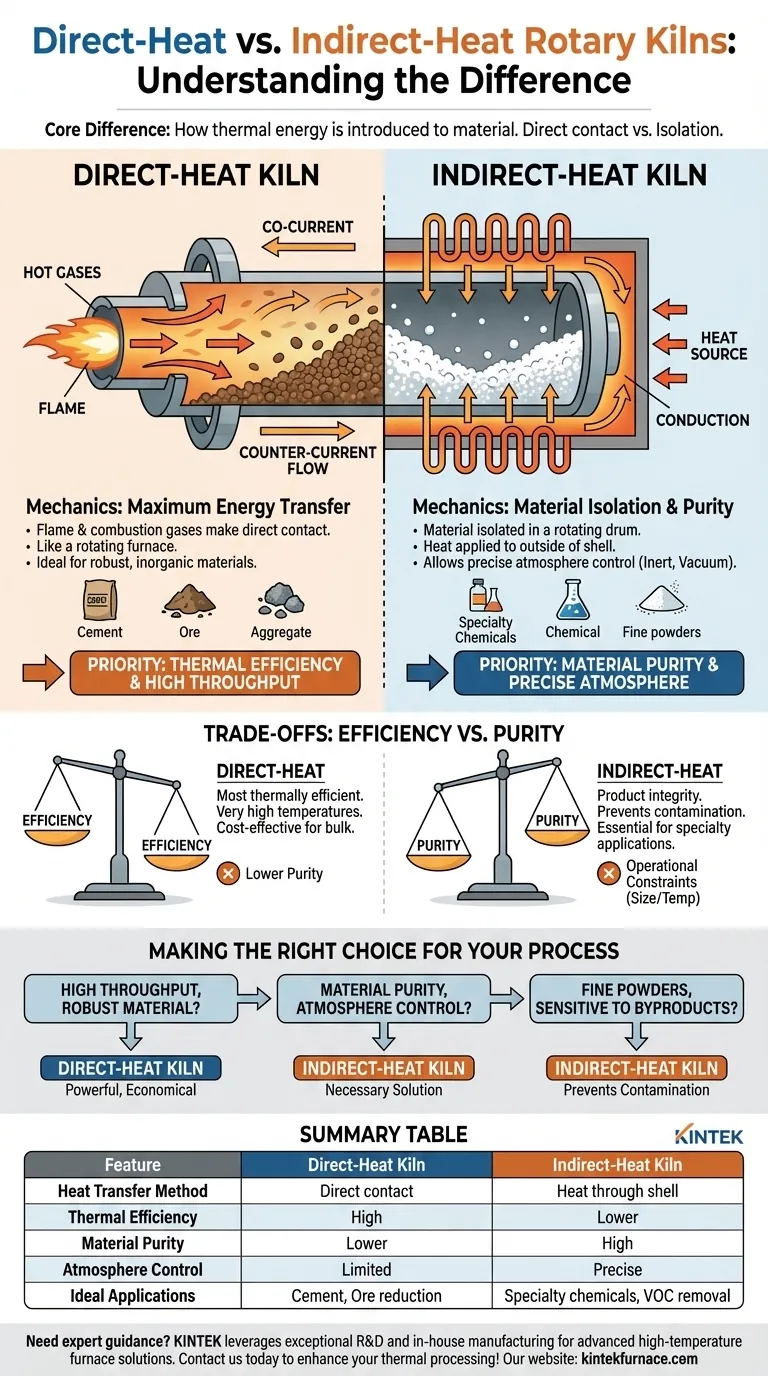
At its core, the difference between direct-heat and indirect-heat rotary kilns lies in how thermal energy is introduced to the material being processed. In a direct-heat kiln, the flame and hot combustion gases make direct contact with the material. In an indirect-heat kiln, the material is isolated within a rotating drum, and heat is applied to the outside of that drum, transferring through the shell wall.
The decision between direct and indirect heating is a fundamental trade-off. Direct heating prioritizes thermal efficiency and high throughput, while indirect heating prioritizes material purity and precise atmospheric control.
