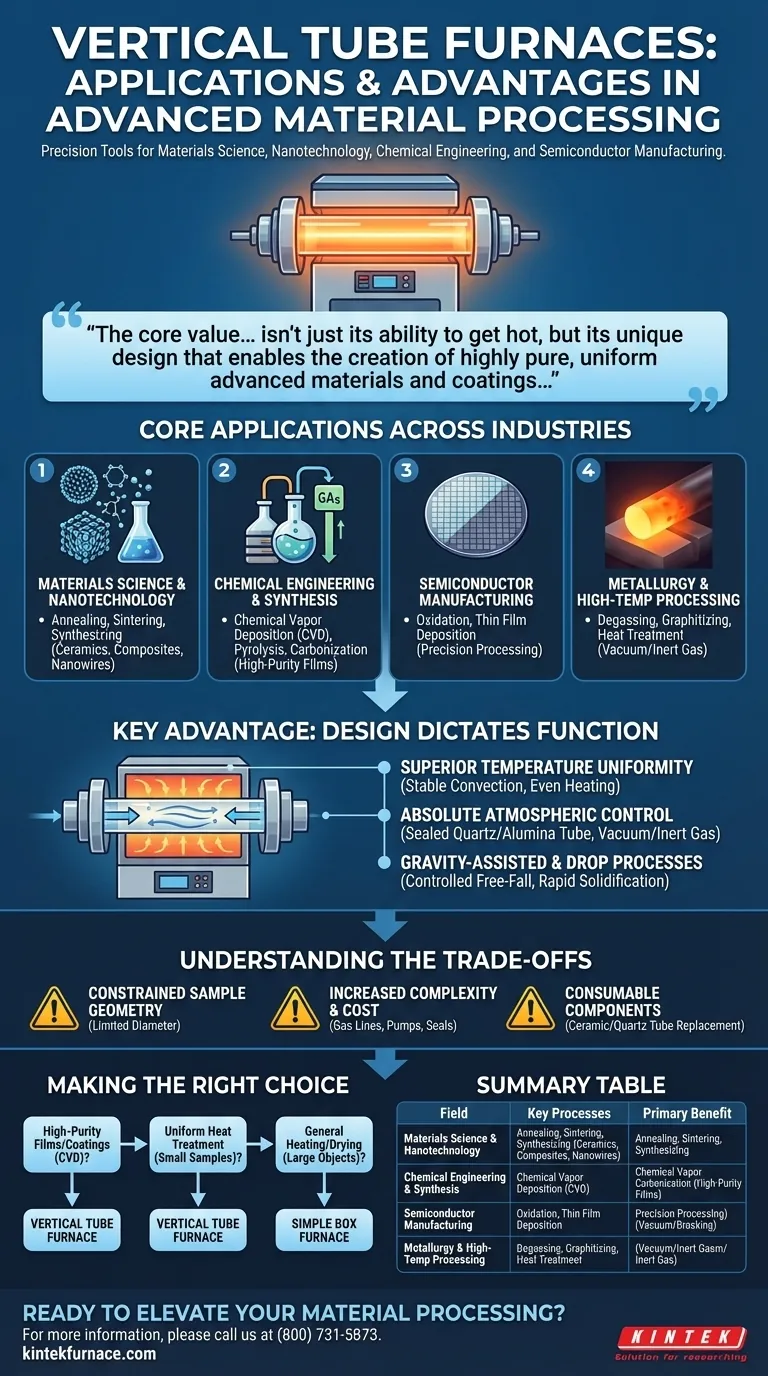
In short, vertical tube furnaces are specialized tools used primarily in materials science, nanotechnology, chemical engineering, and semiconductor manufacturing. They excel at high-temperature processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), annealing, and material synthesis that demand exceptional temperature uniformity and a highly controlled atmosphere.
The core value of a vertical tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its unique design that enables the creation of highly pure, uniform advanced materials and coatings that are impossible to produce in a standard oven.

Core Applications Across Industries
Vertical tube furnaces are not general-purpose ovens. They are precision instruments chosen when the process environment is as critical as the temperature itself. Their applications are concentrated in fields creating next-generation materials.
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
This is the primary domain for vertical tube furnaces. Researchers use them to create and test novel materials with specific properties.
