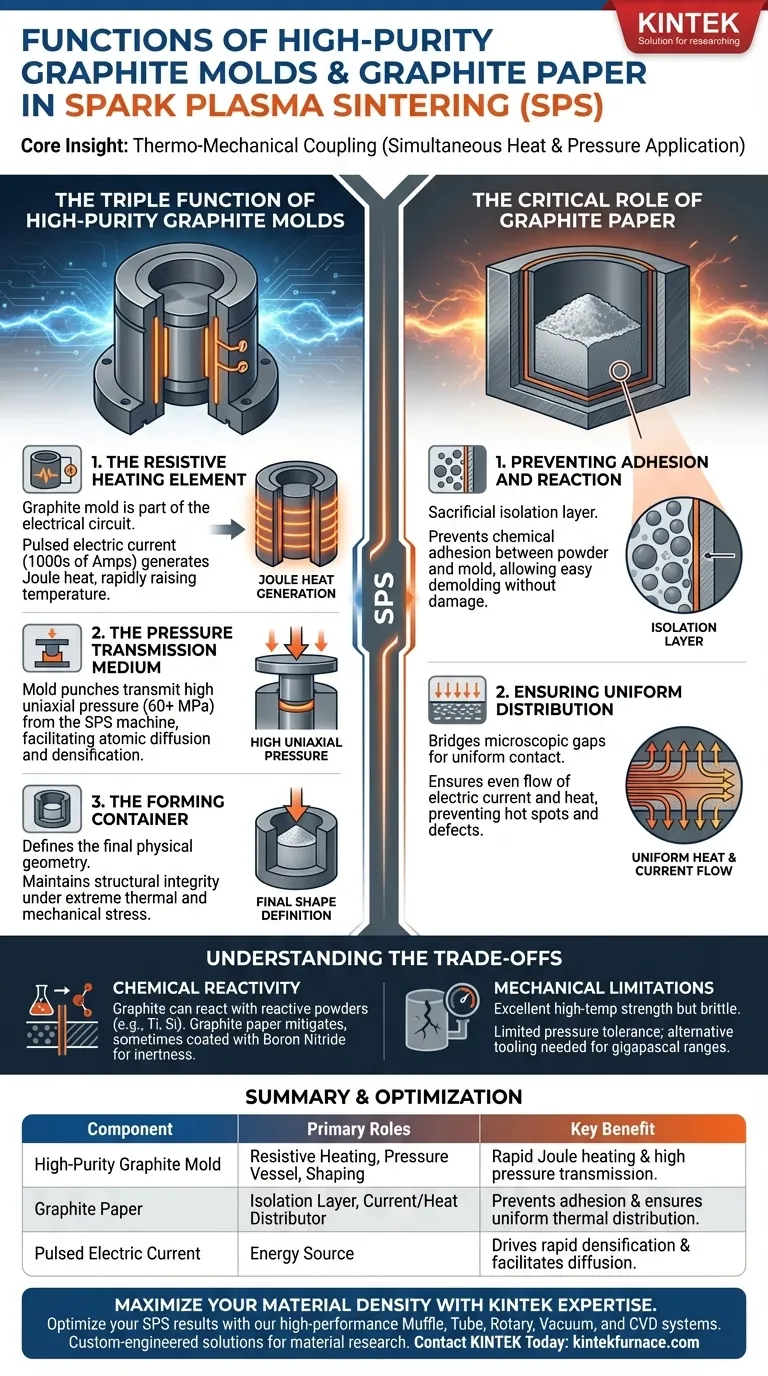
In the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process, high-purity graphite molds function simultaneously as the resistive heating element, the mechanical pressure vessel, and the shaping container. Graphite paper acts as a critical interface layer between the powder and the mold, preventing chemical adhesion while ensuring the uniform distribution of both electric current and heat.
Core Insight: The SPS process relies on "thermo-mechanical coupling"—the simultaneous application of heat and pressure. The graphite mold is not a passive container; it is the active component that generates the heat (via Joule heating) and delivers the pressure required to achieve full material densification.

The Triple Function of High-Purity Graphite Molds
High-purity graphite is chosen for SPS because it possesses a unique combination of high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and high-temperature mechanical strength. It performs three distinct roles during the cycle.
1. The Resistive Heating Element
Unlike conventional sintering where the mold sits inside a separate furnace, the graphite mold in SPS is part of the electrical circuit. Pulsed electric current (often thousands of amperes) passes directly through the graphite. Because graphite acts as a resistor, this current generates significant Joule heat, rapidly raising the temperature of the mold and the sample inside.
