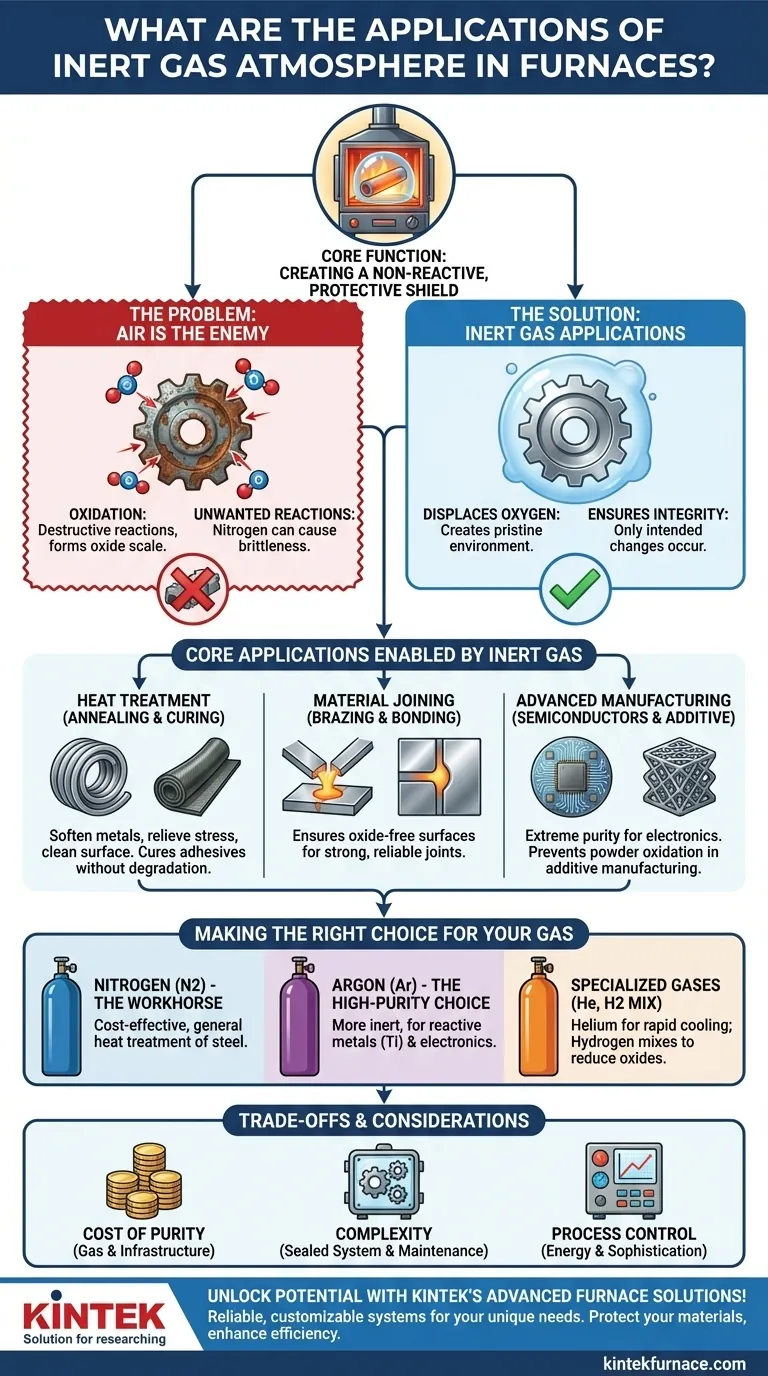
At its core, an inert gas atmosphere is used in furnaces to create a chemically non-reactive environment for processing materials at high temperatures. The primary applications include critical heat treatments like annealing and curing, material joining processes such as brazing and bonding, and advanced manufacturing in fields like additive manufacturing and semiconductors. This protective atmosphere is essential for any process where oxidation or other reactions with ambient air would degrade the quality, integrity, or performance of the final product.
The fundamental purpose of an inert atmosphere is not to heat the material, but to protect it. By displacing reactive gases like oxygen, it creates a pristine environment, ensuring that high-temperature processes alter a material's physical properties without compromising its chemical composition.

The Fundamental Problem: Why Air is the Enemy
To understand the role of inert gas, you must first understand the problem it solves. At high temperatures, the oxygen and moisture in ambient air become highly aggressive, triggering destructive chemical reactions.
The Impact of Oxidation
Oxidation is the most common and damaging reaction. When metals are heated in the presence of oxygen, a layer of oxide scale forms on the surface.
