At their core, rotary furnaces are thermal workhorses used across metallurgy, chemical processing, and environmental management. Their primary applications include the high-temperature processing of loose materials, such as powders and granules, for tasks like calcination, metal recovery, material synthesis, and waste treatment.
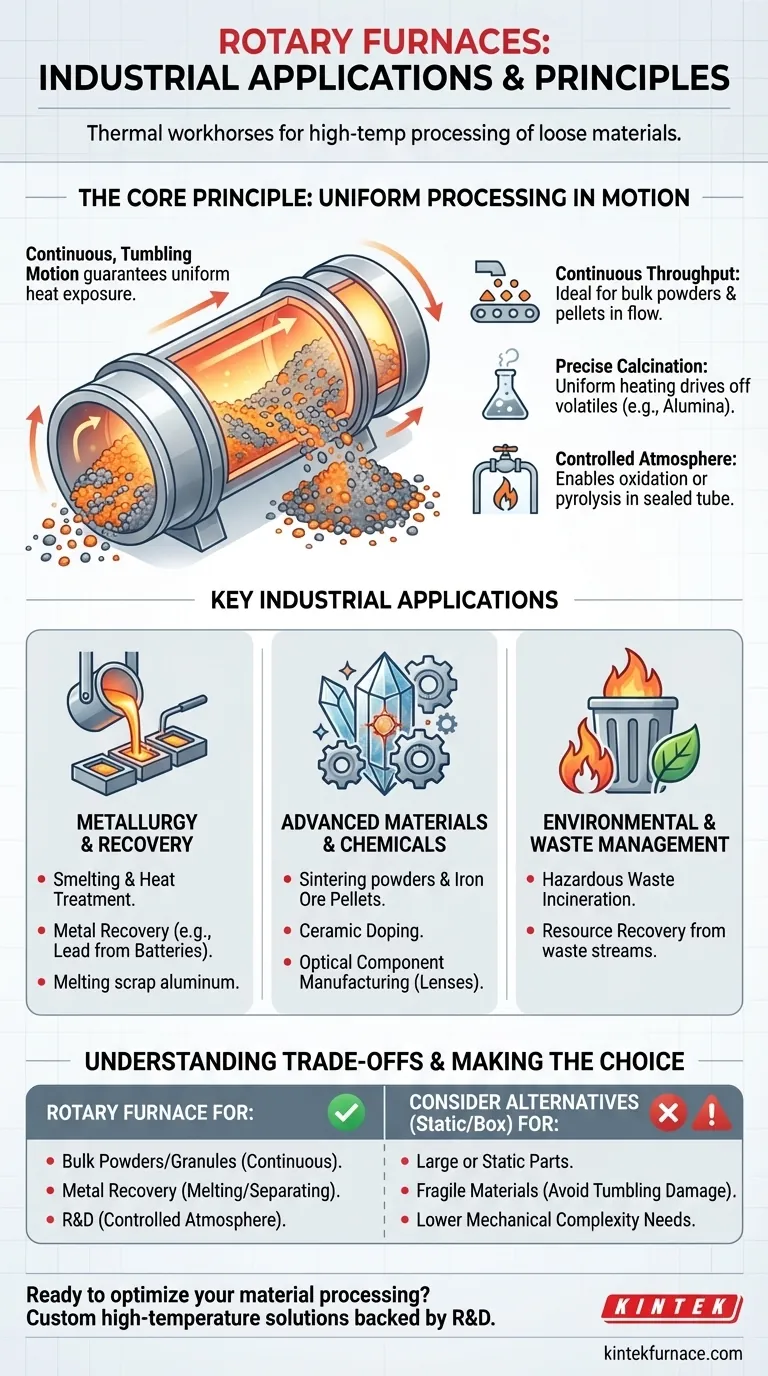
The true value of a rotary furnace lies not just in its high-temperature capability, but in its continuous, tumbling motion. This rotation guarantees uniform heat exposure for every particle, making it the superior choice for processing bulk, non-static materials that require consistent thermal treatment.
