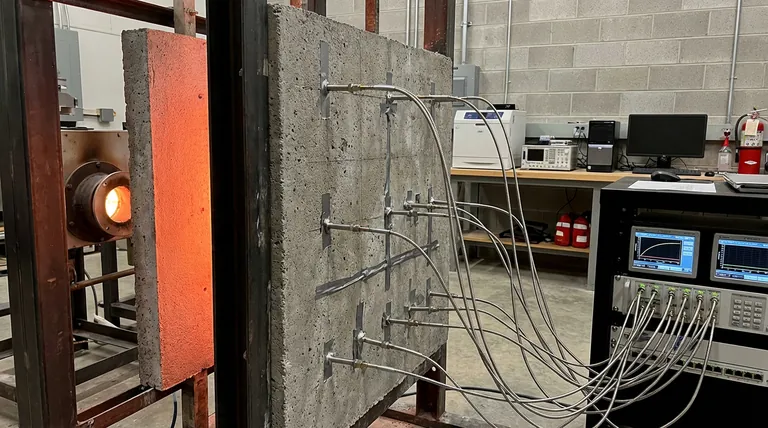
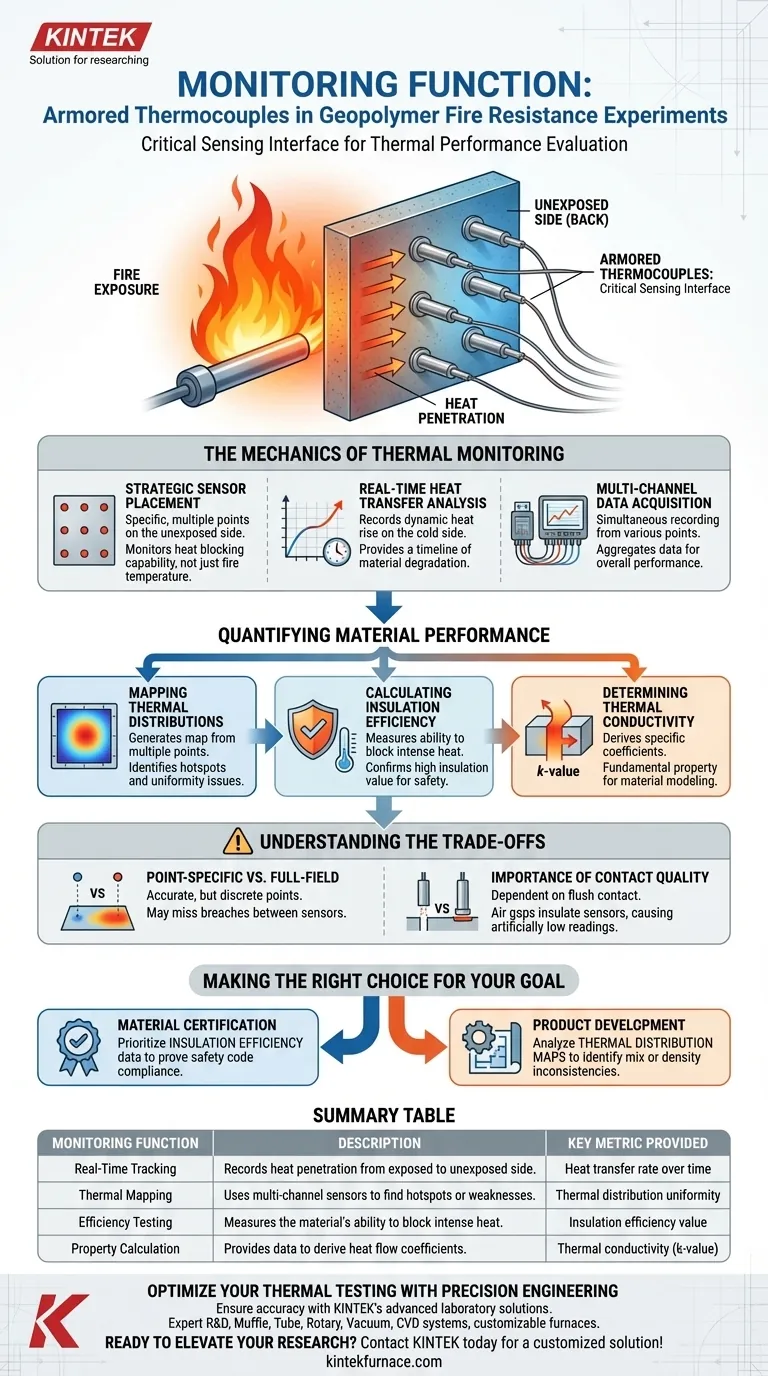
Armored thermocouples serve as the critical sensing interface for evaluating the thermal performance of geopolymer materials under fire conditions. Specifically, these sensors are attached to the unexposed side (the back) of geopolymer panels to capture real-time temperature data as the material is subjected to heat. This setup allows researchers to monitor exactly how much heat penetrates the material over time.
