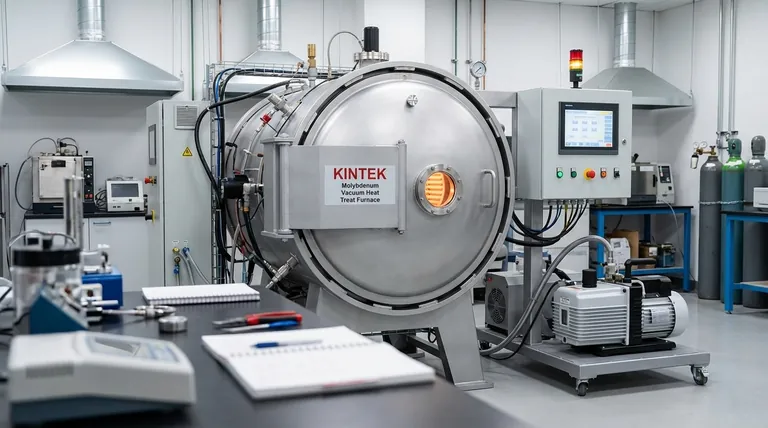
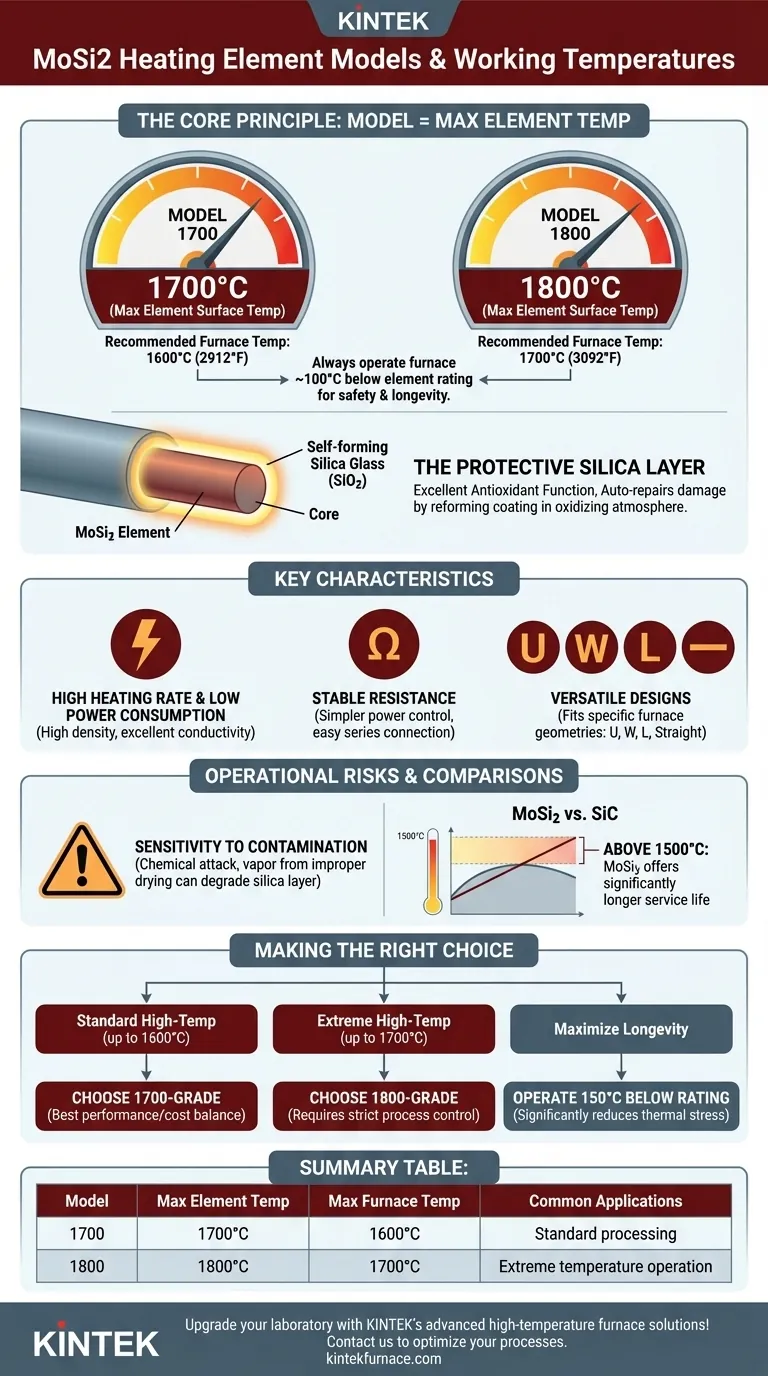
At its core, the model of a Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating element indicates its maximum surface temperature, which in turn dictates the highest practical operating temperature for your furnace. The two most common models are the 1700 and 1800 types, which are designed for maximum furnace temperatures of 1600°C (2912°F) and 1700°C (3092°F), respectively.
