In short, vacuum sintering produces parts with superior purity, mechanical strength, and dimensional accuracy compared to other methods. By performing the process in a vacuum, it fundamentally prevents oxidation and removes trapped gases, leading to a denser, stronger, and cleaner final product that often requires no secondary finishing.
The primary advantage of vacuum sintering is not just the heat, but the chemically pure environment it creates. By eliminating reactive gases like oxygen, it allows metal or ceramic particles to bond more perfectly, unlocking the material's maximum potential for density and strength.
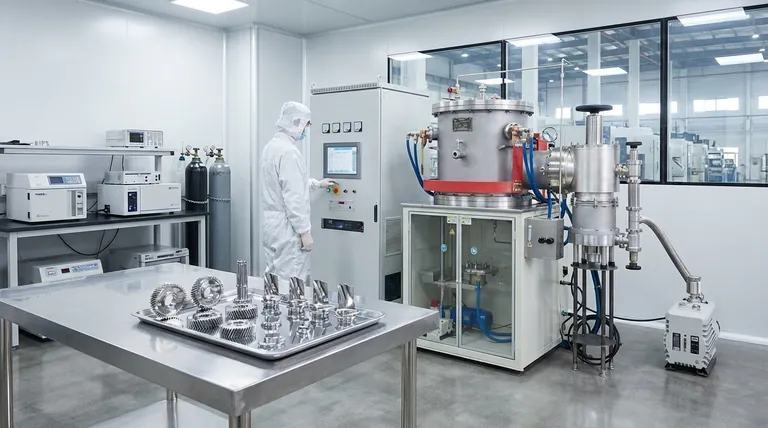

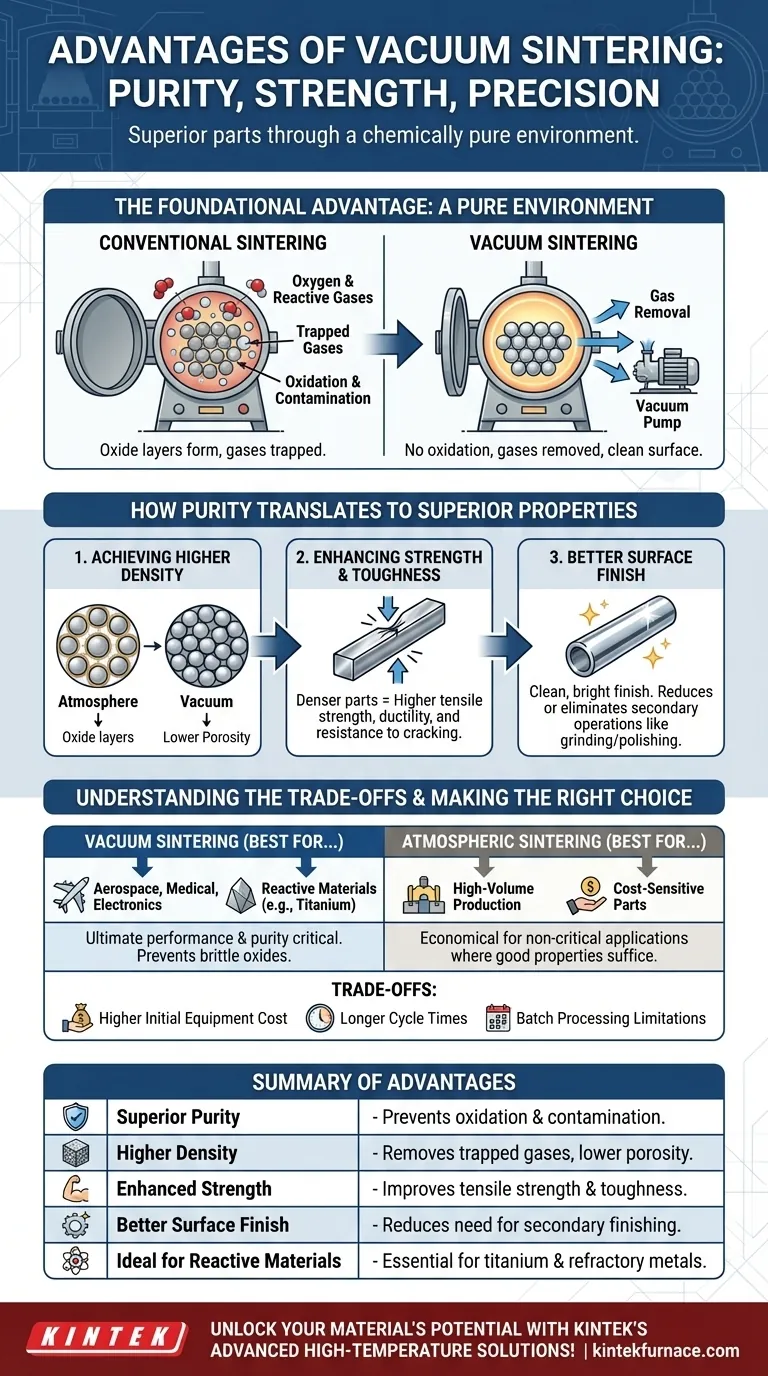
The Foundational Advantage: A Pure Environment
The defining characteristic of vacuum sintering is the removal of the atmosphere from the furnace chamber. This single act is the root cause of its most significant benefits.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
In conventional sintering, the high temperatures cause particles to react with oxygen and other gases in the air, forming oxide layers on their surfaces.
A vacuum environment removes these reactive gases. This prevents the formation of oxide films, resulting in a clean, bright surface finish and ensuring the chemical purity of the final component.
Removing Trapped and Adsorbed Gases
Powdered materials naturally have gases adsorbed onto their particle surfaces and trapped in the voids between them.
During vacuum sintering, these gases are drawn out of the material before the pores close. This "degassing" effect is crucial for achieving a part with minimal internal porosity.
How Purity Translates to Superior Mechanical Properties
By creating a pristine environment, vacuum sintering directly enhances the physical characteristics of the finished part, making it stronger and more reliable.
Achieving Higher Density and Lower Porosity
Oxide layers and trapped gases act as barriers, inhibiting the diffusion and bonding between particles.
By removing these barriers, vacuum sintering promotes more effective particle-to-particle contact. This results in a final part with greater density and significantly lower porosity, which are key indicators of a successful sintering process.
Enhancing Strength and Toughness
Porosity is a direct source of weakness in a sintered part, acting as a potential point for cracks to initiate.
Because vacuum-sintered parts are denser and have fewer internal voids, they consistently exhibit higher tensile strength, ductility, and overall toughness compared to parts sintered in an atmosphere.
Improving Surface Finish and Reducing Rework
