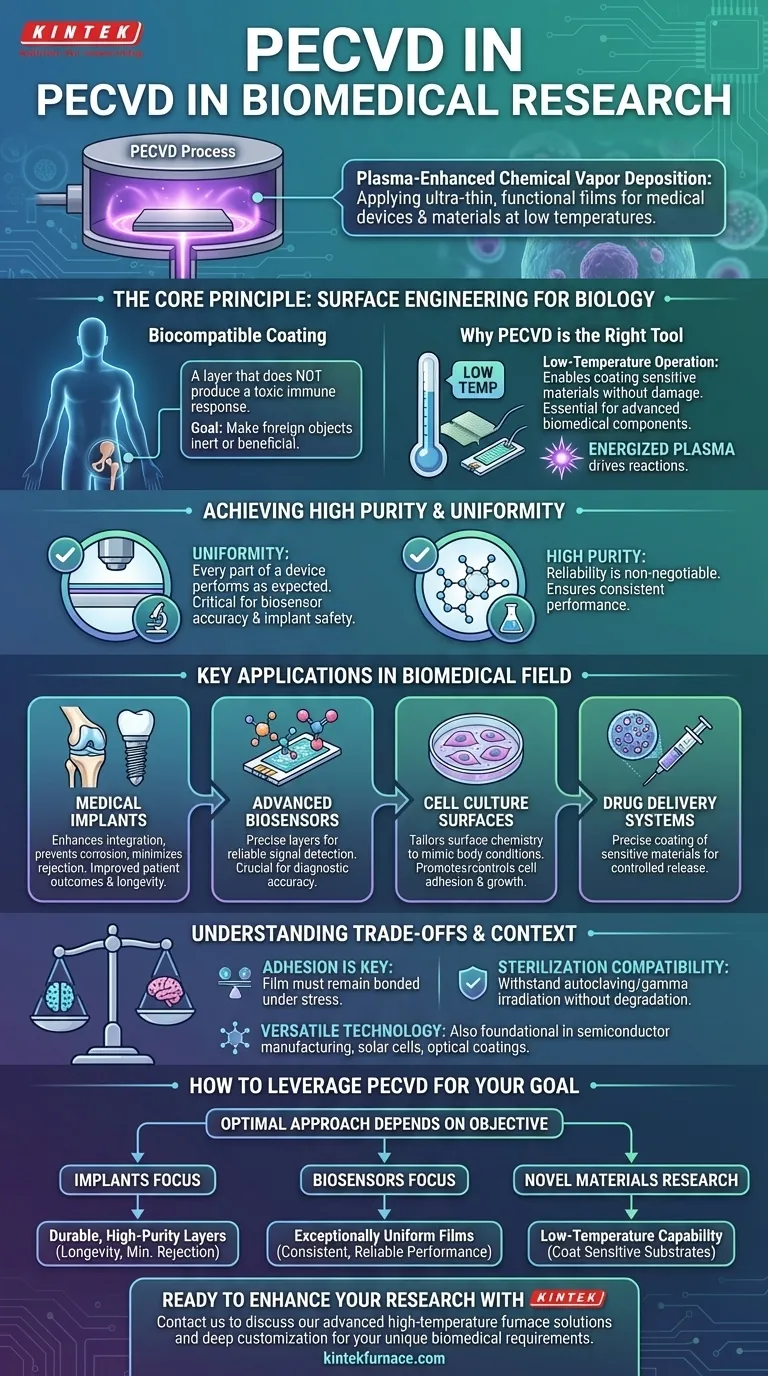
In biomedical research, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a critical technology used to apply ultra-thin, functional films onto the surfaces of medical devices and materials. Its primary applications include creating biocompatible coatings for medical implants, fabricating sensitive biosensors, developing advanced drug delivery systems, and preparing specialized surfaces for cell culture.
