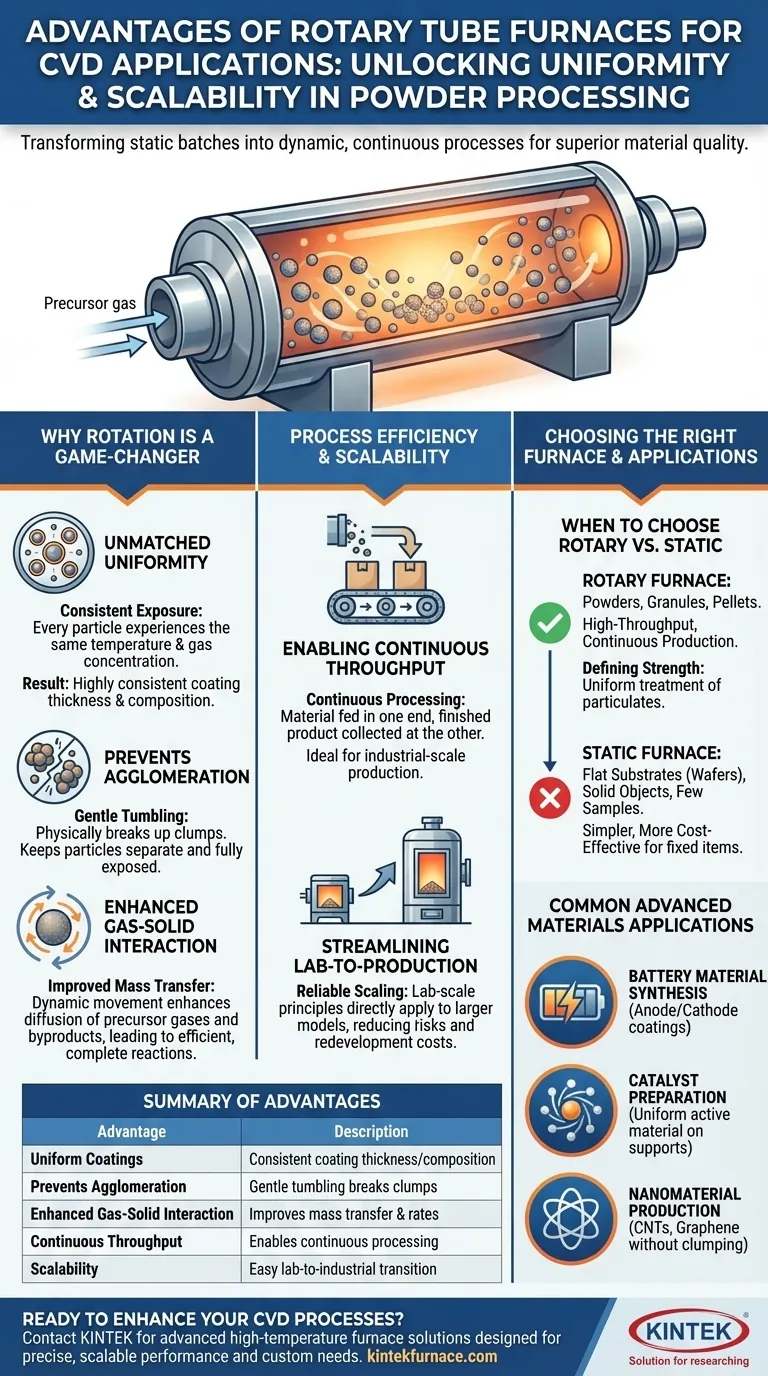
For CVD applications involving powders or particles, the primary advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to deliver exceptionally uniform coatings and material properties. The continuous rotation ensures that every surface of the material is consistently exposed to both heat and precursor gases, a level of homogeneity that is nearly impossible to achieve with loose materials in a stationary furnace.
The core benefit of a rotary tube furnace is that it transforms a static batch process into a dynamic, continuous one. This solves the critical challenge of treating powders and granules uniformly, leading to higher quality materials, improved efficiency, and better scalability from the lab to industrial production.

Why Rotation is a Game-Changer for CVD
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the goal is to deposit a thin, uniform film from a gas phase onto a substrate. When that substrate is a powder, a static furnace presents a fundamental problem: the gas can't reach the particles in the middle and bottom of the pile. A rotary furnace directly solves this.
Unmatched Coating and Thermal Uniformity
In a static tube, the top layer of powder is processed differently than the bottom layer. A rotary furnace gently tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is cyclically brought to the surface.
