For applications requiring extreme heat, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are a leading solution. Their primary benefit is the ability to operate reliably and consistently in furnaces at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). This performance is rooted in their unique material composition, which provides exceptional stability and resistance to high-temperature oxidation.
While many materials can generate heat, Molybdenum Disilicide is engineered to survive it. Its core benefit is not just reaching ultra-high temperatures, but its ability to form a self-healing protective layer that ensures a long service life in oxidizing environments.
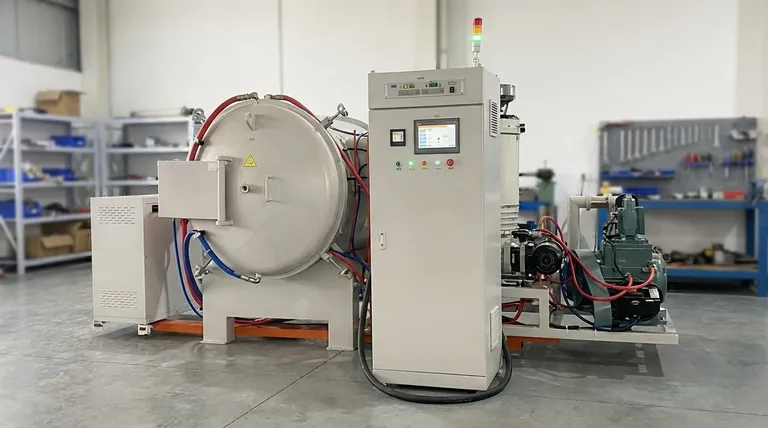

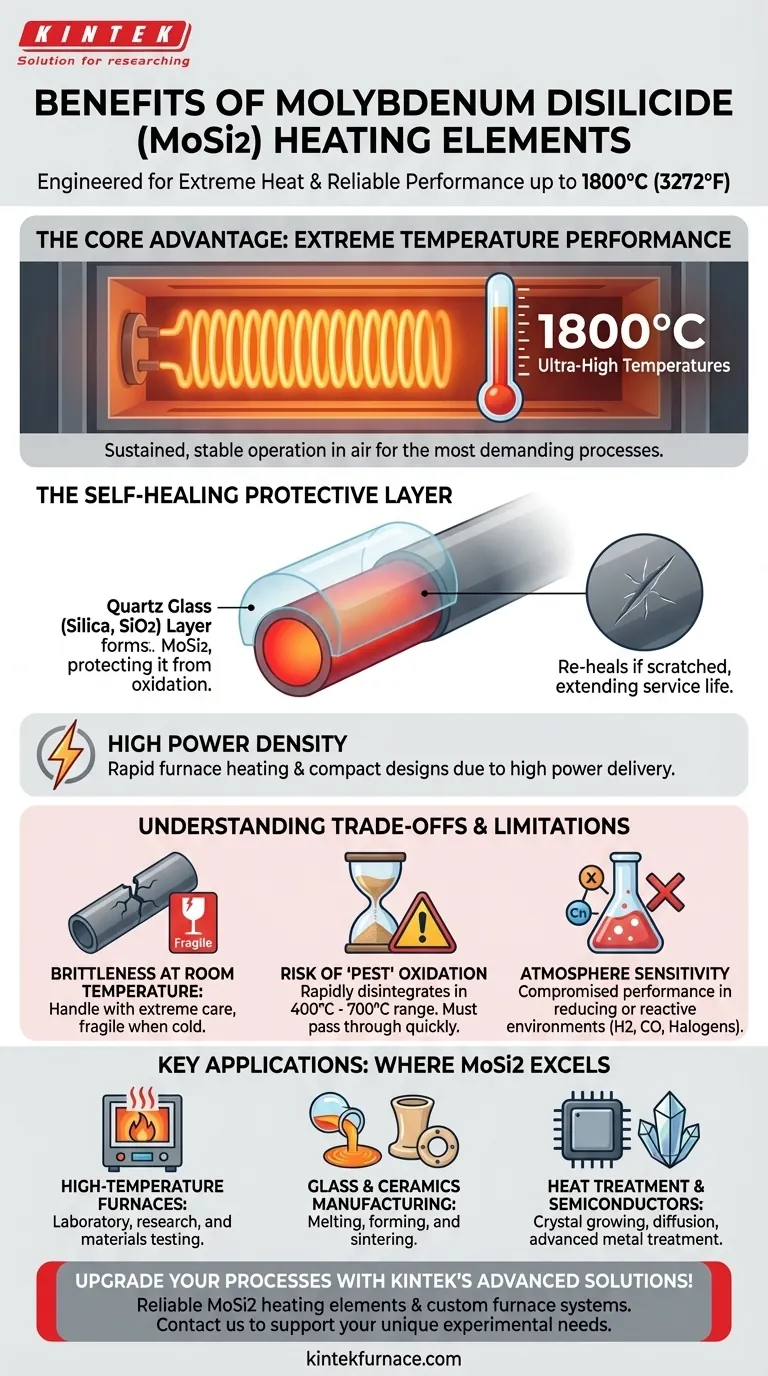
The Core Advantage: Extreme Temperature Performance
The defining characteristic of MoSi2 elements is their capacity to perform where many other materials fail. This capability is not just about a high melting point, but about sustained, stable operation.
