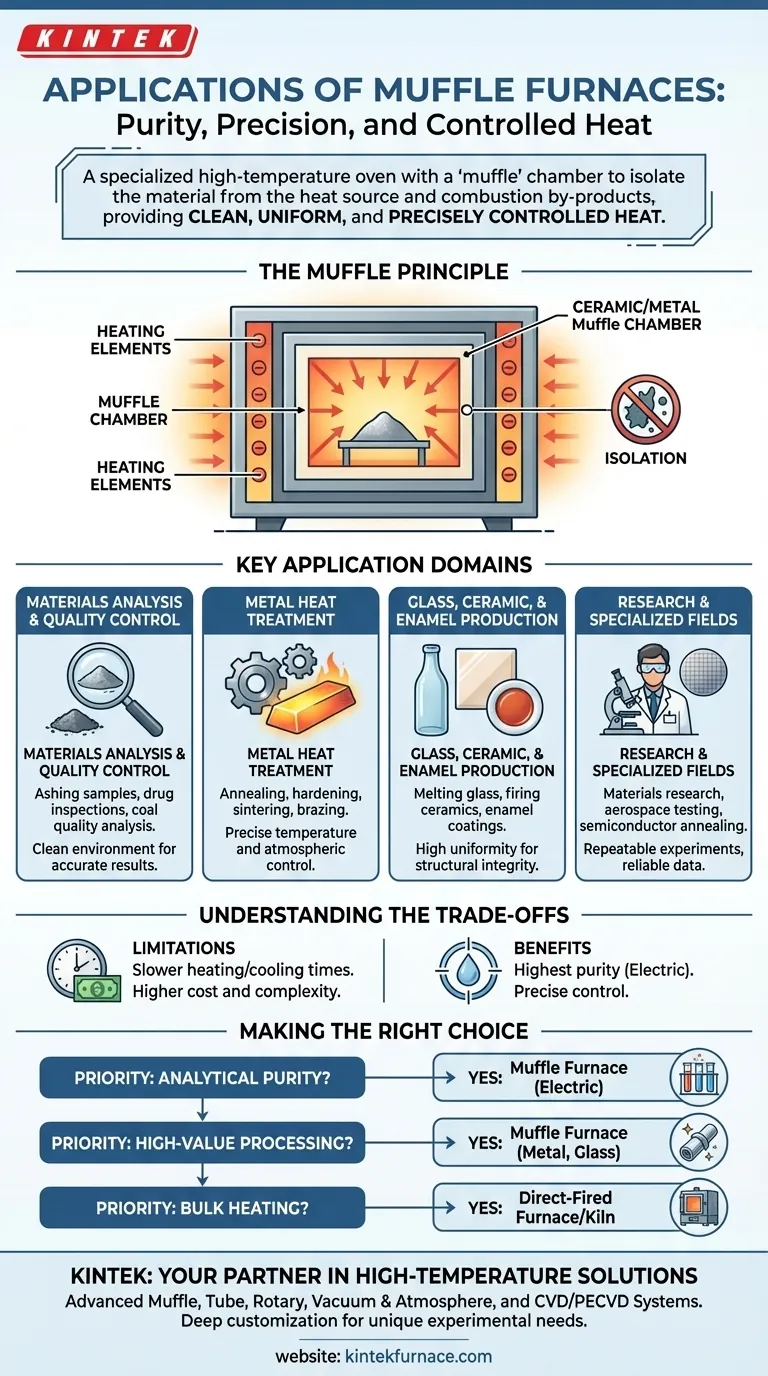
At its core, a muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven, but its applications extend far beyond simple heating. These furnaces are essential tools in fields ranging from materials science and metallurgy to analytical chemistry, used for processes like ashing samples, annealing metals, and creating advanced ceramics. Their defining feature is an inner chamber, or "muffle," that isolates the material being heated from the fuel source and combustion by-products.
The true value of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures. Its primary advantage is providing clean, uniform, and precisely controlled heat by separating the workpiece from heating contaminants, which is critical for sensitive analytical, industrial, and research processes.