2. The Pressure Transmission Medium
SPS requires high uniaxial pressure to densify powder particles. The graphite mold, specifically the punch, transmits mechanical force from the SPS machine to the sample. References indicate these molds can withstand and transmit pressures of 60 MPa or higher, facilitating atomic diffusion and densification even at rapid heating rates.
3. The Forming Container
The mold defines the final physical geometry of the sintered component. It must maintain dimensional stability and structural integrity while subjecting the sample to extreme thermal and mechanical stress. The high purity of the graphite is essential here to prevent impurities from diffusing into the sample matrix.
The Critical Role of Graphite Paper
Graphite paper is a thin, flexible foil placed as a liner between the raw powder and the inner walls of the graphite mold. Its presence is vital for process control and sample quality.
1. Preventing Adhesion and Reaction
At high sintering temperatures, ceramic or metallic powders can chemically react with or physically bond to the rigid graphite mold. Graphite paper serves as a sacrificial isolation layer. This prevents the sample from sticking to the mold, ensuring the sample can be easily removed (demolded) without cracking or damaging the mold surfaces.
2. Ensuring Uniform Distribution
The paper helps bridge microscopic gaps between the mold punches and the powder. This ensures a uniform contact interface, which allows the electric current and heat to flow evenly into the sample. Without this layer, localized hot spots or uneven pressure gradients could lead to defects in the final material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite is the standard for SPS, relying on it involves specific operational constraints that you must manage.
Chemical Reactivity
Graphite is carbon, and at elevated temperatures, it can react with certain reactive powders (like titanium or silicon) to form carbides. Why this matters: While graphite paper mitigates this, the risk of surface contamination remains. In some cases, the paper is coated with boron nitride to provide an inert barrier and further inhibit carbon diffusion.
Mechanical Limitations
Graphite has excellent high-temperature strength, but it is brittle. Why this matters: There is a limit to the pressure a graphite mold can withstand before fracturing (typically tens to hundreds of megapascals). If your project requires pressures in the gigapascal range, graphite molds are insufficient and alternative tooling materials must be considered.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When optimizing your SPS setup, understanding these components allows you to troubleshoot defects effectively.
- If your primary focus is Rapid Densification: Ensure you are using high-density, high-strength graphite molds capable of transmitting maximum pressure without deformation.
- If your primary focus is Surface Quality: Pay strict attention to the graphite paper; ensure it is properly positioned and consider using coated paper if you detect surface reaction layers or sticking.
The success of Spark Plasma Sintering depends on the mold acting as an efficient energy conduit while the paper acts as a protective barrier.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Roles | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Graphite Mold | Resistive Heating, Pressure Vessel, Shaping Container | Enables rapid Joule heating and high uniaxial pressure transmission. |
| Graphite Paper | Isolation Layer, Current/Heat Distributor | Prevents chemical adhesion and ensures uniform thermal distribution. |
| Pulsed Electric Current | Energy Source | Drives rapid densification and facilitates atomic diffusion. |
Maximize Your Material Density with KINTEK Expertise
Are you looking to optimize your Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) results? KINTEK provides the specialized high-temp laboratory solutions you need. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique material research. From selecting the right graphite tooling to achieving precise thermal gradients, our team ensures your lab is equipped for success.
Contact KINTEK Today to discover how our custom-engineered furnaces can enhance your densification processes!
Visual Guide
References
- Bianca Preuß, Thomas Lampke. Wear and Corrosion Resistant Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Al0.3CoCrFeNiMo0.75 Produced by Laser Metal Deposition and Spark-Plasma Sintering. DOI: 10.1007/s11666-024-01711-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why Use Three Independent Heating Elements in Oxidation Kinetics? Achieve Precise Zonal Control for Accurate Data
- How do ceramic heating elements compare to metal ones in terms of size and design flexibility? Unlock Advanced Heating Solutions
- Why is the precise control of electrode input current phase differences critical? Ensure Thermal Uniformity Today
- Which metals can be melted using MoSi2 heating elements? High-Temp Melting Guide
- What is the value of ceramic fiber blankets for cooling slag? Ensuring Precision in Thermal Research
- What are the four main benefits of advanced power control in industrial heating? Boost Efficiency, Precision, and Safety
- What is a key property of silicon carbide as a ceramic material? Discover Its High-Temp and Thermal Conductivity Edge
- What are the efficiency benefits of SiC heating elements? Achieve Faster Heating and Lower Energy Costs