The model number (e.g., 1700, 1800) refers to the element's peak temperature capability in degrees Celsius. To ensure longevity and safety, the maximum continuous operating temperature of the furnace should be set approximately 100°C below this rating.

Decoding MoSi2 Model Numbers and Temperatures
Understanding the relationship between the element's rating and the furnace's atmosphere is the most critical factor in specifying and operating these components correctly.
The Core Principle: Element vs. Furnace Temperature
A MoSi2 heating element always runs hotter than the furnace chamber it is heating. This temperature difference is essential for efficient heat transfer.
A model labeled "1700" can reach a surface temperature of 1700°C. To avoid overheating and premature failure, it should be used in a furnace with a maximum operating temperature of 1600°C.
Similarly, a model labeled "1800" can reach 1800°C and is intended for furnace applications up to 1700°C. Some specialized elements can even reach 1900°C for use in 1800°C furnaces.
The Protective Silica Layer
The remarkable high-temperature performance of MoSi2 elements comes from a self-forming, protective layer of silica glass (SiO2) that develops on the surface in an oxidizing atmosphere.
This layer provides an excellent antioxidant function. If the layer is damaged, it "auto-repairs" by consuming more silicon from the element to reform the protective coating, making these elements ideal for continuous work.
Key Characteristics of MoSi2 Elements
Beyond temperature ratings, several key properties define the performance and versatility of MoSi2 heating elements.
Superior Physical and Electrical Properties
These elements are characterized by high density and excellent electrical conductivity. This translates to a high heating rate and relatively low power consumption.
Their resistance remains stable over time, which simplifies power control system design and allows for new elements to be connected in series with older ones without issue.
Versatility in Design and Configuration
MoSi2 elements can be manufactured in a variety of shapes to fit specific furnace designs. Common forms include U-shape, W-shape, L-shape, and straight rods.
This design flexibility allows for optimized heat distribution in complex furnace geometries, from large industrial units to smaller laboratory furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Risks
While powerful, MoSi2 elements have specific operational requirements and vulnerabilities that must be managed to ensure a long service life.
Sensitivity to Contamination
MoSi2 elements are susceptible to chemical attack and contamination. This is a critical operational risk.
For instance, in applications like dental furnaces, failure to properly dry colored or painted zirconia before heating can release vapors that degrade the element's protective silica layer, leading to rapid failure. Proper furnace maintenance and clean operation are paramount.
MoSi2 vs. SiC Elements
When choosing between MoSi2 and Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements, the primary factor is operating temperature.
Above 1500°C, MoSi2 elements generally offer a significantly longer service life than SiC elements, making them the superior choice for very high-temperature processes.
Excellent Durability with Proper Care
Despite their brittleness at room temperature, MoSi2 elements possess high bending and compression strength at operating temperatures. Special joint molding processes create strong, impact-resistant terminals.
With proper handling during installation and by avoiding chemical contamination, these elements provide an exceptionally long life expectancy, even with frequent thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct MoSi2 element model is a balance between your temperature requirements, your process environment, and your goals for element longevity.
- If your primary focus is standard high-temperature processing (up to 1600°C): The 1700-grade element provides the best balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature operation (up to 1700°C): The 1800-grade element is necessary, but requires stricter process control to manage contamination risks and maximize lifespan.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element longevity: Operate your chosen element at least 150°C below its maximum rated furnace temperature to significantly reduce thermal stress.
Choosing the right element and operating it with an understanding of its properties is the key to achieving reliable and efficient high-temperature performance.
Summary Table:
| Model | Max Element Temperature | Max Furnace Operating Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 | 1700°C | 1600°C | Standard high-temperature processing |
| 1800 | 1800°C | 1700°C | Extreme temperature operation |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable MoSi2 heating elements and custom furnace designs, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your high-temperature processes and extend equipment lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















