The time required for a dental ceramic firing cycle is not a single number. While a specific program can run from under an hour for a simple glaze to many hours for a full zirconia sintering, the total processing time is dictated by the specific ceramic material, the thickness of the restoration, and the number of firing stages required to complete the case.
The duration of a firing cycle is a function of material science, not just a matter of scheduling. Each stage—from drying to heating to cooling—is precisely timed to ensure the ceramic achieves its maximum strength and intended aesthetic properties without introducing internal stress or defects.

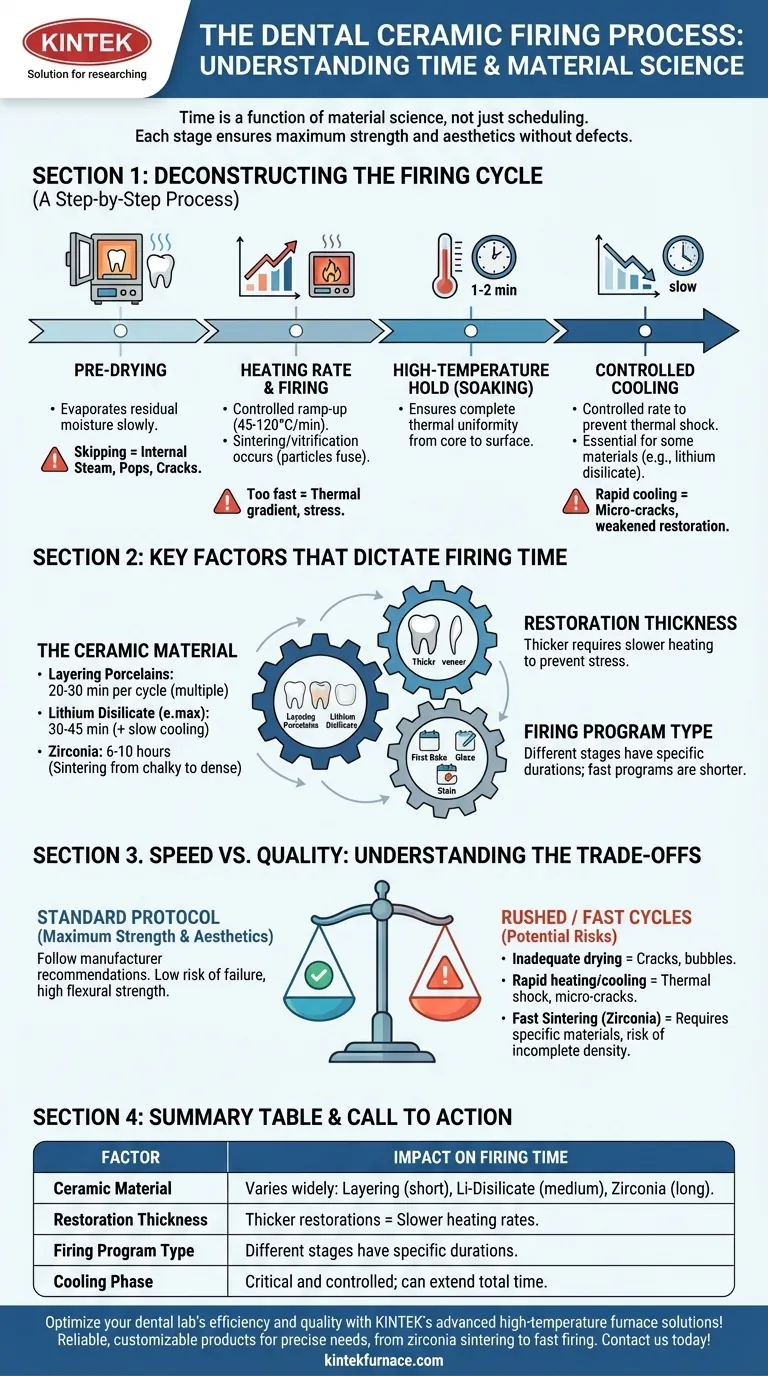
Deconstructing the Firing Cycle: A Step-by-Step Process
A firing cycle is a highly controlled thermal process with distinct stages. Understanding the purpose of each stage clarifies why the time investment is necessary.
Stage 1: Pre-Drying
Before the furnace door closes, the restoration is placed at the opening. This pre-drying stage allows residual moisture from the ceramic buildup or shading liquids to evaporate slowly.
Skipping or rushing this step can cause moisture to turn to steam inside the ceramic during heating, leading to pops, cracks, or internal porosity.
