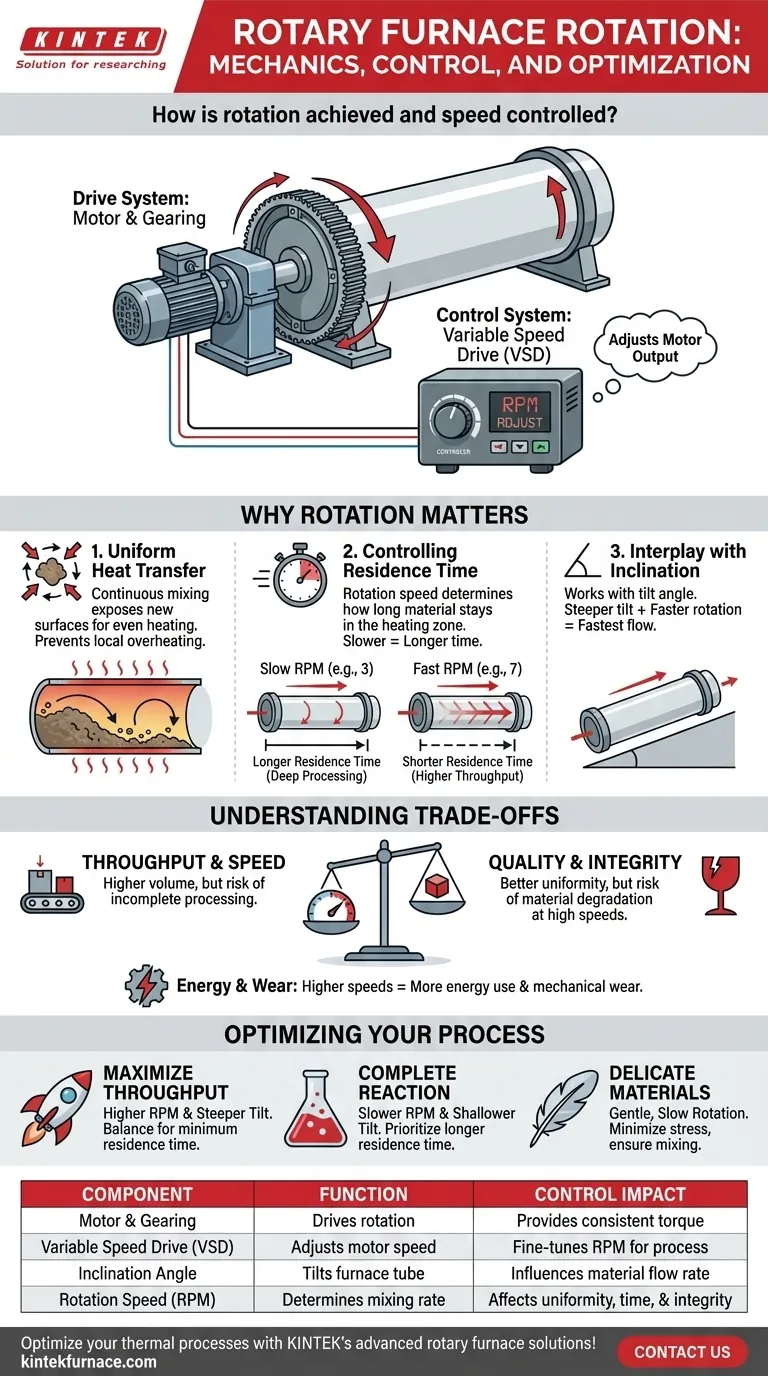
At its core, a rotary furnace's rotation is driven by a dedicated motor connected to a drive gear or a set of driven rollers that support the furnace tube. The speed of this rotation is precisely managed by a variable speed drive (VSD), an electronic controller that adjusts the motor's output to meet specific process requirements.
The mechanical system for rotation is straightforward, but its true significance lies in process control. Adjusting the rotation speed, in conjunction with the furnace's tilt angle, gives you direct command over material mixing, heat transfer efficiency, and residence time—the three pillars that determine final product quality.

The Mechanics of Furnace Rotation
To understand how to control the process, you must first understand the components that enable it. The system is designed for reliability and precise adjustment.