This scale can cause dimensional inaccuracies, weaken the material, and interfere with subsequent processes like welding or coating. An inert atmosphere prevents this by simply removing the oxygen from the equation.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
Beyond simple oxidation, the nitrogen in the air can also react with certain metals at high temperatures to form nitrides, which can make the material brittle. An inert atmosphere ensures that the only changes occurring in the furnace are the ones you intend.
Core Applications Enabled by Inert Gas
By creating this protective shield, inert atmospheres enable a wide range of critical manufacturing and treatment processes that would otherwise be impossible.
Heat Treatment (Annealing & Curing)
Annealing is a process used to soften metals, improve ductility, and relieve internal stresses by heating and then slowly cooling them. Performing this in an inert atmosphere ensures the part emerges with a clean, bright, scale-free surface.
Similarly, curing specialized adhesives or composite materials at high temperatures requires a non-reactive environment to prevent degradation of the polymers and ensure a strong, reliable bond.
Material Joining (Brazing & Bonding)
Brazing uses a filler metal to join two pieces of a base metal. For the filler to flow properly and create a strong joint, the surfaces must be perfectly clean and free of oxides.
An inert atmosphere provides this pristine environment, preventing oxide formation during the heating cycle and ensuring the integrity of the brazed joint.
Advanced Manufacturing (Semiconductors & Additive)
In the semiconductor industry, processes like dopant activation and annealing thin films demand extreme purity. Even trace amounts of oxygen can create defects, ruining the electrical properties of the microscopic components.
In metal additive manufacturing (like powder bed fusion), a fine metal powder is fused layer-by-layer with a laser. An inert atmosphere is non-negotiable here to prevent the tiny powder particles from oxidizing, which would result in a weak, porous, and unusable part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, implementing an inert atmosphere furnace system involves significant practical and economic considerations.
The Cost of Purity
Inert gases, particularly high-purity argon, are a significant operational expense. The cost of the gas itself, along with delivery and storage infrastructure, must be factored into any process.
The Complexity of a Sealed System
The furnace chamber, often called an "atmosphere envelope," must be completely sealed to prevent air from leaking in and contaminating the environment. This requires robust furnace construction (e.g., front-load or top-hat designs) and diligent maintenance of seals, gaskets, and connections.
Energy and Process Control
Maintaining a controlled atmosphere often involves sophisticated systems. For rapid cooling, for instance, the inert gas is circulated through a heat exchanger to remove heat from the part in a controlled manner, adding to the system's energy consumption and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Gas
The choice of inert gas depends on the material being processed and the sensitivity of the application.
Nitrogen: The Workhorse Gas
Nitrogen (N2) is the most widely used gas because it is effective and relatively inexpensive. For most heat treatment applications involving steel and other non-reactive metals, nitrogen provides excellent protection against oxidation.
Argon: The High-Purity Choice
Argon (Ar) is more inert than nitrogen and does not react with metals even at very high temperatures. It is the gas of choice for processing highly reactive metals like titanium or for high-purity applications like semiconductor manufacturing where even potential nitride formation is unacceptable.
Other Specialized Gases
Helium (He) is sometimes used for its high thermal conductivity, making it effective for rapid cooling processes. In some cases, mixtures containing hydrogen (H2) are used not just to prevent oxidation but to actively reduce surface oxides that may already be present.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your choice of atmosphere is dictated by your material and your goal for its final properties.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of steel: Nitrogen is almost always the most cost-effective and sufficient choice for preventing scale.
- If you are working with reactive metals (e.g., titanium) or high-purity electronics: You must use a higher-purity gas like Argon to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
- If process control like rapid cooling is critical: You need a furnace equipped with a gas circulation and heat exchanger system, which will influence both your gas choice and operational costs.
Ultimately, using an inert atmosphere is a deliberate engineering decision to guarantee that your material's final properties are defined by your process, not by contamination from the air.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Heat Treatment (Annealing & Curing) | Prevents oxidation, ensures clean surfaces, improves material properties |
| Material Joining (Brazing & Bonding) | Enables strong joints by keeping surfaces oxide-free |
| Advanced Manufacturing (Semiconductors & Additive) | Maintains purity, prevents defects in sensitive processes |
| Gas Selection (Nitrogen, Argon, Helium) | Cost-effective to high-purity options based on material and application |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, protecting your materials from oxidation and enhancing efficiency. Don't let contamination compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















