At its core, a silicon carbide (SiC) heating rod is a high-performance resistive heating element prized for its ability to operate at extreme temperatures, its exceptional durability, and its chemical stability. These properties stem directly from its unique material composition and manufacturing process, making it a cornerstone technology for demanding high-temperature industrial and laboratory furnaces.
Silicon carbide heating elements are not just about reaching high temperatures; they are about maintaining those temperatures reliably and for extended periods under demanding conditions. Their value lies in a balance of high thermal performance, exceptional physical durability, and resistance to environmental degradation.
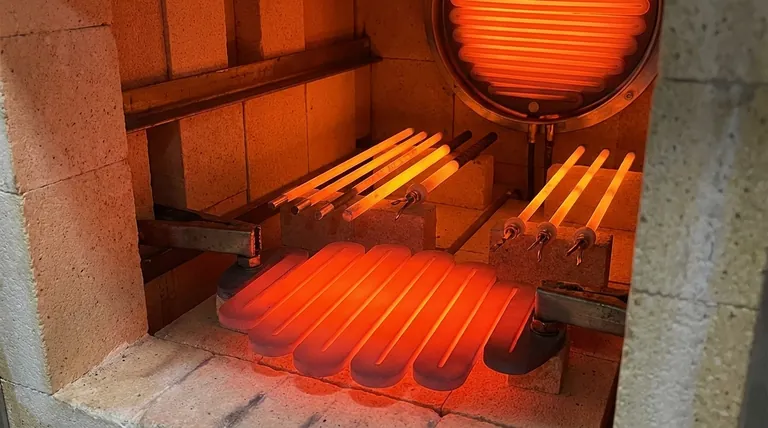

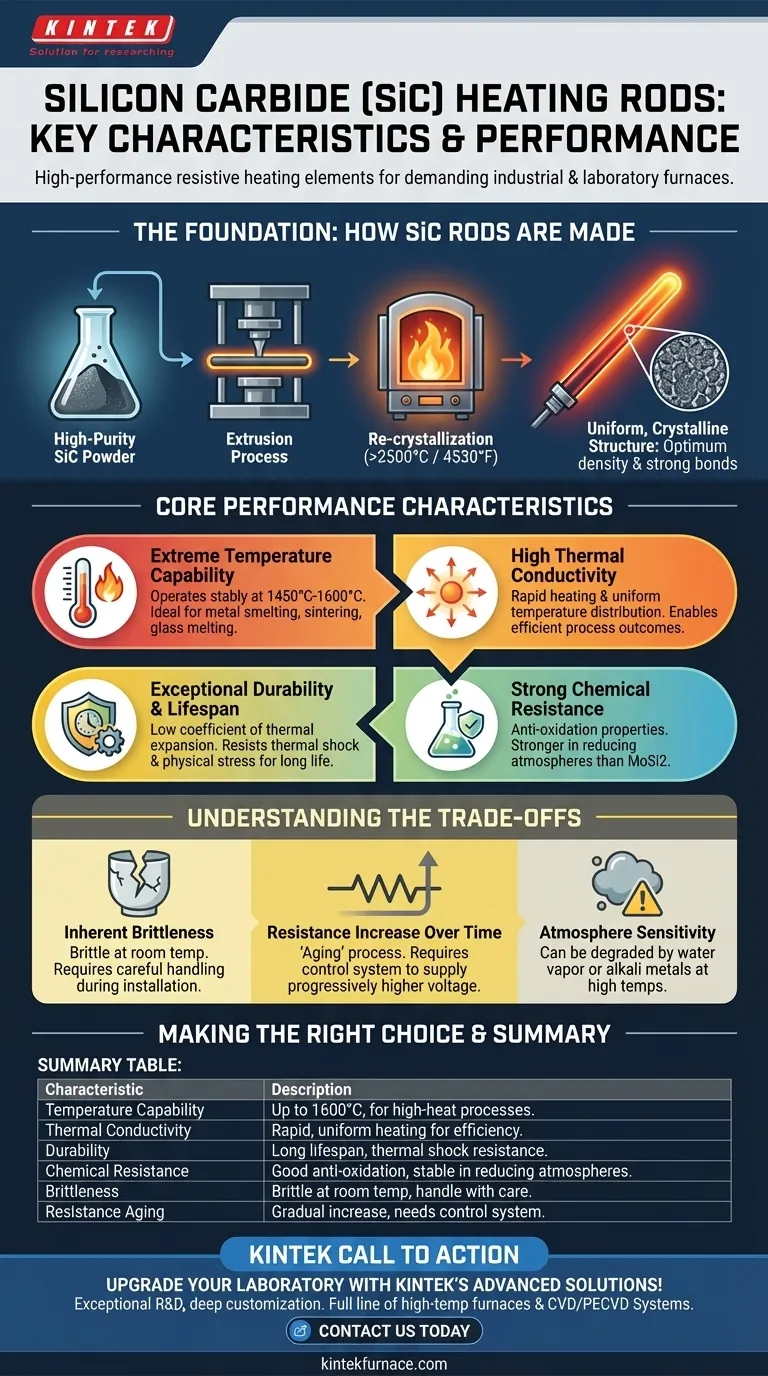
The Foundation: How SiC Rods Are Made
The remarkable properties of SiC rods are a direct result of a meticulous manufacturing process designed to create a material of extreme purity and structural integrity.
