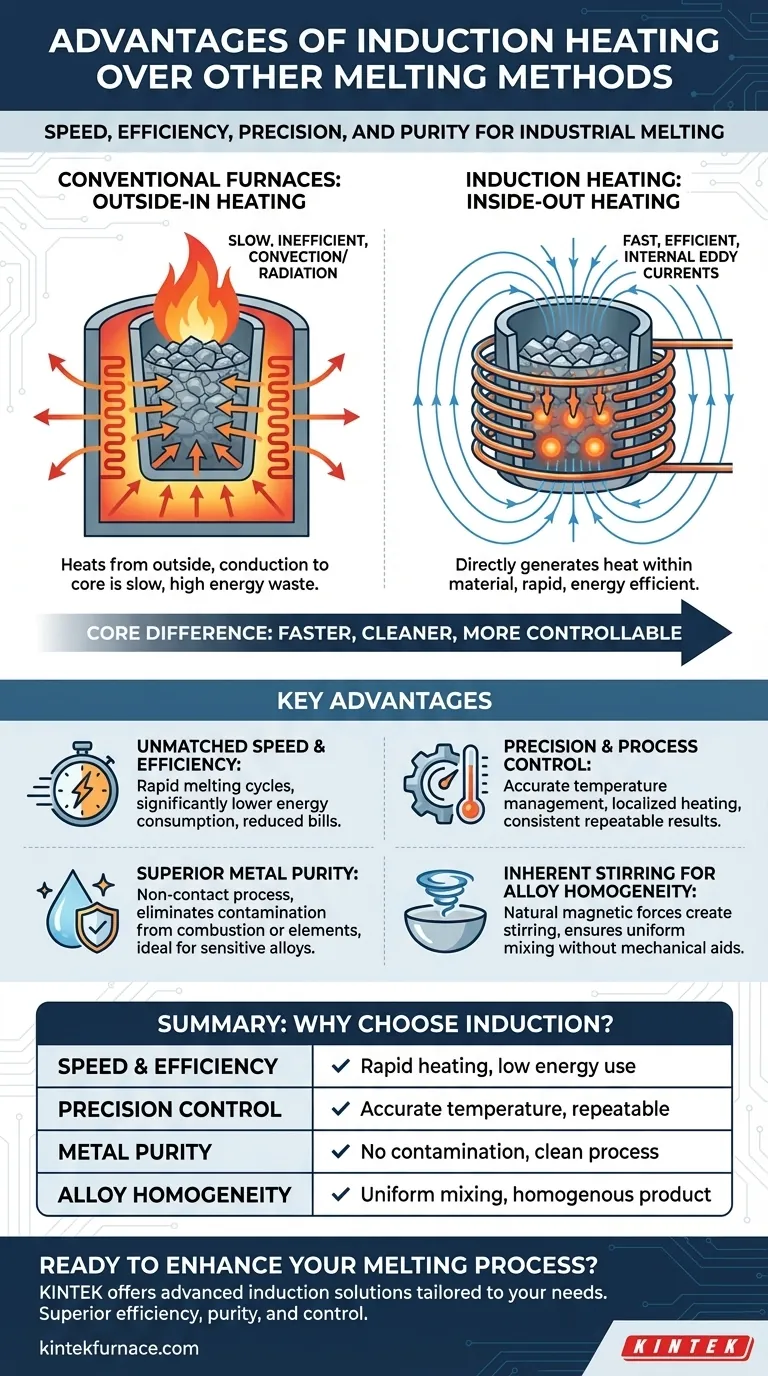
In the world of industrial melting, the primary advantages of induction heating over methods like gas or resistance furnaces are its superior speed, efficiency, precision, and the high purity of the final molten metal. This is because induction generates heat directly within the material itself, rather than applying it from an external source, which leads to a faster, cleaner, and more controllable process.
The core difference is simple yet profound: conventional furnaces heat materials from the outside-in, while induction heating works from the inside-out. This fundamental distinction is the source of nearly every advantage induction offers, from energy efficiency to metallurgical quality.