This constant mixing guarantees that all particles experience the same temperature profile and the same concentration of precursor gas, resulting in highly consistent coating thickness and material composition.
Preventing Particle Agglomeration
Fine powders have a natural tendency to clump together (agglomerate) when heated. This clumping shields the interior surfaces from the CVD process, leading to incomplete reactions and non-uniform products.
The gentle mechanical tumbling action of a rotary furnace physically breaks up these agglomerates as they form, keeping the particles separate and fully exposed.
Enhanced Gas-Solid Interaction
The dynamic movement of the substrate material improves mass transfer. As the powder bed tumbles, it enhances the diffusion of precursor gases to the particle surfaces and the diffusion of reaction byproducts away from them.
This leads to a more efficient and complete chemical reaction, which can increase deposition rates and improve the overall quality of the final material.
Process Efficiency and Scalability
Beyond material quality, rotary furnaces offer significant operational advantages, especially when moving beyond small lab-scale experiments.
Enabling Continuous Throughput
Unlike static furnaces that operate on a fixed batch-by-batch basis, many rotary furnaces are designed for continuous or semi-continuous material processing.
Raw material can be fed into one end of the rotating tube and the finished product collected at the other, dramatically increasing throughput and making it suitable for industrial-scale production.
Streamlining Lab-to-Production Scaling
The principles of a lab-scale rotary furnace are directly applicable to larger industrial models. This makes the process much easier to scale.
Developing a process in a small rotary furnace provides a reliable blueprint for production, reducing the risks and redevelopment costs associated with scaling up.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Static Furnaces
A rotary furnace is a specialized tool, not a universal solution. Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the nature of your substrate and your processing goals.
When to Choose a Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace is the clear choice when your substrate is a powder, granule, or pellet. Its ability to ensure uniform treatment of particulate matter is its defining strength.
It is also the superior option if your goal is high-throughput or continuous production, as its design inherently supports this workflow.
When a Static Furnace Is Superior
For processing flat substrates (like silicon wafers), solid objects, or a small number of fixed samples, a standard static tube furnace is more practical, simpler, and more cost-effective.
In these cases, the complexity and motion of a rotary system offer no benefit and would only complicate the setup unnecessarily.
Key Design Features
Regardless of type, a high-quality furnace for CVD will provide precise atmosphere control for handling inert or reactive gases. Modern designs also feature robust ceramic insulation and double-walled housings to ensure energy efficiency and low external surface temperatures for operator safety.
Common Applications in Advanced Materials
The unique advantages of rotary tube furnaces make them essential for producing a variety of high-performance materials where uniformity is critical.
Battery Material Synthesis
Rotary furnaces are widely used to synthesize and coat anode and cathode materials (like alumina or graphite). The process ensures that every particle has the desired composition and coating, which is vital for battery performance and lifespan.
Catalyst Preparation
When creating catalysts, a thin layer of an active material is often coated onto a high-surface-area powder support. A rotary furnace ensures this coating is applied uniformly, maximizing the number of active sites and the catalyst's overall effectiveness.
Nanomaterial Production
In the synthesis of nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) or graphene, rotary furnaces help produce a more uniform product by preventing the nanoparticles from clumping together during their high-temperature growth phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology is a critical decision that directly impacts the quality of your results and the efficiency of your workflow.
- If your primary focus is processing powders, granules, or pellets: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice for ensuring uniformity and preventing agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is coating flat substrates or single, solid objects: A standard static tube furnace is more practical and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is scaling a powder-based process from lab to production: The continuous processing capability of a rotary furnace makes it a superior long-term investment.
By matching the furnace's core strength—dynamic material handling—to your specific substrate, you can reliably achieve your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Coatings | Ensures consistent coating thickness and material composition for all particles through continuous rotation. |
| Prevents Agglomeration | Gentle tumbling breaks up clumps, keeping particles separate and fully exposed during CVD. |
| Enhanced Gas-Solid Interaction | Improves mass transfer for efficient reactions and higher deposition rates. |
| Continuous Throughput | Enables semi-continuous or continuous processing, ideal for scaling from lab to production. |
| Scalability | Easy transition from lab-scale to industrial models, reducing redevelopment costs. |
Ready to enhance your CVD processes with uniform, high-quality results? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our rotary tube furnaces are designed to deliver precise, scalable performance for powder and particle applications, backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, can optimize your workflow and drive innovation in battery materials, catalysts, and nanomaterials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