The absence of oxidation means parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, often mirror-like finish. This dramatically reduces or eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like grinding, polishing, or cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not the default choice for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems requiring robust chambers, pumping systems, and sophisticated controls. This results in a significantly higher initial capital investment compared to conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to every cycle. Furthermore, cooling is often slower in a vacuum, which can extend the overall processing time and limit throughput.
Batch Processing Limitations
Most vacuum sintering operations are batch processes, which can be less efficient for extremely high-volume, continuous production lines where conveyor-style atmospheric furnaces excel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sintering method depends entirely on the performance requirements and cost constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and material purity: Vacuum sintering is the superior choice for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and electronics where contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-sensitive production: Conventional atmospheric sintering may be more economical for parts where good, but not flawless, mechanical properties are sufficient.
- If you are working with reactive materials like titanium or refractory metals: Vacuum sintering is often the only viable method to prevent the formation of brittle oxides that would destroy the material's properties.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum sintering is an investment in achieving the highest possible part quality and material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Purity | Prevents oxidation and contamination for chemically pure components. |
| Higher Density | Removes trapped gases, resulting in denser parts with lower porosity. |
| Enhanced Mechanical Strength | Improves tensile strength, ductility, and toughness. |
| Better Surface Finish | Reduces or eliminates need for secondary finishing operations. |
| Ideal for Reactive Materials | Essential for sintering titanium and refractory metals without oxide formation. |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with vacuum sintering furnaces, tube furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, strength, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your sintering process and achieve outstanding results for your critical applications in aerospace, medical, and electronics!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















