In short, rotary furnaces are environmentally friendly primarily due to their exceptional energy efficiency and their ability to process a wide variety of materials, including waste streams. Their design inherently minimizes energy loss while converting low-value or waste products into valuable resources, directly supporting circular economy principles.
The core environmental advantage of a rotary furnace lies in its fundamental design. By combining continuous rotation with advanced thermal management, it achieves uniform processing with minimal energy consumption, effectively doing more with less.

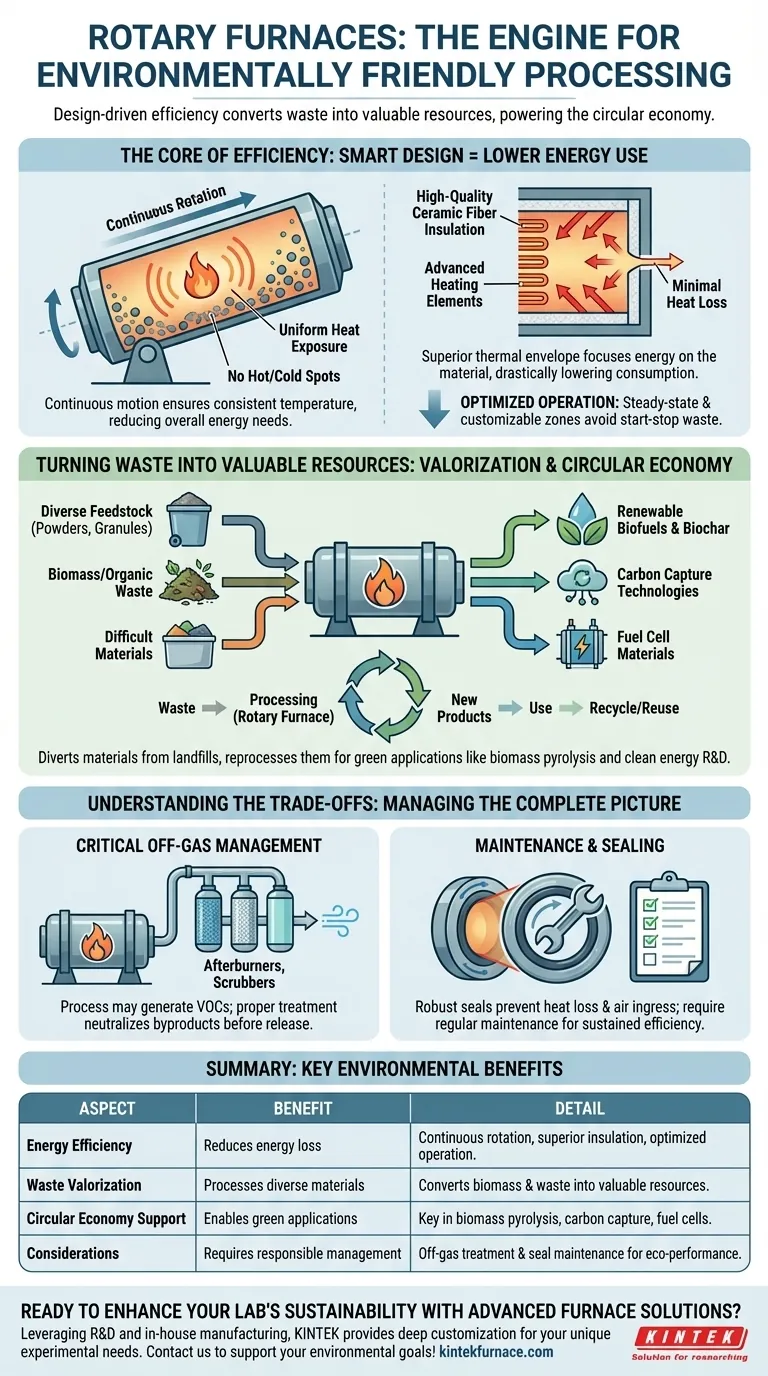
The Core of Efficiency: How Design Reduces Energy Use
The environmental benefits of a rotary furnace are not an add-on; they are a direct result of its core engineering principles. The system is designed from the ground up to maximize heat transfer and minimize waste.