Reaching Ultra-High Temperatures
MoSi2 elements are designed for furnace temperatures reaching 1800°C. The surface temperature of the elements themselves can even get up to 1850°C, providing the thermal energy required for the most demanding industrial processes.
The Self-Healing Protective Layer
The true key to MoSi2's success is its behavior in air at high temperatures. When heated, the material forms a thin, protective layer of quartz glass (silica, SiO2) on its surface. This layer is highly resistant to further oxidation and will even "re-heal" if it gets scratched, dramatically extending the element's lifespan.
High Power Density
Because they can operate at such high temperatures, MoSi2 elements can deliver a great deal of power relative to their size. This allows for rapid furnace heating and potentially more compact furnace designs compared to elements with lower temperature limits.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect for every situation. To use MoSi2 elements effectively, you must understand their specific limitations. Objectivity here is critical for success.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
MoSi2 is a cermet (ceramic-metal composite) and exhibits ceramic-like properties at lower temperatures. It is very brittle and fragile at room temperature and must be handled with extreme care during shipping, installation, and furnace maintenance to avoid fracture.
Risk of "Pest" Oxidation
In a specific low-temperature range, typically 400°C to 700°C, MoSi2 can suffer from accelerated oxidation known as "pest" disintegration. The material can rapidly turn to powder if held in this temperature range for extended periods. Therefore, furnaces using these elements must be designed to pass through this temperature zone quickly.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While MoSi2 elements excel in air and oxidizing atmospheres, their performance can be compromised in certain reducing or reactive environments. The protective silica layer can be damaged by atmospheres containing hydrogen, carbon monoxide, or halogens, leading to premature failure.
Where Molybdenum Disilicide Excels: Key Applications
The unique properties of MoSi2 make it the material of choice for specific, high-stakes industrial processes that require clean, reliable, high-temperature heat.
High-Temperature Furnaces
MoSi2 elements are a staple in laboratory and industrial furnaces used for research, materials testing, and specialized manufacturing where operating temperatures exceed the capabilities of common metallic elements like nickel-chromium.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
The production, melting, and forming of specialty glass and the sintering of advanced ceramics often require the precise, ultra-high temperatures that MoSi2 elements provide.
Heat Treatment and Semiconductors
These elements are used in furnaces for crystal growing, semiconductor diffusion, and advanced heat treatment of metals where a clean, oxidizing environment is necessary to achieve specific material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a heating element requires balancing performance, cost, and operational constraints. Use these points to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature: For processes that must run consistently above 1600°C in an air atmosphere, MoSi2 is one of the few viable and reliable choices.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability: In oxidizing environments, the self-healing nature of MoSi2's protective layer provides a significant advantage for service life over other materials.
- If your process requires extreme robustness: You must account for MoSi2's room-temperature brittleness in your handling procedures and furnace design, or consider a more ductile metallic element if your temperature needs are lower.
By understanding both the powerful benefits and the critical limitations of Molybdenum Disilicide, you can make an informed decision that ensures the success of your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Performance | Operates reliably up to 1800°C with stable, consistent heat in oxidizing atmospheres. |
| Self-Healing Protective Layer | Forms a quartz glass layer that re-heals if damaged, extending service life in air. |
| High Power Density | Delivers significant power for rapid heating and compact furnace designs. |
| Key Applications | Ideal for high-temperature furnaces, glass/ceramics manufacturing, and semiconductor processes. |
| Limitations | Brittle at room temperature, risk of pest oxidation at 400-700°C, sensitive to reducing atmospheres. |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable MoSi2 heating elements and custom furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















