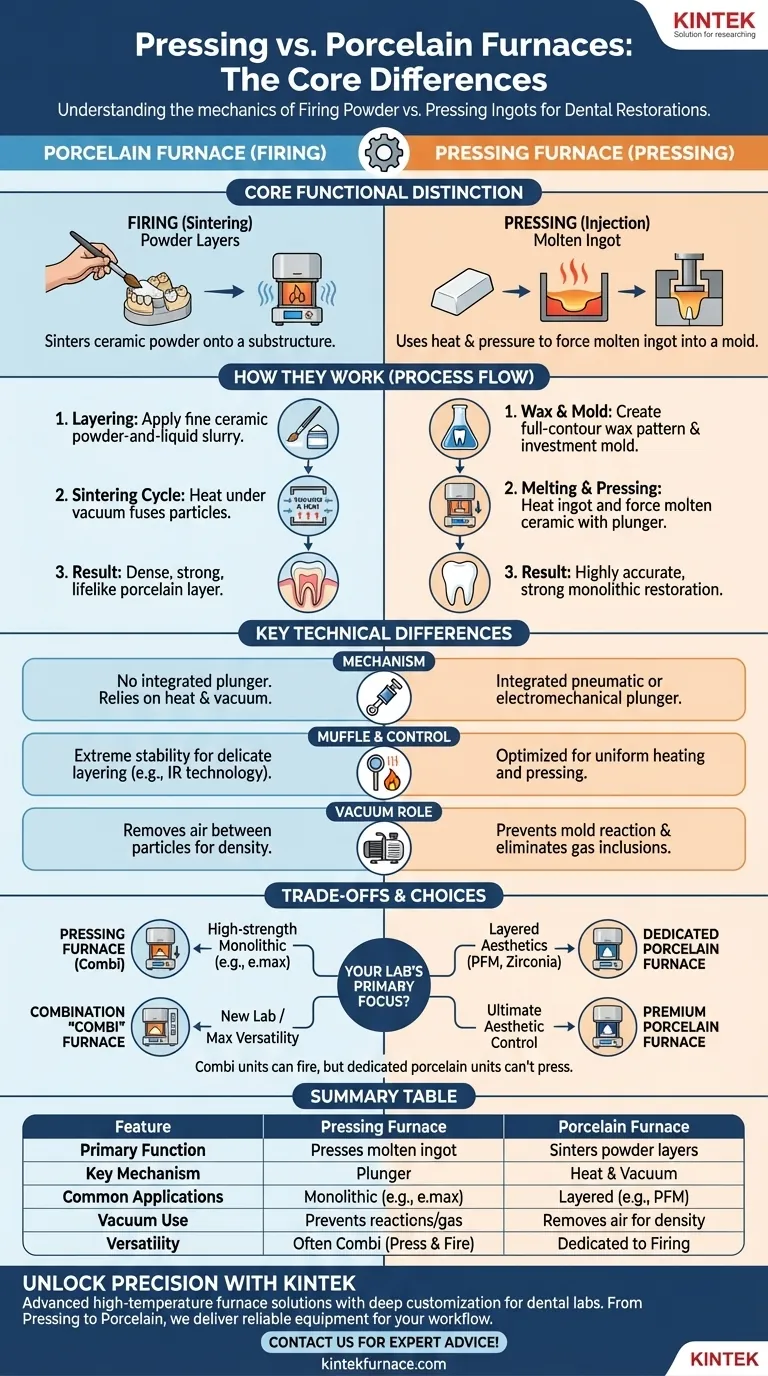
At their core, a pressing furnace and a porcelain furnace perform fundamentally different mechanical actions to create dental restorations. A porcelain furnace is designed to sinter, or fire, layers of ceramic powder onto a substructure, while a pressing furnace uses heat and physical pressure to force a molten ceramic ingot into a mold.
While both are essential tools in modern dental technology, the choice between them is not an "either/or" decision. It is dictated entirely by the type of restoration you need to create. One fires powder, the other presses a solid ingot—a mechanical difference that defines their design, features, and application.
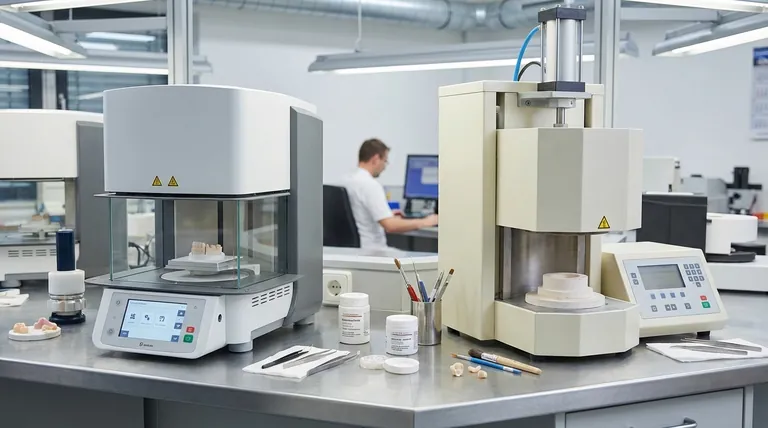

The Core Functional Distinction: Firing vs. Pressing
To understand the equipment, you must first understand the two distinct fabrication processes. The furnace is simply a tool built to execute one or both of these techniques.
