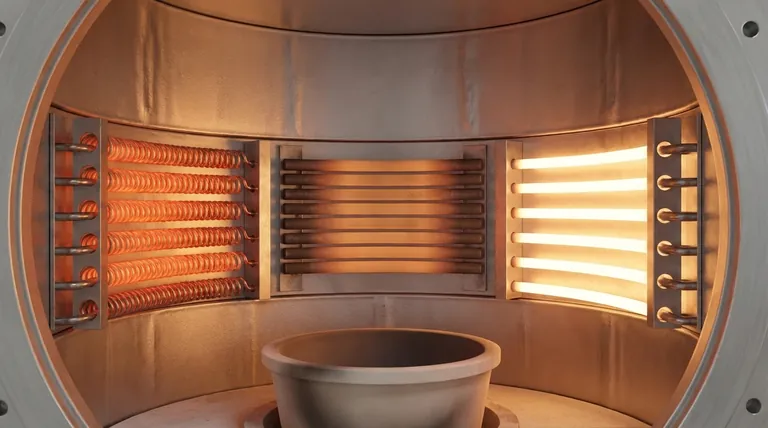
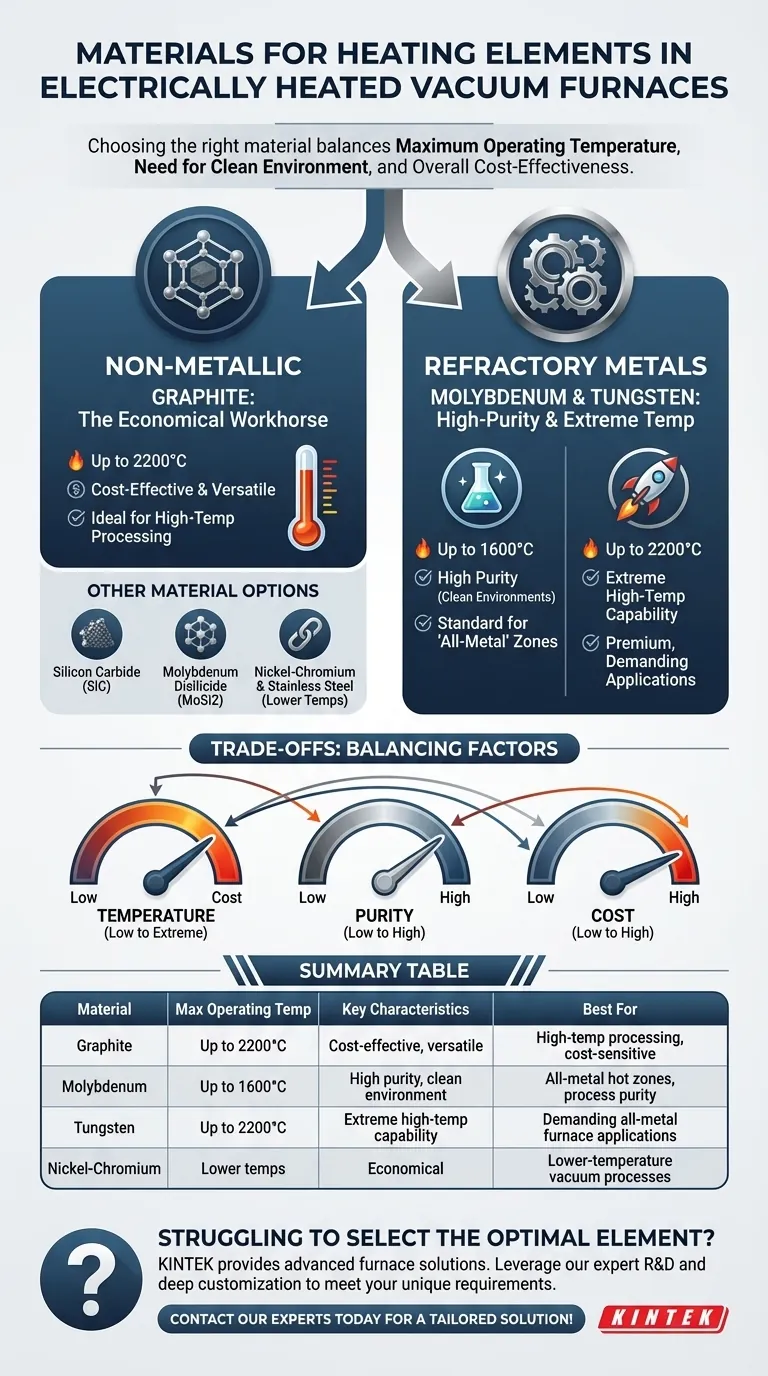
The most common materials for heating elements in electrically heated vacuum furnaces fall into two primary categories: non-metallic materials like graphite and silicon carbide, and high-temperature metallic alloys, predominantly refractory metals such as molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum. Less common alloys like nickel-chromium and stainless steel are also used for lower-temperature applications.
