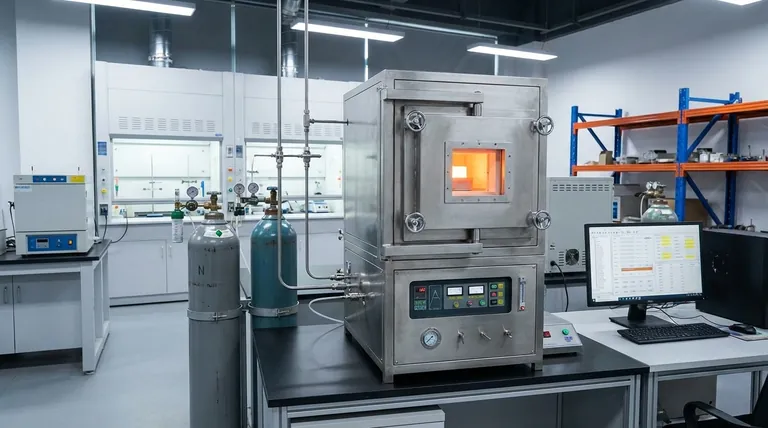
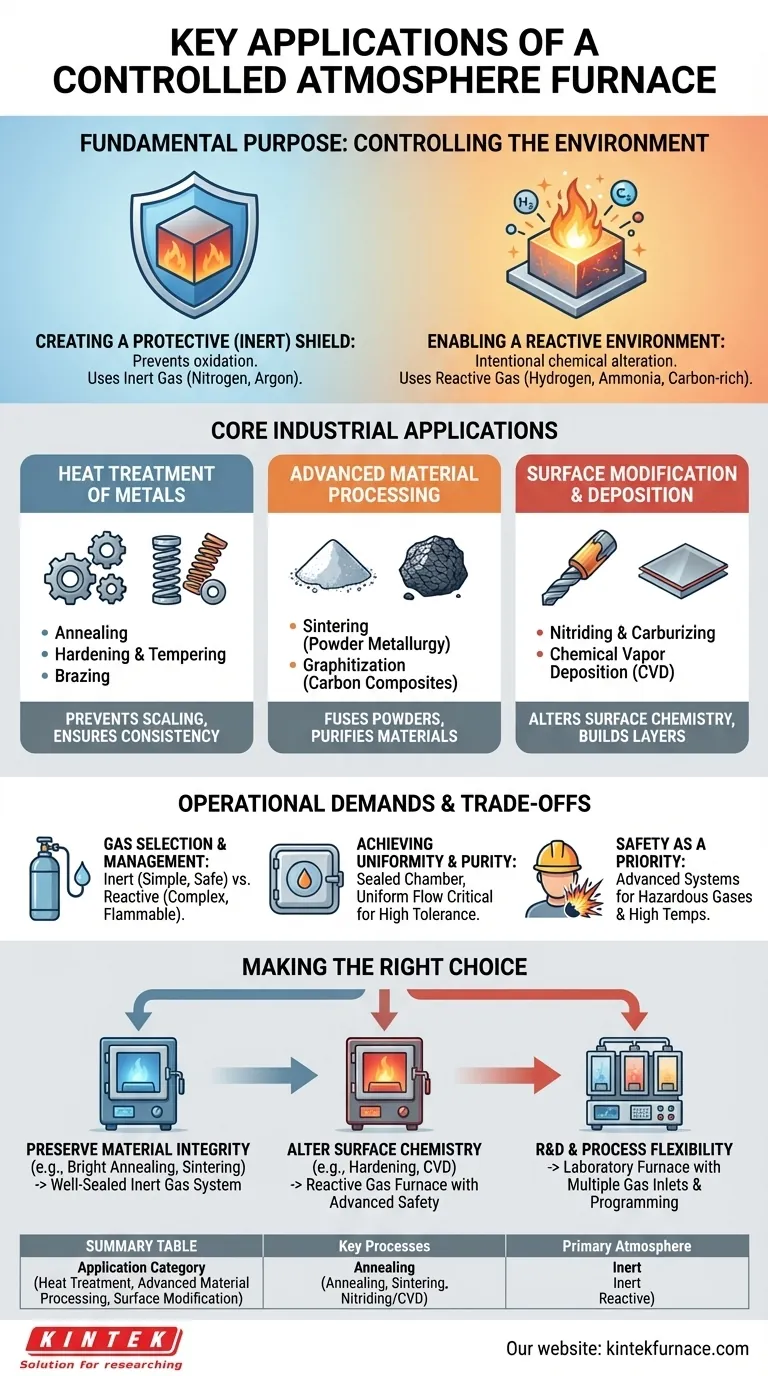
In short, a controlled atmosphere furnace is used for high-temperature material processing where exposure to open air would cause damage or prevent the desired chemical reaction. Key applications range from the heat treatment of metals like annealing and hardening, to advanced processes such as sintering powdered metals, creating carbon composites, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
The core purpose of a controlled atmosphere furnace is not just to heat a material, but to precisely manage the chemical environment around it. This control allows you to either completely protect the material from unwanted reactions like oxidation or to intentionally induce specific chemical changes on its surface.