Stage 2: Heating Rate and Firing
Once drying is complete, the furnace temperature ramps up at a controlled rate (e.g., 45°C to 120°C per minute). This rate is critical.
The furnace then reaches and holds a specific high temperature. This is where sintering or vitrification occurs—the process where ceramic particles fuse together to create a dense, strong, and translucent structure.
Stage 3: High-Temperature Hold (Soaking)
Many programs include a "hold" or "soak" time at the peak temperature for one to two minutes.
This brief period ensures the entire restoration, from its core to its surface, achieves complete thermal uniformity, guaranteeing a fully matured ceramic.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling
Cooling is as critical as heating. The furnace must cool at a controlled rate to prevent thermal shock, which can introduce micro-cracks and significantly weaken the final restoration.
Some materials, like lithium disilicate, require a very slow, controlled cooling phase to allow for proper crystal growth, which is essential for their high strength.
Key Factors That Dictate Firing Time
The exact time parameters for the stages above are determined by three primary variables.
The Ceramic Material
This is the single most important factor. Different materials have fundamentally different processing needs.
- Layering Porcelains (Feldspathic): These typically have multiple, relatively short firing cycles (20-30 minutes each) for the opaque, dentin, and enamel layers, followed by a glaze firing.
- Lithium Disilicate (e.g., e.max): A press or crystallization firing can take 30-45 minutes, but the critical, slow cooling phase can extend the total furnace time.
- Zirconia: This material requires the longest cycle. Sintering a full-contour zirconia restoration from its chalky pre-sintered state into its final, dense form is a process that takes 6 to 10 hours in a conventional furnace.
The Restoration's Thickness and Mass
A thick molar crown requires a slower heating rate than a thin veneer. This ensures the center of the restoration heats up at the same pace as the surface.
Heating too quickly creates a thermal gradient, inducing stress that can compromise the restoration's integrity before it's ever delivered to the patient.
The Type of Firing Program
A single restoration goes through multiple, distinct firing cycles.
A first bake for the opaque or body layer is different from a final glaze firing, which is designed to create a smooth, non-porous surface and is often much shorter. Correction bakes and stain/glaze cycles each have their own specific, shorter time requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Quality
While modern furnaces offer "speed" or "fast" firing programs, it's critical to understand the compromises involved. Deviating from the manufacturer's standard protocol can have direct consequences.
The Risk of Rushed Drying
Inadequate drying is a common source of failure. The resulting internal steam pressure can cause visible cracks or bubbles on the surface, requiring a complete remake of the restoration.
The Danger of Rapid Heating and Cooling
Heating or cooling too quickly induces thermal shock. While the restoration may appear intact, it can harbor internal stresses and micro-cracks that dramatically reduce its long-term flexural strength and increase the risk of clinical failure.
The "Fast Firing" Program Caveat
Fast sintering cycles for zirconia can reduce the time from 8+ hours to around 2-3 hours. However, these programs often require specific, compatible zirconia materials.
Using a fast cycle with a conventional material may not achieve full density, potentially impacting both strength and translucency. Always verify that the material is explicitly approved by its manufacturer for a given speed cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal firing time depends entirely on your clinical or business objective, balanced against the non-negotiable requirements of the material science.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and aesthetics: Always adhere to the ceramic manufacturer's standard, recommended firing programs, especially for multi-unit or complex anterior cases.
- If your primary focus is high-volume laboratory efficiency: Invest in multiple furnaces to run different programs simultaneously and batch restorations made from the same material to optimize each cycle.
- If your primary focus is rapid, single-visit turnaround: Use a fully integrated system (scanner, mill, furnace) and materials that have been specifically designed and validated by the manufacturer for accelerated firing cycles.
Ultimately, the correct firing duration is the one that reliably transforms a fragile powder or milled block into a durable, biocompatible, and aesthetic final restoration.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Firing Time |
|---|---|
| Ceramic Material | Varies widely: Layering porcelains (20-30 min), Lithium disilicate (30-45 min + cooling), Zirconia (6-10 hours) |
| Restoration Thickness | Thicker restorations require slower heating rates to prevent stress and defects |
| Firing Program Type | Different stages (e.g., first bake, glaze firing) have specific durations; fast programs reduce time but may compromise quality |
| Cooling Phase | Controlled cooling is critical; can extend total time, especially for materials like lithium disilicate |
Optimize your dental lab's efficiency and quality with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether you're handling zirconia sintering or fast firing cycles. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow and deliver superior results for your dental restorations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations



















