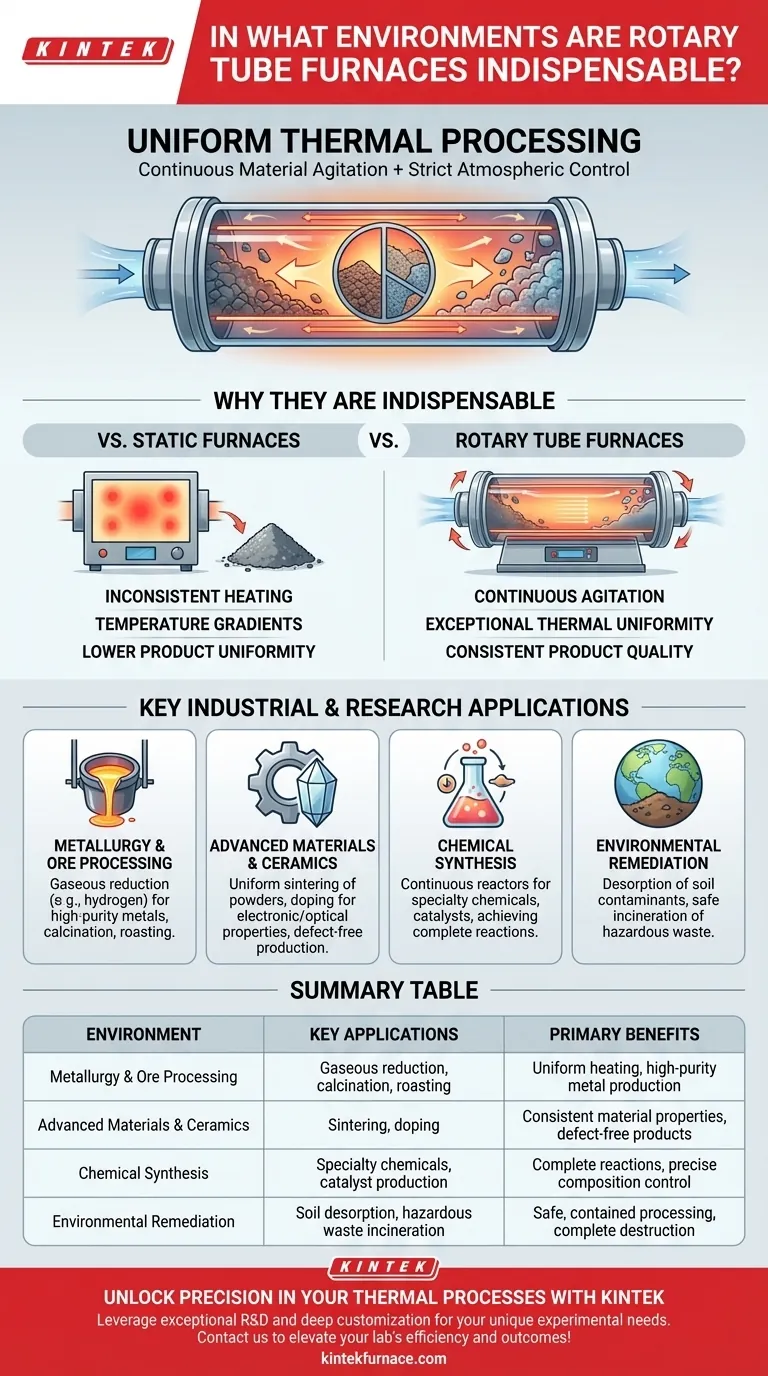
In short, rotary tube furnaces are indispensable in environments where uniform thermal processing of powders, granules, or other small solids under a precisely controlled atmosphere is non-negotiable. They are critical tools in industries ranging from metallurgy and advanced materials research to chemical processing and environmental remediation, excelling at tasks that static furnaces cannot perform efficiently.
The true indispensability of a rotary tube furnace lies not just in its ability to heat materials, but in its unique combination of continuous material agitation and strict atmospheric control. This pairing ensures every single particle undergoes the exact same process, which is the cornerstone of high-purity and high-performance material production.
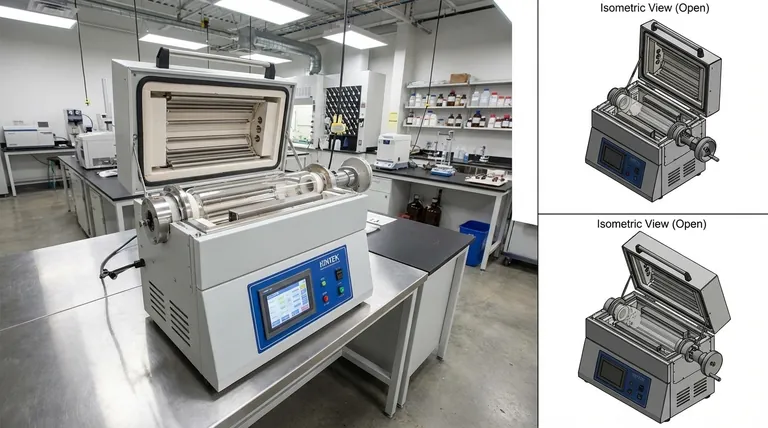

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heating and Atmosphere Control
To understand where these furnaces are essential, you must first grasp their two fundamental advantages over other heating systems, like static box or tube furnaces.
