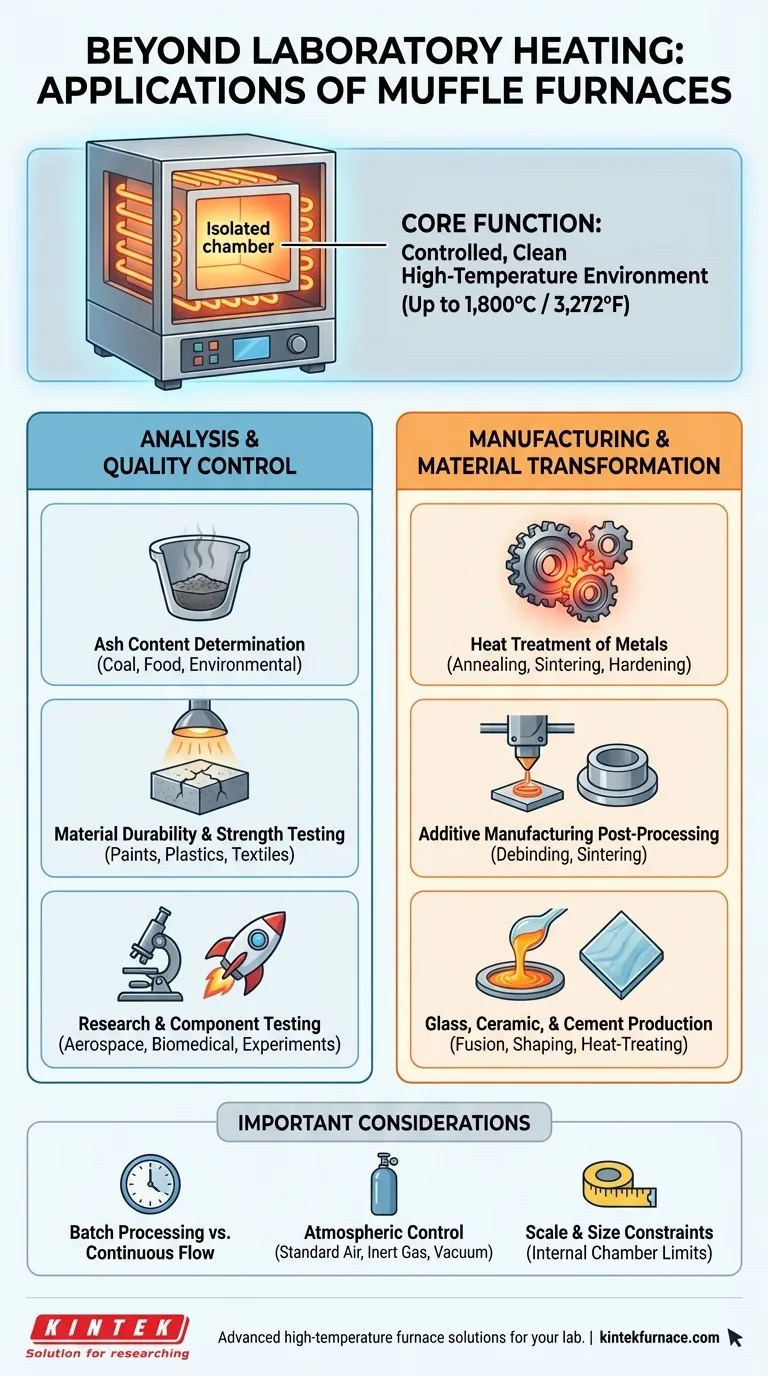
Beyond simple laboratory heating, a muffle furnace is a highly versatile tool used across a wide spectrum of industrial, analytical, and manufacturing processes. Its applications range from determining the ash content of coal and preparing biomedical samples to critical post-processing steps in additive manufacturing and testing materials for aerospace applications.
The core value of a muffle furnace lies in its ability to create a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment that is completely isolated from the heating elements. This "muffle" design ensures samples are heated cleanly, without contamination from combustion byproducts, making it indispensable for both sensitive analysis and material transformation.