The Drive System: Motor and Gearing
An independent electric motor provides the power for rotation. This motor turns a large ring gear fixed to the outside of the furnace tube or, in some designs, drives the rollers on which the tube rests.
This direct-drive or roller-driven approach ensures a consistent and powerful transfer of torque, capable of turning the heavy furnace and its material load smoothly.
The Control System: The Variable Speed Drive (VSD)
The brain of the rotation system is the variable speed drive (VSD). This electronic device modulates the frequency and voltage of the electrical power supplied to the motor.
By adjusting the VSD, an operator can seamlessly increase or decrease the motor's speed, changing the furnace's revolutions per minute (RPM) on the fly. This allows for fine-tuning the process without ever stopping the furnace.
Why Rotation is a Critical Process Variable
The ability to control rotation speed is not merely a feature; it is fundamental to the furnace's function. The speed directly influences the material's behavior and the outcome of the thermal process.
Achieving Uniform Heat Transfer
The primary purpose of rotation is to continuously mix and tumble the material. This action constantly exposes new surfaces to the heat source, whether it's a direct flame or a heated wall.
Without rotation, the material at the top and edges would overheat while the core remained under-processed. Continuous mixing guarantees uniform heating from top to bottom, preventing insufficient local heating and ensuring consistent reactions.
Controlling Material Residence Time
Residence time—the duration a material spends inside the heating zone—is one of the most critical parameters in thermal processing. Rotation speed is a primary lever for controlling it.
A slower rotation (e.g., 3 RPM) causes the material to tumble more in place, increasing its residence time and allowing for deeper heat penetration or more complete chemical reactions.
A faster rotation (e.g., 7 RPM) helps convey the material through the furnace tube more quickly, increasing throughput but reducing the time for heat absorption.
The Interplay with Inclination Angle
Rotation speed does not work in a vacuum. It operates in tandem with the furnace's inclination angle (tilt).
A steeper tilt angle will cause material to flow through the furnace faster due to gravity. A shallow angle will slow it down. The combination of rotation speed and tilt angle gives you precise, two-factor control over the material's journey and its total exposure to heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing rotation requires balancing competing factors. Simply setting the speed to maximum or minimum is rarely the correct approach.
Speed vs. Residence Time
The most significant trade-off is between throughput and processing quality. A high RPM may increase the volume of material you can process per hour, but if the residence time becomes too short, the material may exit the furnace without being fully treated.
Uniformity vs. Material Integrity
While tumbling is essential for uniform heating, excessive rotation speed can be detrimental to fragile or abrasive materials. It can cause unwanted degradation, breakage, or dust generation, impacting final product quality and yield.
Energy Consumption and Mechanical Wear
Running the drive motor at higher speeds and under heavier loads consumes more energy. Furthermore, higher operational speeds increase the rate of mechanical wear on the ring gear, pinion, rollers, and bearings, leading to more frequent maintenance cycles.
Optimizing Rotation for Your Process
The ideal rotation speed is not a single number; it is a function of your material, your equipment, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You will likely operate at a higher RPM, balanced carefully with the inclination angle to ensure the material still achieves the minimum required residence time for processing.
- If your primary focus is achieving a complete chemical reaction: A longer residence time is paramount, which calls for a slower rotation speed and often a shallower furnace tilt to maximize the material's time in the heat zone.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate materials: A gentle, slow rotation is necessary to minimize mechanical stress and breakage while still providing the mixing needed for uniform heating.
Viewing the rotation system as a dynamic process lever, rather than a fixed mechanism, is the key to unlocking the full potential of your rotary furnace.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Control Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Motor & Gearing | Drives rotation via ring gear or rollers | Provides torque for consistent movement |
| Variable Speed Drive (VSD) | Adjusts motor speed electronically | Enables fine-tuning of RPM for process optimization |
| Inclination Angle | Tilts furnace tube to influence material flow | Works with speed to control residence time and throughput |
| Rotation Speed (RPM) | Determines material tumbling and mixing rate | Affects heat transfer uniformity, reaction completeness, and material integrity |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-performance furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















