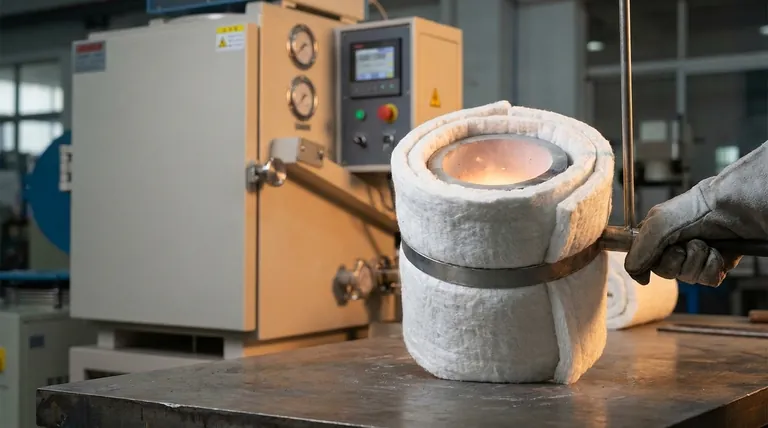
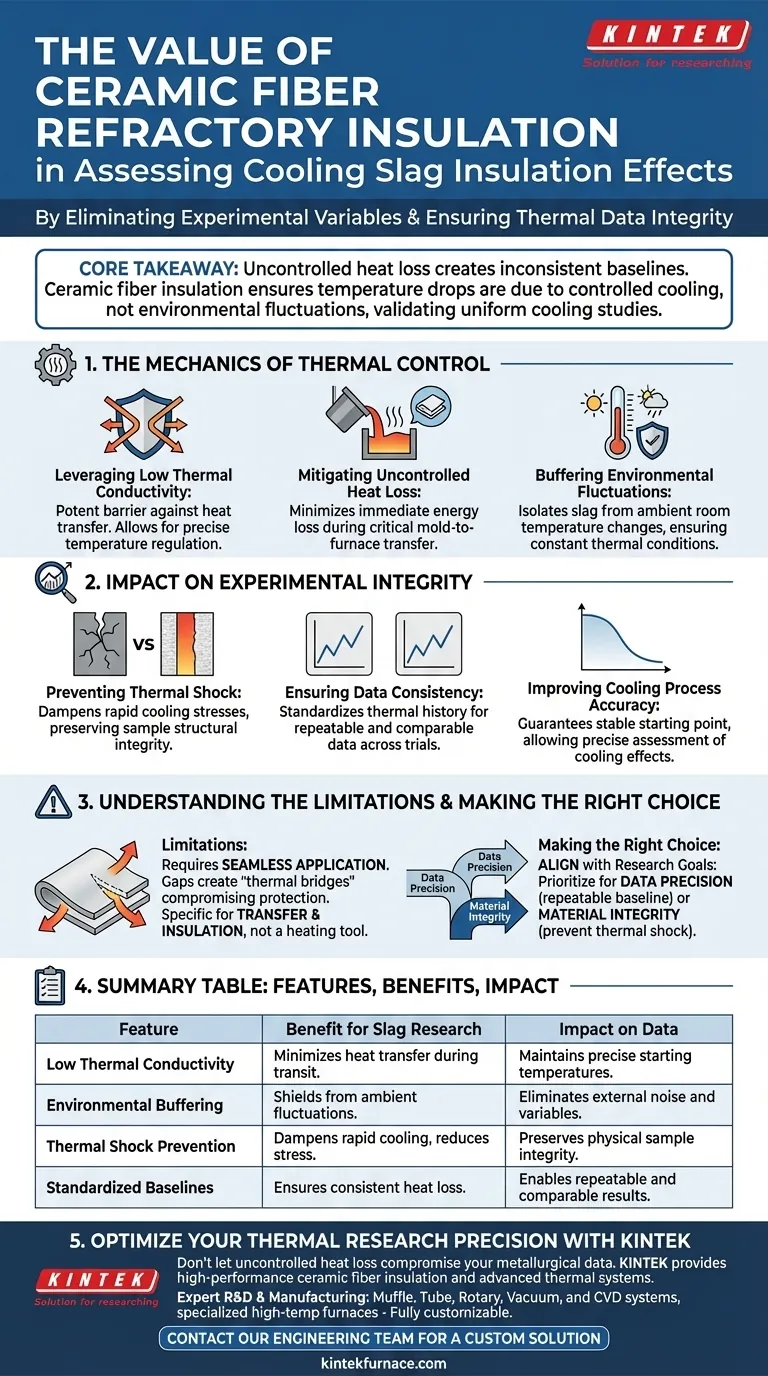
The primary value of ceramic fiber refractory insulation lies in its ability to eliminate experimental variables during high-temperature transfers. By utilizing materials with extremely low thermal conductivity, these blankets prevent uncontrolled heat loss when moving molten slag from the mold to the furnace, directly safeguarding the integrity of thermal research data.
