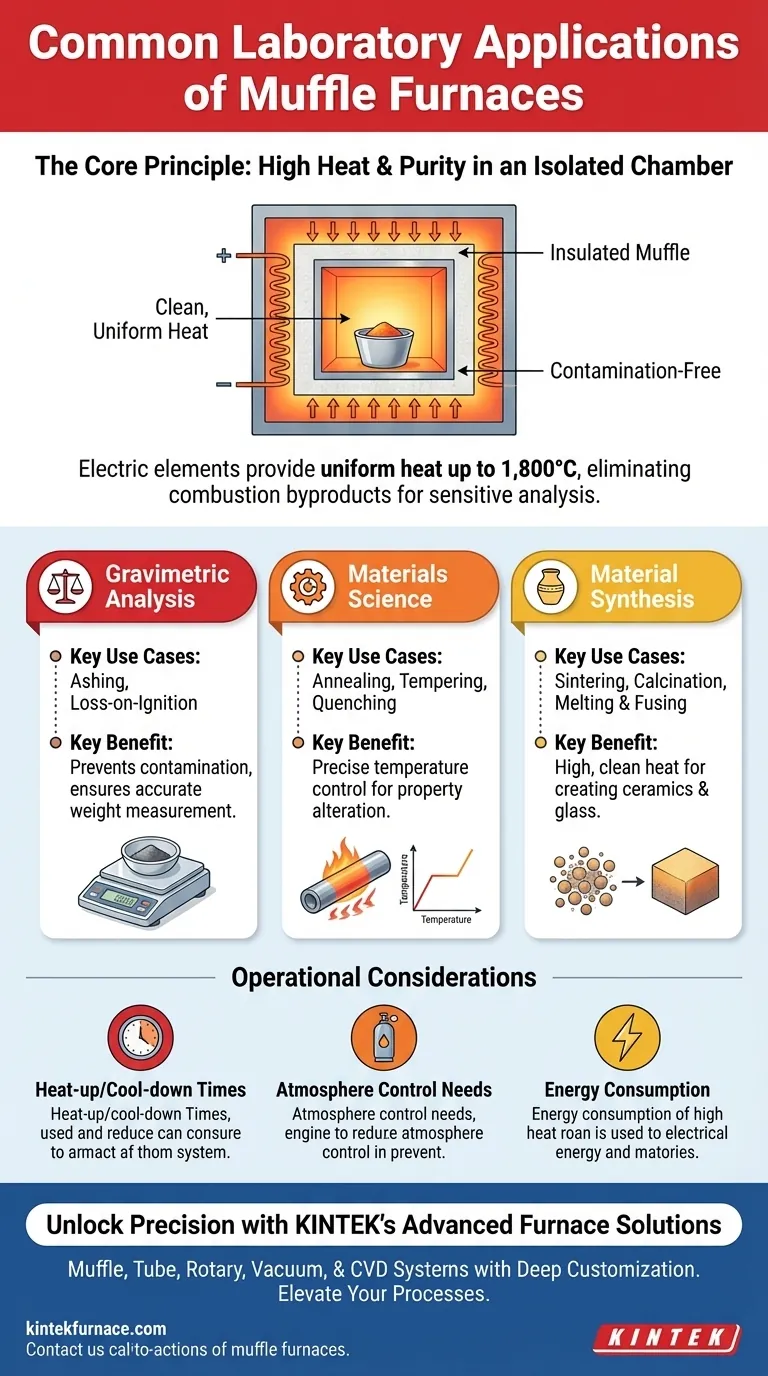
In any advanced laboratory, a muffle furnace is the indispensable tool for processes demanding extreme heat and purity. Its most common applications are gravimetric analysis like ashing, the heat treatment of metals and materials to alter their properties, and the synthesis of new materials such as ceramics, glass, and enamels.
The core value of a muffle furnace isn't just its high temperature, but its ability to provide that heat uniformly within an isolated chamber. This "muffle" prevents contamination from combustion byproducts, ensuring the integrity of the sample and the predictability of the process.