The Core Principle: Heating from the Inside-Out
To understand why induction is so effective, you must first grasp its unique heating mechanism. It is not just an alternative fuel source; it is a completely different approach to transferring thermal energy.
How Induction Works
Induction heating uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field generated by a copper coil. When a conductive material, like metal, is placed inside this field, it induces electrical currents (known as eddy currents) directly within the metal. The material's natural resistance to these currents generates immediate, localized heat.
The Contrast with Conventional Furnaces
Traditional gas and electric resistance furnaces operate on the principles of convection and radiation. They heat an enclosure or a heating element to a very high temperature, which then slowly transfers that heat to the surface of the material. The heat must then conduct from the outside of the material to its core, a process that is slow, inefficient, and difficult to control.
Key Advantages Explained
This "inside-out" heating model delivers tangible benefits in industrial and research settings. Each advantage stems directly from the efficiency and precision of the underlying physics.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated instantly and internally, melting times are dramatically reduced compared to conventional methods. This rapid heating cycle means less time for heat to radiate away, resulting in significantly lower energy consumption and reduced energy bills.
Precision and Process Control
The magnetic field can be precisely shaped and controlled. This allows for localized heating of specific areas without affecting adjacent parts, protecting tooling and minimizing thermal distortion. Temperature can be managed with exceptional accuracy, ensuring consistent, repeatable results batch after batch.
Superior Metal Purity
Induction is a non-contact process. The material being melted never touches a heating element or flame. This completely eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts (as seen in gas furnaces) or from the heating elements themselves, which is critical for producing high-purity metals and sensitive alloys.
Inherent Stirring for Alloy Homogeneity
The same magnetic forces that generate heat also create a natural stirring action within the molten metal. This inductive stirring ensures that all elements of an alloy are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a perfectly uniform and homogenous final product without the need for mechanical stirring.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not the universal solution for every application. Objective analysis requires acknowledging its specific operational considerations.
Initial Equipment Cost
The initial capital investment for an induction furnace system is typically higher than for a simple gas or resistance furnace. The power supplies and custom-designed coils represent a significant upfront cost that must be weighed against the long-term operational savings.
Material Constraints
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It is an excellent choice for most metals and alloys but is completely ineffective for melting non-conductive materials like ceramics or certain glasses without the use of a conductive crucible.
Coil Design and Application
The induction coil must be designed to match the size and shape of the workpiece or crucible for maximum efficiency. While versatile, changing between dramatically different applications may require swapping coils, adding a step to the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct melting technology depends entirely on your primary goals. Use the following points as a guide to your decision.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys or reactive metals: Induction is the superior choice due to its clean, non-contact heating and its ability to operate in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is speed and high-volume throughput: The rapid melting cycles and efficiency of induction offer a definitive advantage for maximizing production.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and process repeatability: Induction's precise control delivers unparalleled consistency and minimizes wasted energy, lowering operational costs.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible initial cost for general-purpose tasks: A conventional furnace may be a more economical starting point, but you must account for higher long-term energy and maintenance costs.
By understanding how heat is generated, you can confidently choose the technology that best serves your metallurgical and financial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Rapid internal heating reduces melting times and energy consumption significantly. |
| Precision Control | Accurate temperature management and localized heating for consistent, repeatable results. |
| Metal Purity | Non-contact process eliminates contamination from flames or heating elements. |
| Alloy Homogeneity | Natural inductive stirring ensures uniform mixing without mechanical aids. |
| Clean & Safe Operation | No combustion byproducts; ideal for vacuum or inert atmosphere melting. |
Ready to enhance your melting process with the precision of induction heating? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you're working with high-purity alloys, reactive metals, or high-volume production, our expertise in induction technology—complemented by our deep customization capabilities—ensures you get a system that delivers superior efficiency, purity, and control.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction heating solutions can optimize your laboratory or industrial operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