From Powder to High-Density Rod
The process begins with high-purity silicon carbide. This material is extruded into the desired shape, typically a rod or tube.
These forms are then subjected to a re-crystallization process at incredibly high temperatures, often exceeding 2500°C (4530°F).
The Result: A Uniform, Crystalline Structure
This intense firing process creates strong, uniform bonds between the SiC grains. The result is a heating element with optimum density and a highly stable, interconnected crystalline structure that is foundational to its performance.
Core Performance Characteristics Explained
Understanding how SiC is made clarifies why it behaves the way it does. Its characteristics are not accidental; they are engineered.
Extreme Temperature Capability
SiC elements can operate stably at temperatures up to 1450°C-1600°C. This capability is essential for processes like metal smelting, ceramic sintering, and quartz glass melting.
High Thermal Conductivity
The material's excellent thermal conductivity allows for rapid heating and helps maintain a uniform temperature within a furnace's hot zone. This leads to more efficient and predictable process outcomes.
Exceptional Durability and Lifespan
SiC has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes it highly resistant to the physical stress of repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Combined with its inherent high hardness and thermal stability, this resistance to thermal shock results in a very long operational lifespan and reduces the need for frequent replacement.
Strong Chemical Resistance
Silicon carbide exhibits strong chemical stability, particularly its anti-oxidation properties and resistance to many acids. It is also notably stronger in reducing atmospheres compared to other common elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging the operational considerations of silicon carbide.
Inherent Brittleness
Like many advanced ceramics, SiC rods are brittle at room temperature. They must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to avoid mechanical shock or fracture.
Resistance Increase Over Time
Over its operational life, a SiC element's electrical resistance will gradually increase. This "aging" is a normal process that must be managed by a control system capable of supplying progressively higher voltage to maintain the desired power output.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While excellent in many environments, SiC can be degraded by certain atmospheres, particularly those containing water vapor or specific alkali metals at high temperatures. The choice between SiC and other elements like MoSi2 often depends on the specific chemical environment of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element is critical for process success, energy efficiency, and operational safety.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature and rapid heating: The high thermal conductivity and 1600°C ceiling make SiC an excellent choice for demanding thermal profiles.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and minimal downtime: SiC's proven durability, resistance to thermal shock, and long service life will minimize maintenance cycles.
- If your primary focus is operating in a specific chemical atmosphere: Carefully evaluate your process environment, noting that SiC performs exceptionally well in reducing atmospheres but may have limitations with others.
By understanding these core characteristics and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if silicon carbide is the optimal material to achieve your specific heating goals.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Capability | Operates up to 1600°C, ideal for high-heat processes like metal smelting and ceramic sintering. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High conductivity enables rapid heating and uniform temperature distribution for efficient outcomes. |
| Durability | Low thermal expansion and high hardness provide long lifespan and resistance to thermal shock. |
| Chemical Resistance | Strong anti-oxidation properties and stability in reducing atmospheres, with limitations in certain environments. |
| Brittleness | Brittle at room temperature, requiring careful handling to avoid fractures. |
| Resistance Aging | Gradual increase in electrical resistance over time, managed by control systems for consistent power. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide silicon carbide heating rods and a full product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve precise temperature control, enhanced durability, and reliable performance for demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your processes and drive efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