The selection of a heating element material is a critical design choice driven by a balance between three factors: the maximum required operating temperature, the need for a non-contaminating or "clean" environment, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Deconstructing the Material Choices
The ideal heating element must withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, and crucially, it must have a low vapor pressure. This ensures the element itself does not vaporize and contaminate the workpiece being processed within the vacuum.
The Non-Metallic Workhorse: Graphite
Graphite is an extremely common choice for vacuum furnace heating elements, particularly for higher-temperature processes.
Its popularity stems from its excellent combination of high-temperature durability, withstanding up to 2200°C, and its relatively low cost. This makes it a versatile and economical option for many applications.
The Refractory Metals: Molybdenum and Tungsten
Refractory metals are a class of materials defined by their exceptionally high melting points and resistance to wear and deformation.
Molybdenum is the most widely used refractory metal for heating elements. It offers excellent stability and a long service life at temperatures up to 1600°C and is prized for its use in clean environments where graphite dust would be a contaminant.
Tungsten is reserved for the most demanding, extremely high-temperature applications. It can operate at temperatures up to 2200°C, making it a direct competitor to graphite at the highest end of the performance spectrum.
Tantalum is another refractory metal used in specific applications, valued for its high resistance to corrosion and high melting point.
Other Material Options
For specific applications, other materials are also employed. Silicon carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are non-metallic options often found in modern sintering furnaces.
For vacuum processes that operate at lower temperatures, more conventional alloys like nickel-chromium or even stainless steel can serve as cost-effective heating elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is not just about picking the one with the highest temperature rating. It's about understanding the compromises between performance, purity, and price.
Temperature vs. Cost
Molybdenum and graphite represent the best balance of cost and performance for a vast range of vacuum furnace processes.
Tungsten is a premium material. Its higher cost is justified only when the process absolutely requires the extreme temperatures it can withstand.
Purity and Environmental Cleanliness
The choice between an all-metal furnace and a graphite furnace is a primary consideration. Molybdenum heating elements are integral to "all-metal" hot zones, which are specified for processes demanding high purity and a very clean vacuum, free from the potential for carbon contamination.
The Critical Role of Vapor Pressure
In the vacuum of a furnace, materials can turn from a solid directly to a gas at high temperatures. All selected heating element materials—graphite, molybdenum, tungsten—have very low vapor pressures, which is essential to minimize contamination and ensure the element has a long operational life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal material is directly tied to the specific thermal and chemical requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-temperature processing (up to 2200°C): Graphite is often the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is process purity in a clean environment (up to 1600°C): Molybdenum is the industry standard for all-metal hot zones.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest temperatures (up to 2200°C) in an all-metal furnace: Tungsten is the necessary material, despite its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is a lower-temperature vacuum process: A more economical alloy like nickel-chromium may be perfectly sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, a deep understanding of your process requirements is the key to selecting the most effective and reliable heating element material.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Operating Temp | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 2200°C | Cost-effective, versatile | High-temperature processing, cost-sensitive applications |
| Molybdenum | Up to 1600°C | High purity, clean environment | All-metal hot zones requiring process purity |
| Tungsten | Up to 2200°C | Extreme high-temperature capability | Demanding all-metal furnace applications |
| Nickel-Chromium | Lower temps | Economical | Lower-temperature vacuum processes |
Struggling to select the optimal heating element for your specific vacuum furnace process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, purity, and cost to ensure maximum performance and reliability. Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- What technological features enhance the efficiency of vacuum furnaces? Boost Performance with Advanced Control & Energy Savings



