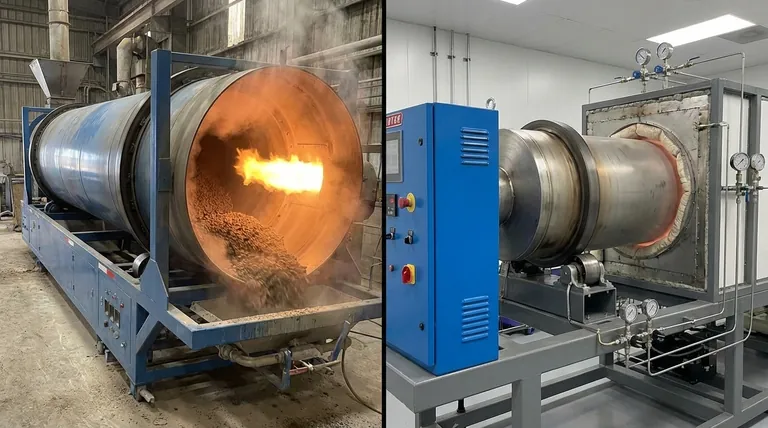

The Mechanics of Direct-Heat Kilns
A direct-heat (or direct-fired) kiln is designed for maximum energy transfer. It functions like a large, rotating furnace where the material tumbles through the hot gases.
How It Works
In a direct-fired system, a burner injects a flame and hot combustion gases directly into the kiln's interior. As the kiln rotates, lifting flights pick up and cascade the material through this stream of hot gas, ensuring thorough and direct contact.
This process can be configured in two ways: co-current flow, where the material and gas move in the same direction, or counter-current flow, where they move in opposite directions for maximum heat exchange.
Ideal Applications
Direct-heat kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. They are ideal for processing robust, inorganic materials that will not be chemically altered or contaminated by contact with flue gas.
Common applications include cement production, ore reduction, and the drying of aggregates, sand, and certain minerals.
The Mechanics of Indirect-Heat Kilns
An indirect-heat kiln, often called a calciner, is designed to isolate the material from the products of combustion, ensuring purity.
How It Works
In this design, the rotating drum containing the material is enclosed within a furnace or surrounded by external heating elements. The heat source warms the outside of the drum's shell, and this energy is transferred via conduction through the shell wall to the material tumbling inside.
Because the material never contacts the flame or flue gas, the internal atmosphere can be tightly controlled. It can be an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen), a vacuum, or a specific reactive gas required for the process.
Ideal Applications
Indirect heating is essential for processes involving materials that are sensitive, fine, or require a controlled atmosphere. This is critical when avoiding contamination or unwanted side reactions is the primary goal.
Typical uses include calcination of specialty chemicals, removal of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and processing of materials that could be damaged by direct flame impingement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Purity
Choosing the right kiln type requires a clear understanding of your process priorities, as each design comes with inherent compromises.
The Efficiency of Direct Firing
Directly contacting the material with hot gas is the most thermally efficient method of heat transfer. This allows direct-fired kilns to achieve very high temperatures and process massive volumes of material, making them cost-effective for bulk processing.
The Purity of Indirect Firing
The key advantage of indirect kilns is product integrity. By preventing contact with combustion byproducts like sulfur or water vapor, the final material remains pure. This is non-negotiable for many chemical and specialty applications.
Operational Constraints
Direct-heat kilns can be built to enormous sizes. Indirect-heat kilns are limited by the material science of the drum shell, which must withstand high temperatures while under mechanical stress. This limits their maximum diameter and operating temperature compared to their direct-fired counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material and your end-goal dictate the correct technology. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and thermal efficiency for a robust material: A direct-heat kiln is the more powerful and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is preserving absolute material purity or controlling the process atmosphere: An indirect-heat kiln is the necessary solution.
- If you are processing fine powders or materials sensitive to combustion byproducts: An indirect-heat kiln is often the only viable option to prevent contamination or loss of product.
Understanding this fundamental difference in heat transfer is the first and most critical step in engineering a successful thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct-Heat Kiln | Indirect-Heat Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Direct contact with flame and gases | Heat through drum shell via conduction |
| Thermal Efficiency | High | Lower |
| Material Purity | Lower (risk of contamination) | High (isolated from combustion) |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited | Precise (inert, vacuum, reactive gases) |
| Ideal Applications | Cement, ore reduction, drying aggregates | Specialty chemicals, VOC removal, sensitive materials |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right kiln for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for diverse laboratories. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processing efficiency and purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results



















