment. Its key features are a vertically oriented furnace tube that allows materials to "drop" through a heated zone, a powerful heating system capable of reaching extreme temperatures, and a sophisticated system for managing the atmospheric conditions within the tube.
A drop tube furnace is more than just a heater; it is a process simulator. Its defining feature—the vertical orientation—is engineered specifically to study the thermal and chemical transformation of particles as they fall freely through a uniform, high-temperature environment.

Deconstructing the Core Components
Understanding a drop tube furnace begins with its three primary systems: the furnace tube, the heating elements, and the control systems that govern temperature and atmosphere.
The Vertical Furnace Tube: The Heart of the Process
The central component is the furnace tube, which contains the sample and the controlled atmosphere. Its material and orientation are critical design choices.
The tube is typically made from high-purity ceramic materials to prevent sample contamination at extreme temperatures. Common choices include quartz for temperatures up to ~1200°C and alumina (corundum) for higher temperatures, often exceeding 1700°C.
The vertical orientation is the defining characteristic of a "drop" tube furnace. This allows powdered or particulate samples to be introduced at the top and fall through the central hot zone, enabling studies of processes like pyrolysis, combustion, or calcination in-flight.
The Heating System: Achieving Extreme Temperatures
The heating system is designed to create a stable and uniform temperature profile along a specific length of the tube, known as the hot zone.
Most drop tube furnaces use resistive heating elements arranged cylindrically around the furnace tube. These elements are made from materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) to generate intense, reliable heat.
To minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency, the heating chamber is heavily insulated with high-temperature ceramic fiber or refractory materials.
The Temperature Control System: Precision and Safety
Precision is paramount. A modern furnace uses a sophisticated temperature control system to manage and maintain the target temperature with high accuracy.
This is typically achieved with a thermocouple placed near the heating elements, which provides real-time feedback to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This controller constantly adjusts the power to the heating elements to hold the temperature steady.
Essential safety features are also integrated, such as over-temperature protection that automatically cuts power if a set limit is exceeded, and interlocks that prevent operation under unsafe conditions.
Mastering the Process Environment
The true power of a drop tube furnace lies in its ability to control the environment inside the tube. Heat is only one part of the equation; atmosphere is the other.
Precise Atmosphere Control
These furnaces are designed to operate under a wide range of atmospheric conditions. A robust sealing and gas delivery system makes this possible.
By using a vacuum pump, the system can be evacuated to remove ambient air. Subsequently, it can be backfilled with a specific gas. This allows for processing under inert conditions (using Argon or Nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or under reactive conditions (using oxidizing or reducing gases) to study specific chemical reactions.
Gas flow is precisely managed using either a simple ball flow meter or a more advanced digital mass flow controller (MFC) for high-precision, repeatable experiments.
Sample Handling: The "Drop" Mechanism
The vertical design requires a specialized mechanism for sample introduction and collection.
A feeder system is used at the top of the furnace to introduce powders or particles at a controlled rate. At the bottom, a collection vessel gathers the processed material after it has fallen through the hot zone.
The Importance of Sealing
Maintaining the integrity of the internal atmosphere depends entirely on the quality of the seals.
Flanges, often made of aluminum, are fitted to both ends of the tube. Silicone or Viton O-rings create an airtight seal between the flanges and the tube. In high-temperature setups, these seals are often water-cooled via a recirculating chiller to prevent them from degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vertical vs. Horizontal Design
The choice between a vertical drop tube furnace and a more common horizontal tube furnace is dictated entirely by the experimental goal. They are not interchangeable.
Why Choose a Vertical "Drop" Tube?
The vertical configuration is purpose-built for processes involving free-falling particles. It is ideal for simulating industrial spray pyrolysis, flash calcination, or coal combustion, where materials have a very short residence time in the hot zone.
When is a Horizontal Tube Better?
A horizontal tube furnace is superior for processing static samples, such as solid substrates, wafers, or powders contained in boats. Its orientation simplifies sample loading and unloading and is perfect for processes requiring long, stable heating times, like annealing or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is the first step toward successful high-temperature research.
- If your primary focus is simulating particle-in-flight processes: A vertical drop tube furnace is the only design that meets this specific need.
- If your primary focus is batch processing solid samples or substrates: A horizontal tube furnace is the more practical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process purity and repeatability: Prioritize a system with a high-purity alumina tube, robust water-cooled seals, and a digital mass flow controller.
Ultimately, understanding these key features empowers you to select not just a furnace, but the precise tool required to achieve your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Furnace Tube | Allows materials to drop through heated zone | Enables study of particle-in-flight processes like pyrolysis and combustion |
| High-Temperature Heating | Uses resistive elements (e.g., SiC, MoSi2) for up to 1700°C+ | Provides stable, uniform heat for reliable material transformations |
| Atmosphere Control | Supports inert/reactive gases with vacuum and MFC systems | Ensures precise environmental conditions for oxidation prevention or reactions |
| Temperature Control | PID controller with thermocouples and safety features | Maintains accuracy and safety in high-temperature experiments |
| Sample Handling | Feeder and collection systems for controlled drop and retrieval | Facilitates efficient processing and analysis of particulate samples |
Ready to elevate your high-temperature research with a custom drop tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your lab's unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're simulating industrial processes or requiring precise atmosphere control, we can design a furnace that meets your exact experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