How a Porcelain Furnace Works
A porcelain furnace is used for the traditional method of building a restoration. This involves painting layers of a fine ceramic powder-and-liquid slurry onto a core material, such as a metal coping or a zirconia framework.
The furnace then runs a programmed cycle, heating the restoration under a vacuum. This process, known as sintering, fuses the powder particles together into a dense, strong, and lifelike layer of porcelain. The key here is precise temperature control to achieve the desired translucency and shade without overheating.
How a Pressing Furnace Works
A pressing furnace is used for creating restorations from pressable ceramic ingots, like lithium disilicate (e.g., IPS e.max). The process begins with a full-contour wax pattern of the final restoration, which is then encased in a special investment material to create a mold.
After the wax is burned out, the mold and a ceramic ingot are placed in the furnace. The furnace heats both until the ingot becomes molten. A plunger mechanism then applies high pressure, forcing the molten ceramic into the mold cavity. This creates a highly accurate and strong monolithic restoration.
Key Differences in Design and Technology
The functional difference between firing and pressing dictates every aspect of the furnace's design, from its mechanical parts to its software.
The Pressing Mechanism
This is the most significant physical difference. A pressing furnace contains an integrated pneumatic or electromechanical drive that moves a plunger to press the ceramic. A standard porcelain furnace has no such mechanism.
Muffle and Temperature Control
Both furnaces use a heated chamber, or muffle, to surround the restoration. However, their control systems are optimized differently.
Porcelain furnaces often require extremely stable and uniform heat for delicate layering work. Advanced models may use infrared (IR) technology to measure the exact temperature of the restoration itself, not just the air in the chamber, ensuring a more accurate firing.
The Role of Vacuum
Both furnaces use a vacuum pump, but for slightly different reasons. In a porcelain furnace, the vacuum removes air from between the powder particles, preventing bubbles and creating a dense final material.
In a pressing furnace, the vacuum prevents the hot investment mold from reacting with the molten ceramic and eliminates the chance of gas inclusions that would weaken the final restoration. Modern high-performance furnaces of both types are often cold-wall vacuum furnaces, which use a water-cooled chamber to allow for much faster heating and cooling cycles and superior temperature uniformity.
Combination "Combi" Furnaces
Many modern pressing furnaces are actually combination (combi) furnaces. They contain the pressing mechanism but can also be programmed to run firing-only cycles, allowing them to function as a porcelain furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right equipment requires understanding the limitations and versatility of each type. This is where most labs make their key investment decisions.
You Cannot Press in a Porcelain Furnace
This is a non-negotiable limitation. Without the integrated plunger mechanism, a porcelain furnace simply cannot perform the pressing function. There is no workaround.
You Can Fire Porcelain in Most Pressing Furnaces
Most contemporary pressing furnaces are sold as combi units, capable of running complex firing programs. This makes them exceptionally versatile tools, especially for labs with limited space or budget.
However, for labs focused exclusively on the highest-end aesthetic layered restorations, a dedicated porcelain furnace may still be preferred. These specialized units are optimized for one task and may offer superior temperature control or features tailored specifically for layering.
Cost and Workflow Implications
A combi furnace is a larger initial investment than a standalone porcelain furnace, but it is less expensive than buying two separate machines. For a high-volume lab, having separate, dedicated furnaces for pressing and firing can streamline workflow, as both processes can be run simultaneously without creating a bottleneck.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lab
Your decision should be based on the primary type of work your lab produces.
- If your primary focus is high-strength monolithic restorations (e.g., e.max crowns, veneers, inlays): A pressing furnace (likely a combi unit) is absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) or layered zirconia crowns: A high-quality porcelain furnace is your workhorse, and a pressing furnace is not required for this workflow.
- If you are a new lab or want maximum versatility in a small footprint: A combination press-and-porcelain furnace is the most logical and efficient investment.
- If your goal is ultimate aesthetic control for complex anterior cases: A premium, dedicated porcelain furnace with advanced features like infrared temperature sensing will provide the greatest precision.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between firing powder and pressing an ingot empowers you to select the precise technology needed to achieve your desired clinical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pressing Furnace | Porcelain Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Presses molten ceramic ingots into molds | Sinters ceramic powder layers onto substructures |
| Key Mechanism | Pneumatic or electromechanical plunger | No pressing mechanism; relies on heat and vacuum |
| Common Applications | Monolithic restorations (e.g., e.max crowns) | Layered restorations (e.g., PFM, zirconia crowns) |
| Vacuum Use | Prevents mold reactions and gas inclusions | Removes air for dense, bubble-free material |
| Versatility | Often a combi unit for both pressing and firing | Dedicated to firing; cannot press |
Unlock Precision in Your Dental Lab with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need a pressing furnace for monolithic restorations or a porcelain furnace for layered aesthetics, we deliver reliable, tailored equipment to enhance your workflow and outcomes.
Ready to elevate your dental lab's capabilities? Contact us today for expert advice and customized solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the hot pressing mechanism enhance TiB2-TiN density? Achieve Superior Hardness in Tool Materials
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the core processing value of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Master AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Density
- How does the programmable pressure function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the quality of IZO targets?
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Achieving High-Density CoCrFeNi(Cu) Coatings



