The Fundamental Purpose: Why Control the Atmosphere?
Understanding the applications begins with understanding the two primary functions of a controlled atmosphere. At high temperatures, most materials are highly reactive with the oxygen and moisture present in normal air.
Creating a Protective (Inert) Shield
The most common goal is to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, primarily oxidation, which can ruin a material's surface finish, structural integrity, or electrical properties.
To achieve this, the furnace chamber is purged of air and filled with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This inert environment acts as a protective shield, ensuring the material remains chemically unchanged during heating and cooling.
This is analogous to vacuum-sealing food to prevent spoilage; the goal is preservation.
Enabling a Reactive Environment
Conversely, some processes require a specific chemical reaction to occur on the material's surface. In these cases, the furnace is filled with a reactive gas.
Gases like hydrogen, ammonia, or carbon-rich gases are introduced to intentionally alter the material's surface chemistry. This is the basis for processes that harden, coat, or otherwise modify a component.
Here, the atmosphere is not a shield but an active ingredient in the manufacturing process.
Core Industrial Applications
This dual capability—to protect or to react—enables a wide range of critical industrial and laboratory processes.
Heat Treatment of Metals
This is a foundational application where the atmosphere prevents scaling (a type of heavy oxidation) and ensures consistent material properties.
- Annealing: The atmosphere prevents surface oxidation, resulting in a clean, "bright" finish that doesn't require secondary cleaning operations.
- Hardening & Tempering: Precise control over carbon potential in the atmosphere is crucial for achieving the exact desired hardness and durability in steel components.
- Brazing: An inert or hydrogen-based atmosphere prevents oxides from forming on the joint surfaces, allowing the brazing alloy to flow freely and create a strong, clean bond.
Advanced Material Processing
These processes are often impossible without strict atmospheric control.
- Sintering: Used in powder metallurgy, this process fuses fine metallic or ceramic powders together just below their melting point. An inert atmosphere is essential to prevent the vast surface area of the powder from oxidizing instantly.
- Graphitization: Transforming carbon precursors into high-purity graphite requires extremely high temperatures in an inert atmosphere to drive off impurities and prevent the carbon from burning away.
Surface Modification and Deposition
These applications rely on a reactive atmosphere to build new layers or change the existing surface.
- Nitriding & Carburizing: Introducing nitrogen or carbon-rich gases causes them to diffuse into the surface of a steel part, creating an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer case.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Precursor gases are introduced into the furnace, where they react and decompose on the hot substrate to form a thin, solid film or coating. This is used to make everything from semiconductor layers to wear-resistant coatings on cutting tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Demands
While powerful, these furnaces require careful management. The choice of furnace and its operational procedures involve significant trade-offs.
Gas Selection and Management
The type of gas dictates cost and complexity. Inert gases like nitrogen are relatively simple and safe, but reactive or flammable gases like hydrogen require extensive safety systems, leak detection, and specialized handling protocols.
Achieving Uniformity and Purity
A perfectly sealed furnace chamber is critical to prevent air from leaking in and contaminating the atmosphere. Likewise, achieving a uniform atmosphere flow ensures every part of the component is processed equally, which is essential for high-tolerance applications. These features add to the furnace's cost and complexity.
Safety as a Priority
Handling high-pressure, flammable, or toxic gases at high temperatures is inherently hazardous. Modern furnaces must include advanced safety interlocks, emergency purge systems, and explosion protection devices, especially when using reactive gases. Adherence to strict operational protocols is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right atmospheric approach depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is preserving material integrity (e.g., bright annealing, sintering, brazing): Your priority is a well-sealed furnace with a reliable inert gas system (nitrogen or argon).
- If your primary focus is altering surface chemistry (e.g., hardening, nitriding, CVD): You need a furnace specifically designed to handle reactive gases, with advanced control systems and robust safety features.
- If your primary focus is R&D and process flexibility: A laboratory furnace with multiple gas inlets and precise programming capabilities will provide the versatility needed to test different materials and atmospheres.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace's atmosphere gives you direct control over the chemistry and final properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Atmosphere Type |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Brazing | Inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) |
| Advanced Material Processing | Sintering, Graphitization | Inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) |
| Surface Modification | Nitriding, Carburizing, CVD | Reactive (e.g., Hydrogen, Ammonia) |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need to protect materials from oxidation or enable reactive processes, our furnaces deliver precise control and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material processing and achieve your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















