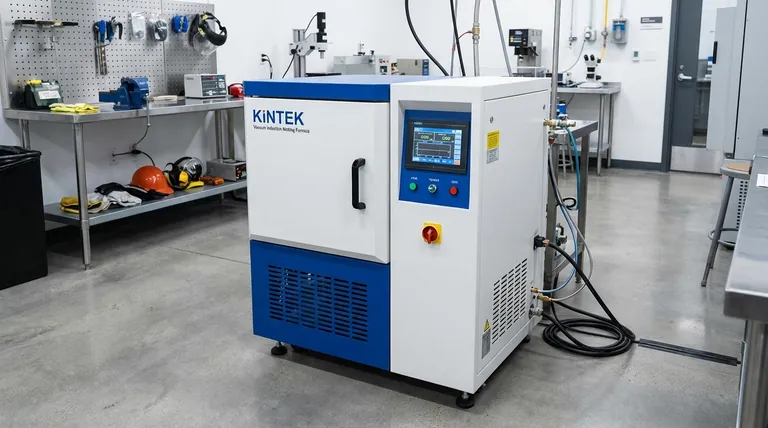
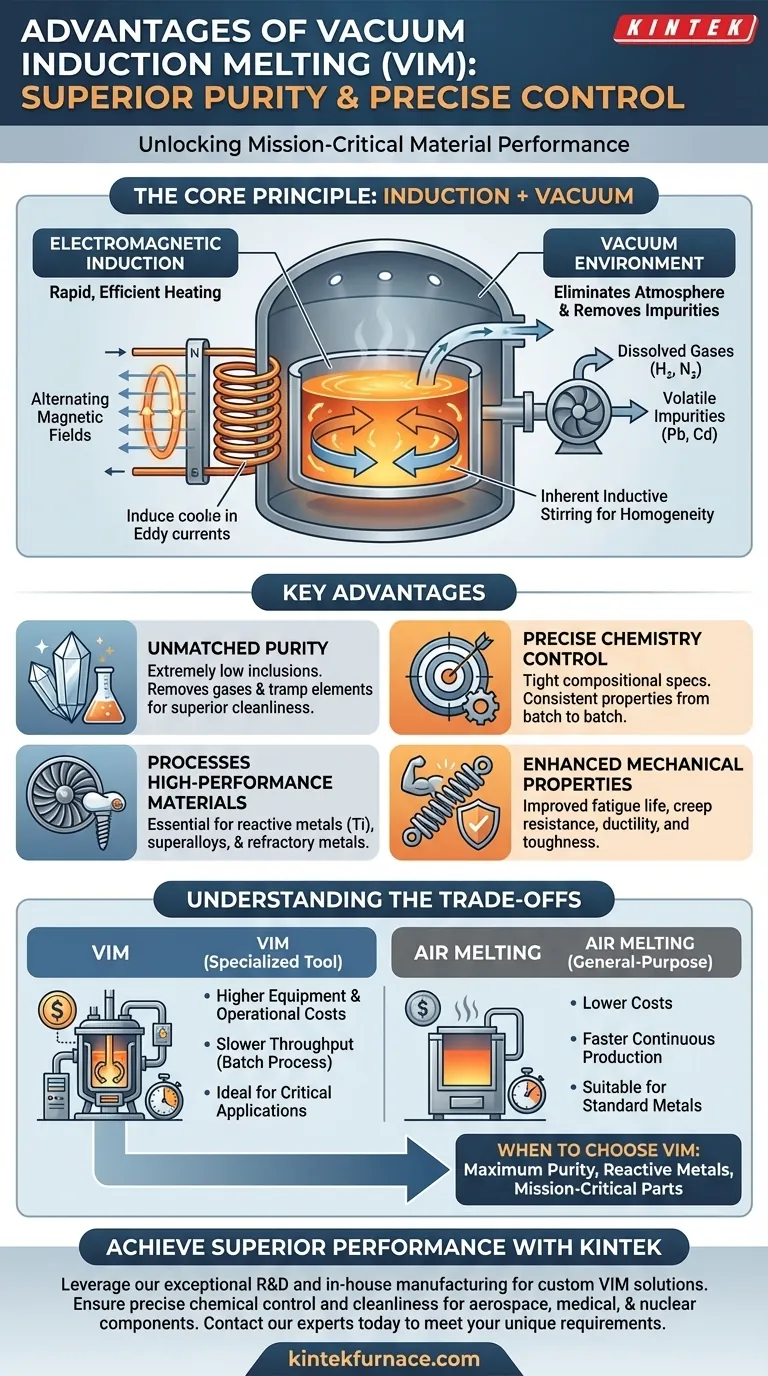
At its core, vacuum induction melting (VIM) delivers superior material purity and precise chemical control. This is achieved by combining the rapid, efficient heating of electromagnetic induction with a high-vacuum environment. The process effectively eliminates atmospheric contamination, allowing for the creation of high-performance alloys that would be impossible to produce in open air.