By feeding continuous data into a multi-channel acquisition system, these sensors allow for the precise mapping of thermal distributions. This data is the foundation for quantifying the material's thermal conductivity and insulation efficiency.

The Mechanics of Thermal Monitoring
Strategic Sensor Placement
In fire resistance experiments, the placement of the sensor is as critical as the sensor itself. Armored thermocouples are positioned at specific, multiple points on the back of the geopolymer panels.
By monitoring the unexposed side, the system does not merely measure the fire's temperature, but rather the material's ability to block that heat.
Real-Time Heat Transfer Analysis
The primary function of these devices is to record real-time heat transfer data.
Fire resistance is not a static property; it is a dynamic process. The thermocouples track the rate at which temperature rises on the cold side of the panel, providing a timeline of the material's thermal degradation or resistance.
Multi-Channel Data Acquisition
Data is rarely collected in isolation. The thermocouples connect to a multi-channel temperature acquisition system.
This allows for simultaneous recording from various points on the panel. This aggregation of data ensures that the results reflect the material's overall performance, rather than an anomaly at a single location.
Quantifying Material Performance
Mapping Thermal Distributions
Because data is collected from multiple points, researchers can generate a map of thermal distribution.
This reveals uniformity in the material. It helps identify hotspots or structural weaknesses where heat creates a "thermal bridge" through the geopolymer matrix faster than in other areas.
Calculating Insulation Efficiency
The ultimate goal of the monitoring is to quantify insulation efficiency.
If the thermocouples report a slow, minimal temperature rise despite intense heat on the front face, the material is confirmed to have high insulation value. This data provides the empirical evidence needed to certify the material for safety applications.
Determining Thermal Conductivity
Beyond general insulation, the data allows for the calculation of specific thermal conductivity.
This is a fundamental physical property that dictates how easily heat flows through the geopolymer. Accurate thermocouple readings are required to derive the mathematical coefficients that engineers use to model the material's behavior in building designs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Point-Specific vs. Full-Field Data
While highly accurate, thermocouples only provide data at discrete points of contact.
They do not measure the entire surface area. Consequently, if a crack or failure occurs between two sensors, the thermal map may initially miss the breach until the heat spreads to a sensor location.
The Importance of Contact Quality
The accuracy of an armored thermocouple is entirely dependent on flush contact with the surface.
If the armor is not perfectly bonded to the back of the geopolymer panel, air gaps can insulate the sensor. This results in artificially low temperature readings, potentially overstating the material's fire resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data derived from these sensors drives different decisions depending on your specific engineering objectives.
- If your primary focus is Material Certification: Prioritize the insulation efficiency data to prove the panel keeps the unexposed side cool enough to meet safety codes.
- If your primary focus is Product Development: Analyze the thermal distribution maps to identify inconsistencies in the geopolymer mix or density.
Accurate thermal monitoring transforms raw fire exposure into actionable engineering data.
Summary Table:
| Monitoring Function | Description | Key Metric Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Tracking | Records heat penetration from the exposed to unexposed side. | Heat transfer rate over time |
| Thermal Mapping | Uses multi-channel sensors to find hotspots or weaknesses. | Thermal distribution uniformity |
| Efficiency Testing | Measures the material's ability to block intense heat. | Insulation efficiency value |
| Property Calculation | Provides data to derive heat flow coefficients. | Thermal conductivity (k-value) |
Optimize Your Thermal Testing with Precision Engineering
Ensure the accuracy of your material certification and product development with KINTEK’s advanced laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for your unique fire resistance and geopolymer testing needs.
Don't let poor data compromise your safety standards. Our high-performance equipment provides the stable thermal environments necessary for precise thermocouple monitoring and material analysis.
Ready to elevate your research? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Marios Valanides, Demetris Nicolaides. Geopolymerization of Recycled Glass Waste: A Sustainable Solution for a Lightweight and Fire-Resistant Material. DOI: 10.3390/recycling9010016
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is power requirement determined for heaters? Calculate Energy Needs for Efficient Heating
- What is Serpentine Technology in heating elements? High-Temp, High-Stakes Heating Solutions
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? Unlock Superior Performance for High-Temp Processes
- Are silicon carbide heating elements customizable? Optimize Your High-Temp Furnace Performance
- Why are alloys used in electrical heating devices? Discover the Key to Durable, Efficient Heat Generation
- Why are high-performance microwave-absorbing materials required in microwave sintering? Solve the 'Cold Start' Challenge
- What are the standard size ranges for silicon carbide heating elements? Ensure Optimal Performance for Your Furnace
- What is the technical significance of MoSi2 furnaces for sintering red mud-alumina? Achieve High-Density Composites








