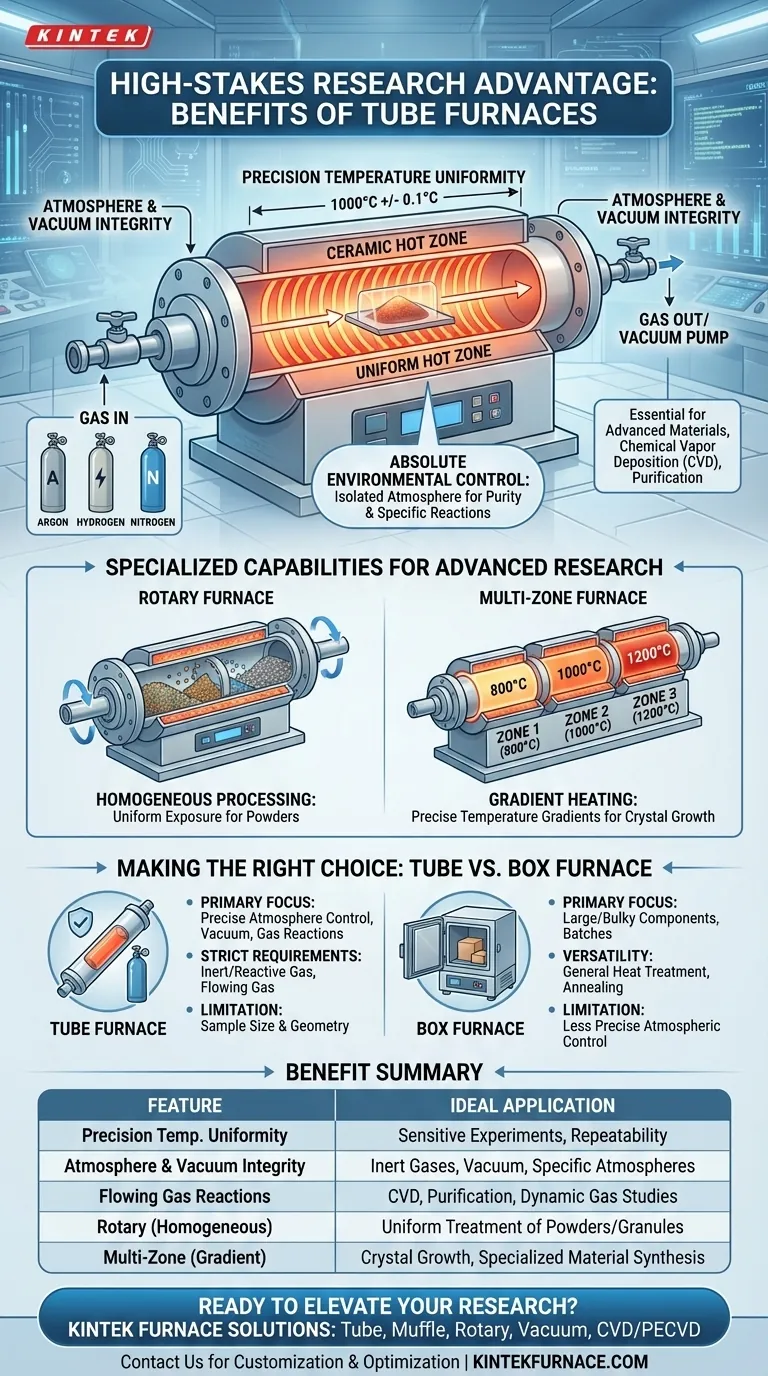
For high-stakes research, a tube furnace offers unparalleled environmental control that standard furnaces cannot match. Its core benefits stem from a sealed tube design that enables precise management of temperature uniformity, atmospheric conditions, and gas flow, which are critical for processing sensitive and advanced materials.
The defining advantage of a tube furnace is not merely its ability to heat, but its power to create a highly specific, controlled, and isolated atmosphere around a sample. This makes it an indispensable tool for research where atmospheric purity or specific gas reactions are paramount to success.

The Core Advantage: Absolute Environmental Control
The unique geometry of a tube furnace is the source of its primary benefits. Unlike a box furnace which heats a large chamber, a tube furnace focuses energy on a contained, cylindrical space.
Precision Temperature Uniformity
The tubular heating chamber naturally promotes a highly uniform "hot zone" along its central axis. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, which is crucial for repeatability and obtaining reliable data in sensitive experiments.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Integrity
This is the most critical differentiator. The ends of the tube can be sealed with flanges, allowing the internal environment to be completely isolated. Researchers can then create a high-vacuum environment or backfill the tube with a specific gas—such as inert Argon or reactive Hydrogen—to prevent oxidation or facilitate a chemical reaction.
Suitability for Flowing Gas Reactions
The sealed design is ideal for processes that require a continuous flow of gas over a sample. This capability is essential for applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), purification, or studying material reactions in dynamic gas environments.
Specialized Capabilities for Advanced Research
The basic tube furnace design can be adapted for highly specific research tasks, further enhancing its value.
Rotary Furnaces for Homogeneous Processing
For powders or granular materials, a rotary tube furnace provides a significant advantage. It simultaneously heats and tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to both the heat and the controlled atmosphere, preventing clumping and ensuring consistent results.
Multi-Zone Furnaces for Gradient Heating
Advanced models feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows researchers to create precise temperature gradients, a requirement for processes like crystal growth or specialized material synthesis.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tube vs. Box Furnace
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding its limitations compared to other common types, like a box furnace.
When to Choose a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is the superior choice when your process is defined by strict atmospheric requirements. If you need to work under a vacuum, in an inert gas, or with a specific flowing gas, the tube furnace is the correct tool. Its primary limitation is sample size and geometry.
When a Box Furnace is a Better Fit
A box furnace offers greater versatility in sample size and shape. Its large, accessible chamber and simple front-loading door make it ideal for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, or sterilizing large components where precise atmospheric control is not the main priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Your final decision should be guided by the single most critical variable in your process.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control, vacuum, or gas reactions: A tube furnace is the definitive choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is treating powders or granules with perfect uniformity: A rotary tube furnace is the specialized tool you need.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating large, bulky components or batches of samples: A box furnace provides the capacity and ease of use you require.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching the equipment's capabilities to the specific environmental demands of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Uniformity | Uniform hot zone along central axis | Sensitive experiments requiring repeatable thermal conditions |
| Atmosphere and Vacuum Integrity | Sealed tube with flanges for isolation | Processes needing inert gases, vacuum, or specific atmospheres |
| Flowing Gas Reactions | Continuous gas flow capability | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), purification, and dynamic gas studies |
| Homogeneous Processing (Rotary) | Simultaneous heating and tumbling | Uniform treatment of powders or granular materials |
| Gradient Heating (Multi-Zone) | Independently controlled heating zones | Crystal growth and specialized material synthesis |
Ready to elevate your high-stakes research with advanced furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace systems. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Don't let equipment limitations hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your research environment and drive reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