Ensuring Uniformity Through Rotation
A static furnace heats a stationary batch of material, often leading to temperature gradients. The material on the outside gets hotter than the material in the middle, resulting in an inconsistent product.
The rotary tube furnace solves this by constantly tumbling the material. This continuous mixing guarantees that every particle is exposed to the heat source and process gas equally, eliminating hot spots and ensuring exceptional thermal uniformity.
This dynamic heating is crucial for processes where final material properties depend heavily on consistent temperature exposure.
Mastering the Process Atmosphere
Many modern material processes require atmospheres other than ambient air to prevent unwanted reactions (like oxidation) or to drive desired ones (like reduction).
Rotary tube furnaces are engineered with advanced sealing systems that allow for the use of a wide range of atmospheres. This can include inert gases like nitrogen or argon, reducing gases like hydrogen, or even reactive and toxic gases like chlorine or methane. This capability is fundamental to their role in advanced manufacturing.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes rotary furnaces the only viable choice for several high-value processes.
Metallurgy and Ore Processing
In metallurgy, converting raw ore (often a metal oxide) into a pure metal is a primary goal. This frequently requires a process called gaseous reduction, where a gas like hydrogen is used at high temperatures to strip oxygen from the ore.
A rotary furnace is ideal for this. It efficiently tumbles iron ore pellets or other metal powders, ensuring the reducing gas reaches every particle to produce high-purity metals and alloys. The same principle applies to calcination and roasting, which prepare ores for further processing.
Advanced Materials and Ceramics
The creation of high-performance ceramics or catalysts often starts with fine powders. To create a dense, strong final product, these powders must be heated in a process called sintering.
Uniform sintering is critical to avoid defects. The gentle tumbling action of a rotary furnace ensures powders are sintered evenly, resulting in a dense, homogenous material. It is also used for doping ceramics with other elements, where uniform distribution is paramount for the material's final electronic or optical properties.
Chemical Synthesis
Rotary furnaces are used as continuous reactors for producing specialty chemicals and catalysts. The consistent heat and gas exposure across the material's surface area are essential for driving chemical reactions to completion and achieving the desired final product composition.
Environmental Remediation
In environmental applications, these furnaces are used for their contained, high-temperature processing capabilities.
They are used for the desorption of soil contaminants, where heat is used to vaporize and remove pollutants from soil. They are also used for the incineration of hazardous waste, as the continuous movement and high temperatures ensure complete and safe destruction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable for certain tasks, rotary tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their unique design comes with specific trade-offs.
Mechanical Complexity and Sealing
The rotating tube requires a sophisticated and robust sealing system to maintain atmosphere integrity, especially when using flammable or toxic gases. These seals are points of mechanical wear and represent a higher level of maintenance and cost compared to static furnaces.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are designed for free-flowing solids like powders, granules, and small pellets. They are not suitable for processing very large single parts, liquids, or materials that become sticky or melt at processing temperatures, as this would cause them to coat the tube wall.
Throughput vs. Other Kilns
While capable of continuous industrial production, for extremely high-volume bulk materials like cement, larger dedicated rotary kilns are often more economical. Rotary tube furnaces occupy a space that prioritizes process precision over sheer massive throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision to use a rotary tube furnace should be based on the specific requirements of your material and end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material production (e.g., metals, catalysts): The precise atmospheric and thermal control makes a rotary furnace the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing of powders or granules: A rotary furnace is explicitly designed for this task and will deliver more uniform results than a static batch system.
- If your primary focus is R&D and process validation: The smaller, lab-scale versions of these furnaces are perfect for cost-effectively determining the ideal processing parameters before scaling up.
- If your primary focus is environmental treatment of granular waste or soil: The contained, continuous-feed nature of a rotary furnace provides a safe and effective processing method.
Ultimately, a rotary tube furnace becomes indispensable when the quality, purity, and performance of your final product depend on every particle receiving the exact same treatment.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Ore Processing | Gaseous reduction, calcination, roasting | Uniform heating, high-purity metal production |
| Advanced Materials & Ceramics | Sintering, doping | Consistent material properties, defect-free products |
| Chemical Synthesis | Specialty chemicals, catalyst production | Complete reactions, precise composition control |
| Environmental Remediation | Soil desorption, hazardous waste incineration | Safe, contained processing, complete destruction |
Unlock Precision in Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, materials research, or environmental remediation, our rotary tube furnaces ensure uniform heating and strict atmospheric control for high-purity results. Don't let inconsistent processing hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution to elevate your lab's efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