Core Takeaway: Uncontrolled heat loss creates inconsistent baselines in metallurgical research. Ceramic fiber insulation ensures that temperature drops are strictly a result of the controlled cooling process, not environmental fluctuations, thereby validating the accuracy of uniform cooling studies.

The Mechanics of Thermal Control
Leveraging Low Thermal Conductivity
High-performance ceramic fiber blankets are characterized by their exceptional resistance to heat transfer. When applied to transfer units, they act as a potent barrier between the molten slag and the cooler surrounding environment. This property is the fundamental mechanism that allows for precise temperature regulation.
Mitigating Uncontrolled Heat Loss
Moving slag from a mold to a furnace represents a critical window of vulnerability where rapid cooling typically occurs. Without protection, this transfer results in immediate, unpredictable energy loss. Ceramic fiber blankets effectively minimize this loss, maintaining the slag's thermal state during transit.
Buffering Environmental Fluctuations
Ambient room temperatures can vary, introducing significant noise into experimental data. Insulation shields the slag from these external shifts. By isolating the material, researchers ensure that the thermal conditions remain constant regardless of the surrounding environment.
Impact on Experimental Integrity
Preventing Thermal Shock
Rapid cooling during the transfer phase induces unwanted thermal stresses within the slag. These stresses can alter the material's physical properties before the controlled experiment even begins. Insulation dampens this shock, preserving the structural integrity of the sample.
Ensuring Data Consistency
Reliable research requires repeatable conditions. If the heat loss during transfer varies from test to test, the resulting data becomes incomparable. Insulation standardizes the thermal history of the slag, ensuring consistency across multiple experimental trials.
Improving Cooling Process Accuracy
The ultimate goal in this context is often to study uniform cooling processes. If the starting temperature is compromised by transfer loss, the cooling curve becomes unreliable. Ceramic fiber guarantees a stable starting point, allowing for precise assessment of cooling effects.
Understanding the Limitations
The Requirement of Seamless Application
The effectiveness of ceramic fiber is dependent on complete coverage. Even minor gaps in the insulation blanket can create "thermal bridges," allowing localized heat to escape. If the application on the transfer unit is not perfectly uniform, the protection against thermal stress is compromised.
The Specificity of Use
These blankets are specifically designed to address transfer and insulation challenges. They do not actively heat the material; they only retard heat loss. Therefore, they are a preservation tool, not a correction tool for slag that has already cooled below the desired threshold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To effectively utilize ceramic fiber insulation in your slag assessment, align its application with your specific research goals.
- If your primary focus is Data Precision: Prioritize insulation during the mold-to-furnace transfer to eliminate environmental noise and establish a repeatable thermal baseline.
- If your primary focus is Material Integrity: Use these blankets to prevent thermal shock and stress fractures caused by rapid air cooling during transport.
By stabilizing the thermal environment, ceramic fiber insulation transforms slag cooling from a variable-prone procedure into a controlled, measurable science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Slag Research | Impact on Data |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Minimizes heat transfer during mold-to-furnace transit. | Maintains precise starting temperatures. |
| Environmental Buffering | Shields slag from ambient room temperature fluctuations. | Eliminates external noise and variables. |
| Thermal Shock Prevention | Dampens rapid cooling to reduce internal material stress. | Preserves physical sample integrity. |
| Standardized Baselines | Ensures consistent heat loss across multiple trials. | Enables repeatable and comparable results. |
Optimize Your Thermal Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let uncontrolled heat loss compromise your metallurgical data. KINTEK provides high-performance ceramic fiber insulation and advanced thermal systems designed to eliminate experimental variables.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique research needs. Ensure your cooling processes are accurate and repeatable today.
Contact Our Engineering Team for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What is the monitoring function of armored thermocouples in geopolymer fire resistance experiments?
- In what applications are silicon carbide heating rods commonly used? Essential for High-Temp Metallurgy, Ceramics & More
- What function do 220V armored electric heaters serve in SA-178 Gr A steel pipe heat treatment? Expert Precision Heating
- What are the properties and uses of pure platinum as a heating element? Ideal for High-Temp Precision and Purity
- Why Is a Graphite Shield Essential in Silicon Crystal Growth? Master Thermal and Chemical Purity
- How does advanced power control extend heating element lifespan? Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
- What are the principles and characteristics of thermistors? Unlock Precision Temperature Sensing
- What are the models of MoSi2 heating elements and their working temperatures? Choose the Right Model for Your High-Temp Needs
