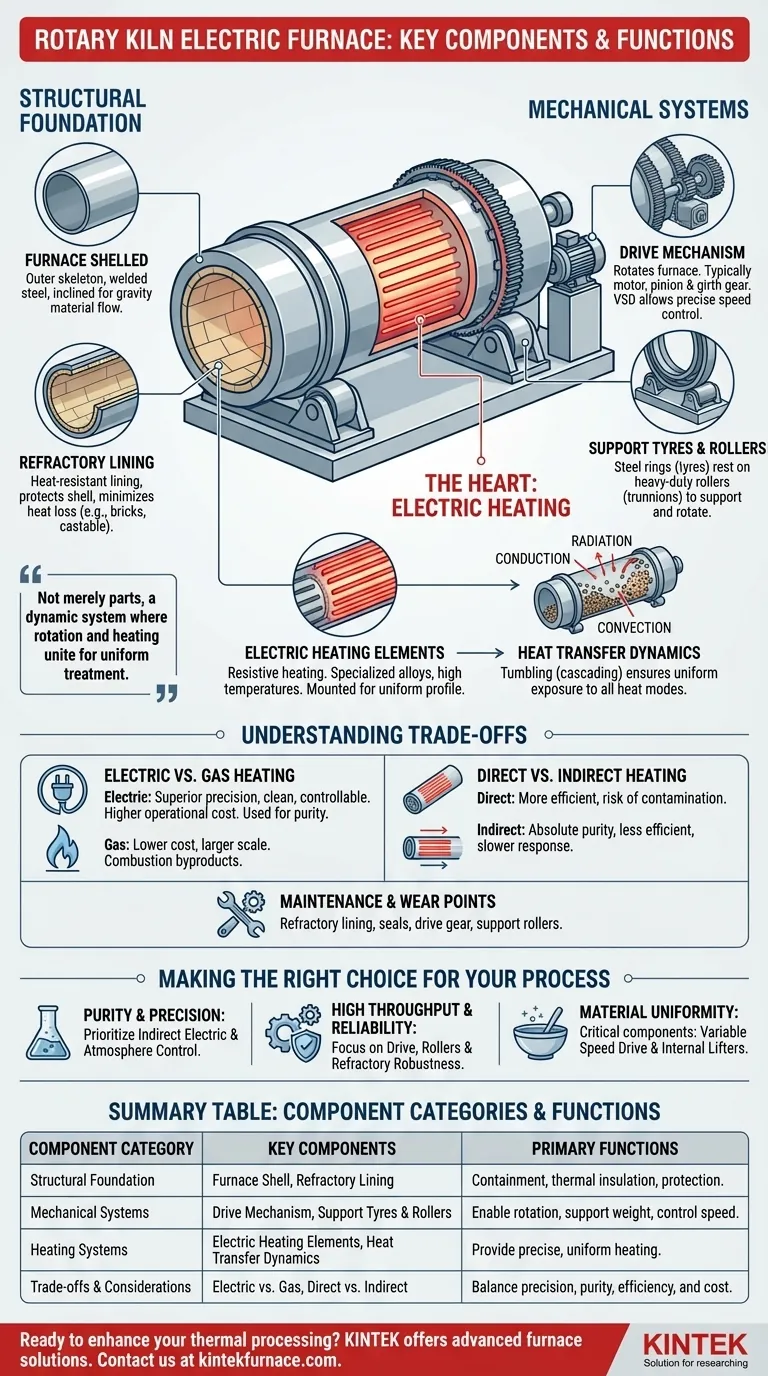
At its core, a rotary kiln electric furnace is an integrated system designed for continuous thermal processing. Its key components are the furnace body with its heat-resistant lining, the mechanical drive and support structure that enables rotation, the electric heating elements that provide energy, and the systems for material handling and process control.
A rotary kiln is not merely a collection of parts. It is a dynamic system where controlled rotation and precise heating work in unison to ensure every particle of material is treated uniformly, achieving results that static furnaces cannot.

The Structural Foundation: Body and Lining
The physical structure of the furnace must provide containment, support, and thermal insulation. These roles are split between the outer shell and the inner lining.
The Furnace Shell
The furnace shell, or body, is the outer skeleton of the kiln. It is typically a long, cylindrical barrel constructed from welded steel plates to withstand the immense structural and thermal stresses of operation.
