In terms of design flexibility, ceramic heating elements are fundamentally superior to metal ones. They can be manufactured into a vast array of custom shapes and sizes, from large, uniform panels to complex, three-dimensional geometries. This adaptability is a direct result of their material properties and manufacturing process, a capability that traditional metal heating elements cannot replicate.
While metal heaters are a proven solution for simple heating tasks, the choice between metal and ceramic is ultimately a decision about design intent. Ceramic technology unlocks advanced engineering possibilities by combining superior material stability with unparalleled geometric freedom.

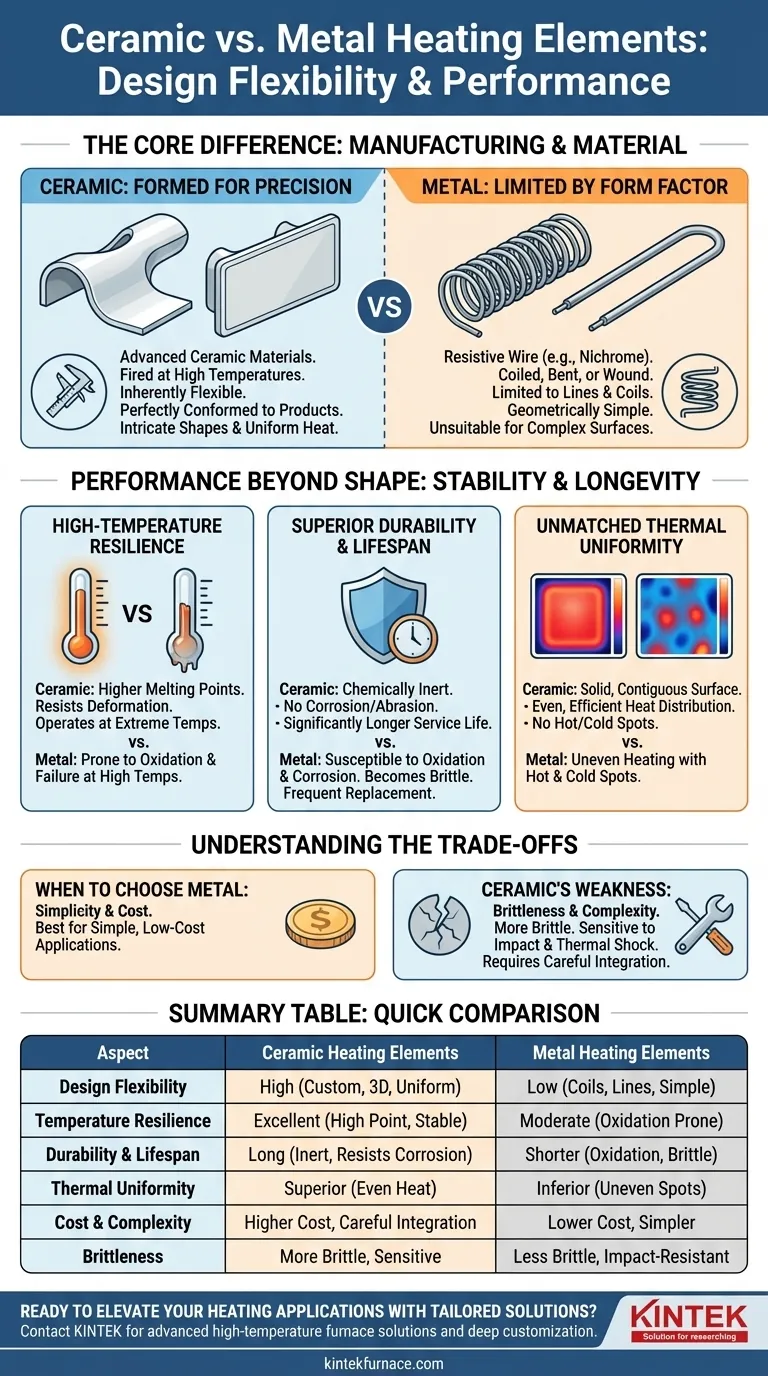
The Core Difference: Manufacturing and Material
The design limitations of a heating element are rooted in its base material and how it is formed. Ceramic and metal differ profoundly in this regard.