Core Function: A Controlled, High-Temperature Environment
A muffle furnace's unique design is the key to its broad utility. Understanding its two primary capabilities explains why it is used in so many different fields.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The defining feature is the muffle—a sealed chamber, typically made of ceramic or high-temperature alloy, that separates the material being heated from the actual heating elements.
Modern electric furnaces heat this chamber via conduction, convection, and radiation. This design prevents any byproducts of fuel combustion from contaminating the sample, ensuring a clean heating process essential for laboratory analysis and sensitive material science.
Achieving Sophisticated Temperatures
Muffle furnaces can achieve extremely high temperatures, with some models reaching up to 1,800°C (3,272°F).
This capability enables sophisticated metallurgical applications and the processing of advanced materials like ceramics and composites that require intense heat to achieve their desired properties.
Applications in Analysis and Quality Control
One of the furnace's primary roles is to test and analyze materials by subjecting them to controlled thermal stress.
Ash Content Determination
This is a foundational use in many industries. A sample is heated at a high temperature to burn off all organic matter, leaving only the non-combustible ash residue.
This process is critical for coal quality analysis, food science, and environmental testing to determine the percentage of inorganic filler or contaminants.
Material Durability and Strength Testing
Muffle furnaces are used to simulate extreme environmental conditions. This includes testing the heat resistance of paints, the strength of plastics after thermal exposure, and the durability of textile fibers.
Research and Component Testing
In specialized fields, furnaces are essential for research and development. They are used for testing aerospace materials, preparing biomedical samples, and conducting other scientific experiments that require a sterile, high-heat environment.
Applications in Manufacturing and Material Transformation
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are a key tool for permanently altering the physical and chemical properties of materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy, furnaces are used for various heat-treating processes to alter the properties of metals like steel and copper.
Common applications include annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility), sintering (to fuse metallic powders together), and other treatments to enhance hardness or strength.
Additive Manufacturing Post-Processing
Muffle furnaces are critical in the workflow for 3D-printed metal and ceramic parts. They are used for debinding, a process that removes the binding polymer from the "green" part.
This is followed by sintering, where the part is heated to a high temperature to fuse the material particles into a dense, solid object.
Glass, Ceramic, and Cement Production
The furnace's ability to reach and hold precise high temperatures makes it ideal for working with glass and ceramics. It is used for glass fusion, shaping, and creating ceramic components.
In the building materials industry, it is used to heat-treat materials during cement production and in foundry work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, muffle furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
Muffle furnaces are fundamentally batch-processing tools. You place a sample (or samples) inside, run a heating cycle, and remove them. They are not designed for the continuous, high-volume throughput seen in large-scale industrial ovens.
Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace heats samples in the presence of ambient air. While this is sufficient for many applications, processes requiring a specific inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum typically demand more specialized and complex furnace designs.
Scale and Size Constraints
The size of the internal chamber limits the size and quantity of the parts you can process. While industrial-scale models exist, they are primarily suited for small-to-medium-sized workpieces, not massive components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing: Its clean, controlled environment is ideal for quantifiable analysis like determining ash content or testing material properties.
- If your primary focus is material property modification: Its high-temperature capabilities are perfect for metallurgical heat treatment, sintering powders, and altering material microstructures.
- If your primary focus is small-scale production or crafting: It is an excellent tool for creating custom ceramic parts, fusing glass, or post-processing 3D-printed components.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace excels wherever a clean, precisely controlled, high-temperature batch process is required.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Analysis & Quality Control | Ash content determination, material durability testing, biomedical sample preparation |
| Manufacturing & Material Transformation | Metal heat treatment (e.g., annealing, sintering), additive manufacturing post-processing, glass and ceramic production |
| Research & Development | Aerospace material testing, scientific experiments requiring sterile high-heat environments |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in processes such as ash testing, heat treatment, and additive manufacturing. Ready to elevate your operations? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