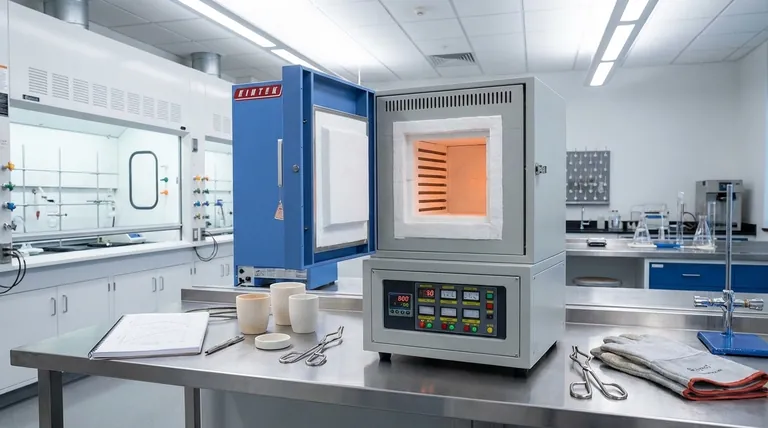

The Core Principle: Why a "Muffle" Matters
A muffle furnace’s design is key to its function. Unlike a simple forge or kiln where a flame might directly contact the material, a muffle furnace isolates the sample completely.
High Temperatures, High Purity
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the actual heating elements.
In modern electric furnaces, heat is generated cleanly through conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation. This design eliminates the combustion byproducts and impurities that would be present in a fuel-fired furnace, which is critical for sensitive chemical analysis and materials science.
Uniform and Precise Heat Control
These furnaces provide exceptionally uniform and stable heat, with modern units reaching temperatures as high as 1,800°C (3,272°F).
This precise control is not a luxury; it is essential for achieving repeatable results in experiments and for creating materials with specific, predictable microstructures and properties.
Key Applications in Detail
The combination of clean, high, and uniform heat makes the muffle furnace essential for several distinct categories of laboratory work.
Gravimetric Analysis: Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
Ashing is a process used to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. The material is heated to a high temperature until all organic substances burn away, leaving only the mineral ash.
The muffle furnace is ideal for this because its high, controlled heat ensures complete combustion. Crucially, the isolated chamber guarantees that the remaining ash is not contaminated, allowing for accurate weight measurement. Loss-on-ignition (LOI) is a similar process that measures the total weight lost upon heating.
Materials Science: Heat Treatment and Property Alteration
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling materials, primarily metals, to alter their physical and mechanical properties. A muffle furnace's precision is paramount for this.
Common processes include:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material to soften it and relieve internal stresses.
- Tempering: Heating a hardened material to a lower temperature to increase its toughness.
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling a material to harden it.
The exact temperature and duration directly influence the material's final grain structure, hardness, and ductility.
Material Synthesis: Creating and Fusing
Many advanced materials are created at extreme temperatures. The muffle furnace provides the necessary environment for these transformations.
Key synthesis applications include:
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) into a solid mass by heating them below their melting point.
- Calcination: Decomposing a solid through heating to induce a chemical change, often to remove a volatile fraction.
- Melting and Fusing: Creating glass, enamel coatings, and technical ceramics that require very high, clean heat to form.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with operational factors that must be understood.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Times
Due to their significant thermal insulation and mass, muffle furnaces do not heat up or cool down instantly. A cycle can take several hours, which must be factored into lab workflow and scheduling.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with the air that is inside its chamber. If a process requires an inert atmosphere (like argon) or a reactive one to prevent oxidation, a specialized furnace with ports for gas exchange is necessary.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1,000°C or higher requires a substantial amount of electrical energy. This is a significant operational cost and safety consideration for any laboratory.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific application of a muffle furnace is always tied to its fundamental strengths: high heat, purity, and control.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (e.g., ash content): You need the furnace for its ability to ensure complete combustion and prevent sample contamination for accurate measurement.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties (e.g., metals): You rely on the furnace's precise and uniform temperature control for predictable results from heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials (e.g., ceramics): The furnace's capacity for extremely high, clean heat is the critical factor for processes like sintering and calcination.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool for any laboratory process where high heat and high purity are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Cases | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Gravimetric Analysis | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition | Prevents contamination, ensures accurate weight measurement |
| Materials Science | Annealing, Tempering, Quenching | Precise temperature control for property alteration |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Calcination, Melting | High, clean heat for creating ceramics and glass |
Unlock precision and purity in your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with tailored furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