Ceramic: Formed for Precision
Ceramic heaters are typically produced by forming advanced ceramic materials into a desired shape and then firing them at high temperatures. This process is inherently flexible.
It allows for the creation of heaters that are perfectly conformed to a product's surface, intricate shapes for medical or scientific devices, or large, flat panels that provide perfectly uniform heat distribution.
Metal: Limited by Form Factor
Most metal heating elements rely on a resistive wire, like Nichrome, that is coiled, bent, or wound. This fundamentally limits their shape to variations of lines and coils.
While these coils can be embedded within other materials to create heated plates, the element itself remains geometrically simple. This makes them unsuitable for applications requiring a complex, integrated heating surface.
Performance Beyond Shape: Why Stability Matters
The advantages of ceramic extend far beyond just shape. The material's inherent stability delivers superior performance and longevity, especially in demanding applications.
High-Temperature Resilience
Ceramic materials possess higher melting points and greater resistance to heat-induced deformation compared to metals. They can operate reliably at extreme temperatures where a metal element would quickly oxidize, weaken, and fail.
Superior Durability and Lifespan
Metal elements are highly susceptible to oxidation and corrosion, especially when cycled to high temperatures. This process causes them to become brittle and lose performance, necessitating frequent replacement.
Ceramics are chemically inert and do not suffer from this degradation. They resist corrosion and abrasion, ensuring a significantly longer service life and consistent performance over many years.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
Because a ceramic heater can be a solid, contiguous surface, it distributes thermal energy evenly and efficiently. This eliminates the hot and cold spots typical of spaced-out metal coil heaters, making ceramics ideal for applications where precise and consistent temperature is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a technology requires acknowledging its potential downsides. While ceramics offer superior performance, metal elements still hold a place for specific use cases.
When to Choose Metal: Simplicity and Cost
For straightforward heating applications, such as in simple appliances or where cost is the absolute primary driver, metal coil heaters are a mature and highly economical choice. Their simplicity is their strength when advanced performance is not a requirement.
Ceramic's Weakness: Brittleness
While highly resistant to heat and corrosion, ceramics are inherently more brittle than metals. They are more susceptible to failure from physical impact or extreme thermal shock (very rapid temperature changes), requiring careful handling and integration during product design.
Integration Complexity
The flexibility of ceramic shapes can sometimes introduce complexity into the mounting and assembly process. Designs must account for the material's rigidity and prevent mechanical stress that could lead to cracking over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your application's core requirements should dictate your choice of heating technology.
- If your primary focus is complex geometry or uniform surface heating: Ceramic elements are the only viable option, as they can be manufactured to fit intricate designs precisely.
- If your primary focus is longevity in a high-temperature or corrosive environment: The inherent chemical stability of ceramic provides a significantly longer and more reliable service life.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost solution for a simple, non-critical heating task: Traditional metal coil heaters offer the most economical and straightforward path.
By understanding these fundamental material differences, you can select the heating technology that not only fits your design's shape but also achieves its long-term performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Ceramic Heating Elements | Metal Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Design Flexibility | High; custom shapes, 3D geometries, uniform panels | Low; limited to coils, lines, simple forms |
| Temperature Resilience | Excellent; high melting point, resists deformation | Moderate; prone to oxidation and failure at high temps |
| Durability & Lifespan | Long; chemically inert, corrosion-resistant | Shorter; susceptible to oxidation and brittleness |
| Thermal Uniformity | Superior; even heat distribution, no hot spots | Inferior; uneven heating with hot and cold spots |
| Cost & Complexity | Higher cost, may require careful integration | Lower cost, simpler for basic applications |
| Brittleness | More brittle, sensitive to impact and thermal shock | Less brittle, more impact-resistant |
Ready to elevate your heating applications with tailored solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements with precision. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your project's performance and longevity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