The core challenge in biomedical engineering is making synthetic materials perform safely and effectively within biological systems. PECVD is uniquely suited to solve this by depositing high-purity, uniform, and biocompatible films at low temperatures, enabling advanced devices without damaging the sensitive materials they are made from.

The Core Principle: Surface Engineering for Biology
What is a Biocompatible Coating?
A biocompatible coating is a material layer that, when applied to a medical device, does not produce a toxic or adverse immune response from the body.
The goal is to make a foreign object, like a metal implant or a polymer sensor, appear inert or even beneficial to the surrounding living tissue.
Why PECVD is the Right Tool for the Job
The defining advantage of PECVD is its low-temperature operation. Many advanced medical devices are built from polymers or other materials that would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures required by traditional deposition methods.
PECVD generates an energized plasma to drive the chemical reactions, allowing high-quality films to be deposited at or near room temperature. This capability is essential for preserving the integrity of sensitive biomedical components.
Achieving High Purity and Uniformity
For any medical device, reliability is non-negotiable. PECVD excels at producing films that are exceptionally uniform across a surface and have high purity.
This ensures that every part of a device performs as expected, a critical factor for the accuracy of a biosensor or the safety of a long-term implant.
Key Applications in the Biomedical Field
Enhancing Medical Implants
PECVD is used to apply durable, biocompatible coatings to implants like artificial joints or dental screws.
These coatings can enhance integration with bone, prevent corrosion, and minimize the risk of the body rejecting the implant, thereby improving patient outcomes and device longevity.
Fabricating Advanced Biosensors
Biosensors rely on specific surface interactions to detect biological molecules. PECVD is used to deposit the precise dielectric or functional layers required for these sensors to work.
The uniformity of PECVD films ensures that every sensor on a chip provides a reliable and repeatable signal, which is crucial for diagnostic accuracy.
Creating Ideal Surfaces for Cell Culture
In research, scientists need to grow cells on surfaces that mimic conditions inside the body. PECVCD can tailor the surface chemistry of glass or plastic labware to promote or control cell adhesion and growth.
This allows for more accurate experiments and a better understanding of cellular behavior.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
A Versatile Technology Beyond Medicine
While its low-temperature capability makes PECVD ideal for biomedical work, it is a foundational technology across many high-tech industries.
Its primary use is in semiconductor manufacturing for integrated circuits. Other major applications include fabricating solar cells, optical coatings for lenses, and protective layers in food packaging.
Key Technical Considerations
The success of a PECVD coating in a biomedical application depends heavily on adhesion. The film must remain securely bonded to the substrate throughout the device's lifetime, even when subjected to mechanical stress.
Furthermore, the coating and the device must be able to withstand standard sterilization methods, such as autoclaving or gamma irradiation, without degrading or losing their essential properties.
How to Leverage PECVD for Your Goal
For teams working in the biomedical space, PECVD is less a single solution and more a versatile platform. The optimal approach depends on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is medical implants: Use PECVD to deposit durable, high-purity biocompatible layers that improve device longevity and minimize tissue rejection.
- If your primary focus is biosensors: Leverage PECVD's ability to create exceptionally uniform films, which is critical for ensuring consistent and reliable sensor performance.
- If your primary focus is novel materials research: Exploit PECVD's low-temperature capability to experiment with coating a wide range of sensitive substrates, from advanced polymers to biological scaffolds.
Ultimately, PECVD is a powerful tool for precisely engineering the critical interface between the synthetic and the biological.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Medical Implants | Enhances biocompatibility and durability for better integration |
| Biosensors | Ensures uniform, reliable film deposition for accurate detection |
| Drug Delivery Systems | Enables precise coating of sensitive materials at low temperatures |
| Cell Culture Surfaces | Tailors surface chemistry to control cell adhesion and growth |
Ready to enhance your biomedical research with tailored PECVD solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities. We help diverse laboratories meet unique experimental requirements for medical devices, biosensors, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab



