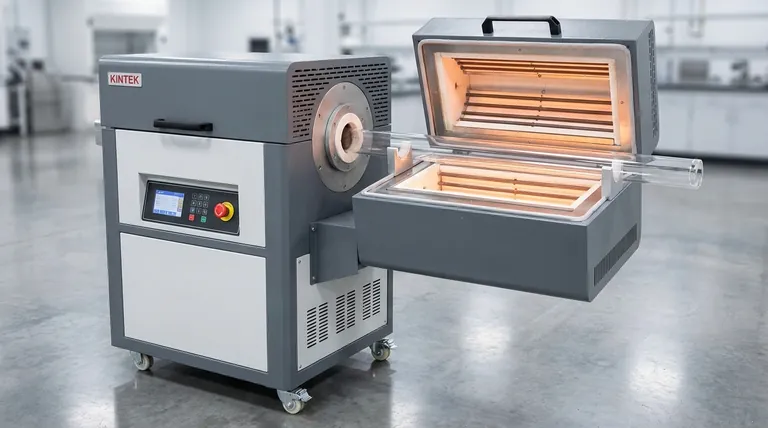

The Core Principle: Uniform Processing in Motion
The defining feature of a rotary furnace is its slowly rotating cylindrical chamber, which is typically tilted at a slight angle. This design is not arbitrary; it is the key to its effectiveness in specific industrial processes.
Continuous Throughput for Bulk Materials
The gentle tumbling motion ensures that the entire volume of material is constantly mixed and exposed to the heat source. This is ideal for processing loose materials like powders, pellets, and aggregates in a continuous flow.
This contrasts with static furnaces, where material at the bottom of a crucible may receive less heat than material at the top.
Achieving Precise Thermal Decomposition (Calcination)
Calcination is a process that uses heat to drive off volatile substances (like water or CO₂) and induce thermal decomposition. Rotary furnaces excel at this.
Applications like producing alumina or roasting ores rely on this uniform heating to ensure the final product has the desired chemical composition and purity.
Controlled Atmospheric Reactions
The sealed tube of a rotary furnace allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere. This is critical for processes that must occur in specific gaseous environments.
This capability is used for oxidation (introducing oxygen to alter a material's chemistry) or pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment).
Key Industrial Applications
The unique design of rotary furnaces makes them indispensable in several key sectors. Their versatility allows them to handle everything from raw ore processing to hazardous waste destruction.
Metallurgy and Metal Recovery
In metallurgy, these furnaces are used for smelting metals and alloys, melting scrap aluminum, and performing heat treatments on forged components.
A significant application is the recovery of valuable metals from industrial byproducts, such as reclaiming lead from battery scrap. The furnace efficiently melts the materials, allowing for separation.
Advanced Materials and Chemicals
Rotary furnaces are instrumental in manufacturing advanced materials. This includes sintering powders to increase their density and strength, creating iron ore pellets, and doping ceramics to alter their properties.
They are also used to apply coatings to powders and even to manufacture high-precision optical components like lenses and telescope mirrors, where thermal uniformity is paramount.
Environmental and Waste Management
The high, contained temperatures of a rotary furnace make it an effective tool for incinerating hazardous industrial or medical waste safely.
Beyond destruction, they are also used to recover valuable substances from waste streams, turning a liability into an asset.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not for Large or Static Parts
The fundamental tumbling action makes these furnaces unsuitable for heat-treating large, single-piece components or objects that must remain stationary during the process. A batch or box furnace is the correct tool for that job.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including seals, bearings, and drive systems, adds mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. This translates to specific maintenance requirements to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
Potential for Material Damage
The tumbling motion, while gentle, can cause attrition or damage to extremely friable or delicate materials. The suitability of the material for this type of processing must be considered.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal equipment depends entirely on your material type and process goals.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders or granular materials continuously: A rotary furnace is likely the ideal solution due to its efficient, uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is metal recovery from scrap or byproducts: The tumbling action and high-temperature capability make it highly effective for melting and separating materials.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, large, or static component: You should consider a static alternative, like a box or batch furnace, as the tumbling action is unsuitable.
- If your primary focus is R&D on new materials in a controlled atmosphere: A laboratory-scale rotary tube furnace offers the precise control and versatility needed for sample preparation and testing.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace excels wherever uniform, continuous processing of loose materials is the critical path to success.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Smelting, metal recovery (e.g., lead from batteries), heat treatment |
| Chemical Processing | Calcination (e.g., alumina production), material synthesis, pyrolysis |
| Environmental Management | Hazardous waste incineration, resource recovery from waste streams |
| Advanced Materials | Sintering, iron ore pellet production, ceramic doping, optical component manufacturing |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a custom rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental and industrial requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, chemical processing, or environmental management, we can help you achieve uniform heating and continuous throughput. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