The fundamental advantage of VIM is not just melting metal, but refining it. By removing dissolved gases and volatile impurities in a vacuum, the process produces exceptionally clean, homogenous materials with superior mechanical properties required for the most demanding applications.

The Core Principle: Combining Control with Efficiency
Vacuum induction melting is a sophisticated process built on two key technologies working in concert: electromagnetic induction and a vacuum chamber. Understanding how they interact reveals why VIM is so effective.
How Induction Heating Works
Induction heating uses a powerful alternating magnetic field generated by a copper coil. When a conductive material like metal is placed within this field, it induces electrical eddy currents within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid, and highly localized heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place inside a sealed chamber from which air has been removed. This vacuum environment is the key differentiator, as it prevents the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen. This step is crucial for reactive metals like titanium and for maintaining the integrity of complex superalloys.
Furthermore, the vacuum actively pulls dissolved gases (like hydrogen and nitrogen) and low-boiling-point impurities (like lead and cadmium) out of the molten bath, resulting in a cleaner, purer final product.
Inherent Stirring for Homogeneity
A natural side effect of the strong electromagnetic forces is an inductive stirring action within the molten metal. This constant, gentle mixing ensures that all alloying elements are distributed evenly, leading to a perfectly homogenous melt with no chemical segregation.
Key Advantages for Mission-Critical Applications
The combination of a clean environment, precise heating, and natural stirring gives VIM a distinct set of advantages, making it the process of choice for materials where failure is not an option.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
By eliminating atmospheric gases and removing volatile tramp elements, VIM produces alloys with extremely low levels of inclusions and impurities. This "cleanliness" is directly linked to superior material performance and reliability.
Precise Control Over Alloy Chemistry
With no risk of atmospheric reaction, engineers can make highly precise additions of alloying elements to the melt. This allows for the production of alloys that meet extremely tight compositional specifications, ensuring consistent properties from batch to batch.
Processing High-Performance and Reactive Materials
VIM is one of the only viable methods for melting reactive metals (like titanium) and high-temperature superalloys (used in jet engines). It can also achieve the very high temperatures needed to melt refractory metals with precision.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The high purity and homogeneity of VIM materials directly translate to improved mechanical properties. This includes better fatigue life, creep resistance, ductility, and toughness—all critical characteristics for components in aerospace, medical implants, and nuclear applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, VIM is a specialized tool. Its advantages come with practical and economic considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum induction furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to build and maintain than their air-melt counterparts. The need for vacuum pumps, sophisticated controls, and robust chamber engineering drives up the initial capital investment.
Slower Throughput
VIM is a batch process. The cycle time includes not only melting but also the time required to pump the chamber down to a high vacuum and cool the ingot under controlled conditions. This results in lower production volume compared to continuous or semi-continuous air-melting methods.
Unnecessary for General-Purpose Metals
For common materials like standard-grade steel, iron, or aluminum used in construction or general manufacturing, the extreme purity offered by VIM is overkill. More cost-effective melting techniques are better suited for these high-volume applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting process requires aligning the technology's capabilities with your material's end-use requirements and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for mission-critical parts (aerospace, medical): VIM is the industry standard and often the only acceptable choice.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals (titanium) or complex superalloys: VIM is essential to prevent catastrophic contamination and achieve the desired chemistry.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard-grade metals: VIM is not economically viable; conventional air-melting furnaces are the appropriate tool.
Ultimately, vacuum induction melting is an enabling technology, chosen when the performance and reliability of the final material justify the investment.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Purity | Removes dissolved gases and volatile impurities for clean, reliable materials. |
| Precise Chemistry Control | Enables tight compositional specifications and batch-to-batch consistency. |
| Homogeneous Melting | Inductive stirring ensures uniform distribution of alloying elements. |
| Processes Reactive Metals | Essential for melting titanium, superalloys, and refractory metals without contamination. |
Ready to achieve superior material purity and performance for your mission-critical applications?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom vacuum induction melting systems. Our expertise ensures you get the precise chemical control and cleanliness required for aerospace, medical, and nuclear components.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a custom VIM solution can meet your unique material requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