This cylinder is almost always mounted at a slight inclination to the horizontal, using gravity to help move material from the feed end to the discharge end as it rotates.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the steel shell is the refractory lining. This critical layer is made from heat-resistant materials like refractory bricks, castable cement, or other insulating compounds.
Its primary purpose is twofold: to protect the steel shell from the extreme internal temperatures and to minimize heat loss, improving the furnace's thermal efficiency. The choice of refractory material also depends on the chemical properties of the material being processed to resist corrosion and reaction.
The Mechanical Systems: Rotation and Support
The "rotary" aspect of the kiln is what enables its unique processing capabilities. This motion is managed by a robust set of mechanical components.
The Drive Mechanism
The drive mechanism is the system that rotates the furnace body. It typically consists of a large ring gear (the girth gear) fixed to the shell, which is turned by a smaller pinion gear connected to a high-torque electric motor.
Modern systems almost always include a variable speed drive (VSD). This allows operators to precisely control the rotational speed, which is a critical parameter for dictating how long the material stays in the furnace and how well it tumbles and mixes.
Support Tyres and Rollers
Given the massive weight of the furnace body and its contents, a specialized support system is necessary. Large steel rings, known as support tyres or riding rings, are attached to the outside of the furnace shell.
These tyres rest on a set of heavy-duty support rollers (or trunnions), which bear the entire load of the kiln and allow it to rotate with minimal friction.
The Heart of the Furnace: Electric Heating
Unlike fuel-fired kilns, an electric furnace relies on resistive heating, which offers distinct advantages in control and process purity.
Electric Heating Elements
The heat source consists of electric heating elements. These are made from specialized alloys that can withstand very high temperatures while converting electrical energy into thermal energy.
These elements are typically mounted inside the furnace chamber or, in some designs, externally to heat the shell, which then radiates heat inward. Their placement is crucial for achieving a uniform temperature profile along the length of the kiln.
Heat Transfer Dynamics
Rotation is the key to uniform heating. As the kiln turns, it continuously lifts and tumbles the material, a process known as cascading.
This action exposes every particle directly to the three modes of heat transfer: radiation from the hot refractory walls and heating elements, conduction through particle-to-particle contact, and convection from the hot atmosphere within the kiln.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a rotary electric furnace involves balancing competing priorities.
Electric vs. Gas Heating
Electric heating provides superior temperature precision and a clean, controllable atmosphere free from combustion byproducts. However, it can have a higher operational cost depending on electricity prices and is often used for smaller-scale or high-purity applications compared to massive, gas-fired kilns.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A furnace can be directly heated, with elements inside the processing chamber, or indirectly heated, where the rotating tube is heated from the outside. Direct heating is more efficient but risks contaminating sensitive materials. Indirect heating ensures absolute product purity but is less energy-efficient and has a slower thermal response.
Maintenance and Wear Points
The primary wear components are the refractory lining, which eventually degrades from thermal cycling and abrasion, and the seals at the feed and discharge ends. The drive gear and support rollers also require regular lubrication and inspection to prevent mechanical failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding how these components function as a system allows you to select or operate a furnace that aligns with your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is process purity and precision: Prioritize a design with indirect electric heating and advanced atmosphere control systems.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and reliability: Pay close attention to the robustness of the drive mechanism, support rollers, and the quality of the refractory lining.
- If your primary focus is material uniformity: The variable speed drive and the design of internal lifters (fins that help tumble the material) are your most critical components.
By understanding the function of each component, you move from simply operating a machine to mastering a sophisticated thermal processing system.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Components | Primary Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Foundation | Furnace Shell, Refractory Lining | Containment, thermal insulation, protection from heat |
| Mechanical Systems | Drive Mechanism, Support Tyres and Rollers | Enable rotation, support weight, control speed |
| Heating Systems | Electric Heating Elements, Heat Transfer Dynamics | Provide precise, uniform heating via radiation, conduction, convection |
| Trade-offs and Considerations | Electric vs. Gas Heating, Direct vs. Indirect Heating | Balance precision, purity, efficiency, and cost |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with a custom rotary kiln electric furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