The Impact of Continuous Rotation
A key feature is the slow, continuous rotation of the furnace's inclined cylindrical barrel. This constant tumbling motion ensures every particle of the material is exposed to the heat source uniformly.
This eliminates hot spots and cold spots, meaning the entire batch reaches the target temperature consistently. The result is a more efficient process that requires less overall energy input to achieve the desired outcome.
Superior Thermal Management
Modern rotary furnaces utilize high-quality ceramic fiber insulation and advanced heating elements. This combination creates a highly efficient thermal envelope.
This strong insulation performance drastically reduces heat loss to the surrounding environment, keeping the energy focused where it matters: on the material being processed. This directly lowers fuel or electricity consumption per unit of product.
Optimized and Continuous Operation
These furnaces are designed for continuous or high-throughput batch processing. This steady-state operation is inherently more energy-efficient than processes that require frequent starting and stopping, which wastes significant energy during heat-up cycles.
Furthermore, many designs allow for customizable heating zones along the length of the furnace, enabling tailored temperature profiles that apply energy precisely when and where it's needed, avoiding waste.
Turning Waste into Valuable Resources
Beyond energy efficiency, a rotary furnace's greatest environmental strength is its versatility, which allows it to be a key tool in waste valorization and recycling.
Versatility in Feedstock
Rotary furnaces are not limited to pristine raw materials. They excel at processing a diverse range of feedstocks, including powders, granules, solids, and even certain waste materials that are difficult to handle in other systems.
This capability allows industries to divert materials from landfills and reprocess them into new products.
Key Applications in the Circular Economy
This technology is central to several green processes. It's used in biomass pyrolysis to convert organic waste into renewable biofuels and biochar.
It is also used in research and development for carbon capture technologies and the preparation of materials for fuel cells, directly supporting the transition to cleaner energy systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, no technology is without its considerations. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the complete operational picture.
Initial Energy Input
Like any high-temperature furnace, a rotary furnace requires a substantial amount of energy to reach its initial operating temperature. For processes that are intermittent or very short, this start-up energy can offset some of the operational efficiency gains.
Off-Gas Management is Critical
Processing waste materials, especially through pyrolysis or chemical reactions, can generate volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful emissions. The furnace itself does not eliminate these.
A complete environmental solution requires a properly designed off-gas treatment system (e.g., afterburners, scrubbers) to capture and neutralize these byproducts before they are released into the atmosphere.
Maintenance and Sealing
The rotating seals at either end of the furnace are critical components that prevent heat loss and uncontrolled air ingress. Wear and tear on these seals can reduce efficiency and potentially release process gases, requiring a robust preventative maintenance schedule.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage the environmental benefits of a rotary furnace, you must align its capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize a furnace with high-quality insulation, reliable seals, and the ability to operate continuously to minimize heat-up and cool-down cycles.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization: Confirm the furnace's material compatibility and temperature range are suitable for your specific feedstock, and budget for a comprehensive off-gas management system.
- If your primary focus is process control for R&D: Choose a system with customizable heating zones and precise rotation speed control to develop and optimize new green processes.
By understanding how its design drives performance, you can effectively apply the rotary furnace as a powerful tool for sustainable industrial processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy loss through continuous rotation, superior insulation, and optimized operation. |
| Waste Valorization | Processes diverse materials like biomass and waste into valuable resources, reducing landfill use. |
| Circular Economy Support | Enables applications in biomass pyrolysis, carbon capture, and fuel cell material preparation. |
| Considerations | Requires off-gas management and maintenance for optimal eco-performance. |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for energy efficiency and waste recycling. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your environmental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