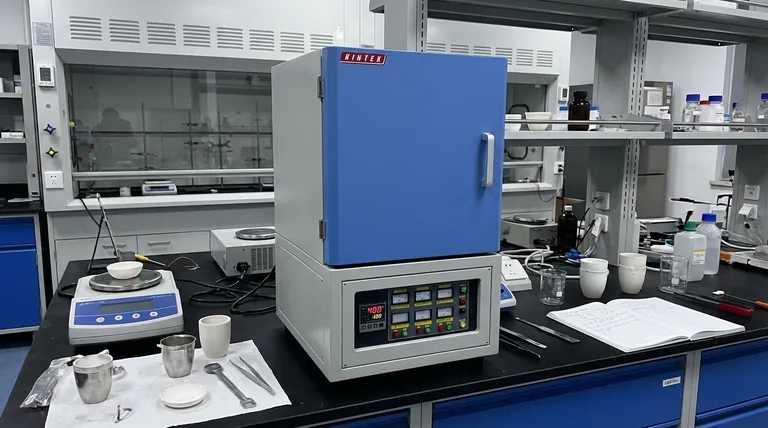

The Principle: Why the "Muffle" is Critical
The name "muffle furnace" directly describes its key functional component. Understanding this principle is essential to understanding its applications.
What is a Muffle?
A muffle is a sealed inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or a metal alloy. It acts as a radiant heat box.
The heating elements (electric coils) or flames (in a gas-fired model) heat the outside of this chamber. The heat then radiates uniformly into the interior, heating the sample without any direct contact.
The Power of Isolation
This separation is the furnace's most important feature. By isolating the sample from the raw heating source, it prevents contamination from soot, unburnt fuel, or other gaseous by-products of combustion.
This is indispensable for processes where chemical purity and surface finish are paramount.
Enabling Controlled Atmospheres
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, the internal atmosphere can be carefully controlled. Air can be removed and replaced with inert or reactive gases.
For example, introducing nitrogen or argon can prevent oxidation during metal heat treatment, a process known as bright annealing.
Key Application Domains
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace make it the ideal tool for specific, high-stakes tasks across various industries.
Materials Analysis and Quality Control
This is a primary application in analytical laboratories. The furnace provides the extreme heat needed to burn off all organic matter and water from a sample, leaving only the inorganic ash.
Common uses include ashing samples to determine filler content, performing drug inspections, analyzing coal quality, and testing the properties of plastics, paints, and textiles. The clean environment ensures the remaining material is not contaminated by the heating process itself.
Metal Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, controlling a metal's properties through heating and cooling is fundamental. Muffle furnaces offer the precise temperature control and atmospheric purity required for these processes.
Applications include annealing (softening metal), hardening, sintering (fusing powdered metal), brazing, and soldering. The uniform heat prevents thermal stress and cracking.
Glass, Ceramic, and Enamel Production
These processes demand high temperatures and exceptional uniformity to avoid defects. A muffle furnace provides the perfect environment.
It is used for melting and annealing glass, creating durable enamel coatings on metal, and firing technical ceramics used in aerospace and electronics. The absence of contaminants ensures the optical clarity of glass and the structural integrity of ceramics.
Research and Specialized Fields
For scientists and engineers developing new materials, the muffle furnace is an essential research tool.
It is used in materials research, testing components for the aerospace industry, annealing semiconductor wafers, and preparing sensitive biomedical samples. Its precision allows for repeatable experiments and reliable data.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not always the right choice. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Heating Rate and Efficiency
Because the heat must first transfer through the muffle wall, these furnaces can have slower heat-up and cool-down times compared to direct-fired furnaces. This can impact throughput in high-volume industrial settings.
Cost and Complexity
The sealed chamber, control systems, and high-quality materials required for the muffle make these furnaces more complex and expensive than a simple high-temperature oven or kiln.
Electric vs. Gas-Fired Models
Electric furnaces offer the highest level of purity and the most precise temperature control, making them standard for laboratory and analytical work. Gas-fired furnaces can be more economical to run at large industrial scales but carry a small risk of contamination if the muffle ever develops a crack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a muffle furnace depends entirely on your need for process purity and thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace, particularly an electric model, is non-negotiable for tasks like ashing, trace mineral analysis, or preparing sensitive samples.
- If your primary focus is high-value material processing: This furnace is essential for metal treatments like bright annealing or creating flawless ceramics and glass where surface finish and integrity are critical.
- If your primary focus is simply bulk heating: If contamination is not a concern, a less expensive direct-fired furnace or kiln is likely a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Understanding this core principle of controlled, isolated heat is the key to leveraging the power of a muffle furnace in your work.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Analysis | Ashing, drug inspections, coal quality testing | Clean environment prevents contamination, ensures accurate results |
| Metal Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, sintering, brazing | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, prevents oxidation |
| Glass, Ceramic, and Enamel Production | Melting glass, firing ceramics, enamel coatings | High uniformity, no contaminants for structural integrity |
| Research and Specialized Fields | Materials research, aerospace testing, semiconductor annealing | Repeatable experiments, reliable data for innovation |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring purity, precision, and efficiency to your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