Key processes include annealing, which alters a material's microstructure to improve ductility; sintering, which fuses powders into a solid mass; and synthesizing advanced materials like ceramics, composites, and nanowires under tightly controlled thermal conditions.
Chemical Engineering and Synthesis
The sealed tube design is perfect for processes that involve reactive gases or require an inert atmosphere to prevent contamination.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cornerstone application. In this process, precursor gases are introduced into the tube where they react at high temperatures to deposit a thin, high-purity film or coating onto a substrate. This is crucial for optics and aerospace components. Other common processes are pyrolysis (thermal decomposition without oxygen) and carbonization.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry relies on absolute purity and precision, making vertical tube furnaces essential for specific fabrication steps.
They are used for processes like oxidation, where a thin layer of silicon dioxide is grown on a wafer, and for depositing various films. Their excellent temperature uniformity ensures that every part of a delicate wafer receives the exact same treatment.
Metallurgy and High-Temperature Processing
In specialized metallurgy, these furnaces are used for precise heat treatments where atmospheric control is critical to the final properties of the metal.
This includes processes like degassing (removing trapped gases from a material), graphitizing, and other heat treatments that must be performed in a vacuum or an inert gas environment to prevent oxidation.
The Key Advantage: Design Dictates Function
The capabilities of a vertical tube furnace are a direct result of its physical structure. Understanding this design explains why it is chosen over other heating equipment.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
By orienting the tube vertically, convection currents are more stable and predictable. This allows for the creation of an exceptionally uniform "hot zone" along the length of the tube, ensuring a sample is heated evenly from all sides.
Absolute Atmospheric Control
The defining feature is the cylindrical tube, typically made of quartz or alumina. It can be completely sealed from the outside air.
This allows users to pull a vacuum or, more commonly, introduce a continuous flow of specific gases. This control is non-negotiable for processes like CVD or for protecting sensitive materials from oxygen at high temperatures.
Gravity-Assisted and Drop Processes
The vertical orientation enables unique experimental setups. In a drop tube furnace, a specific variant, materials can be dropped through the hot zone.
This allows for the study of processes like combustion or rapid solidification in a controlled, free-fall environment, a capability impossible in a horizontal furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vertical tube furnace is a specialized instrument with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for general-purpose heating.
Constrained Sample Geometry
The primary limitation is the diameter of the tube. These furnaces can only accommodate relatively small, cylindrical, or vertically aligned samples that fit within the tube. They are not designed for large or irregularly shaped objects.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Compared to a simple box furnace, a vertical tube furnace system is more complex. It requires gas lines, flow controllers, vacuum pumps, and specialized seals, all of which add to the initial cost and operational complexity.
Consumable Components
The ceramic or quartz tube is the heart of the furnace, but it is also a consumable. It can become brittle with thermal cycling or contaminated by process materials, requiring periodic replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding if a vertical tube furnace is appropriate depends entirely on the requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity films or coatings (CVD): The vertical tube furnace is the industry standard due to its unmatched atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is uniform heat treatment of small, sensitive samples: Its excellent temperature uniformity makes it a superior choice for annealing, sintering, or tempering.
- If your primary focus is general heating or drying of larger objects: A simpler and more cost-effective box furnace is the appropriate tool for the job.
Ultimately, you choose a vertical tube furnace when the process environment is just as critical to your outcome as the heat itself.
Summary Table:
| Field/Industry | Key Processes | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science & Nanotechnology | Annealing, Sintering, Material Synthesis | Exceptional temperature uniformity for novel materials |
| Chemical Engineering | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Pyrolysis | Absolute atmospheric control for high-purity reactions |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Oxidation, Thin Film Deposition | Precision processing for delicate wafers |
| Metallurgy | Degassing, Graphitizing, Heat Treatment | Controlled environments for metal property enhancement |
Ready to Elevate Your Material Processing with Precision?
At KINTEK, we understand that your research and production demands are unique. Our vertical tube furnaces are engineered to deliver the exceptional temperature uniformity and atmospheric control required for advanced applications like CVD, annealing, and material synthesis.
Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let's discuss how a KINTEK vertical tube furnace can be tailored to your specific needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized solution that drives your innovation forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















