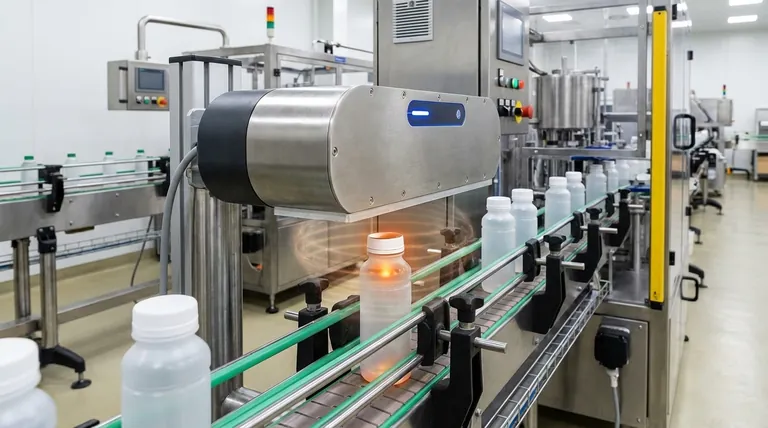
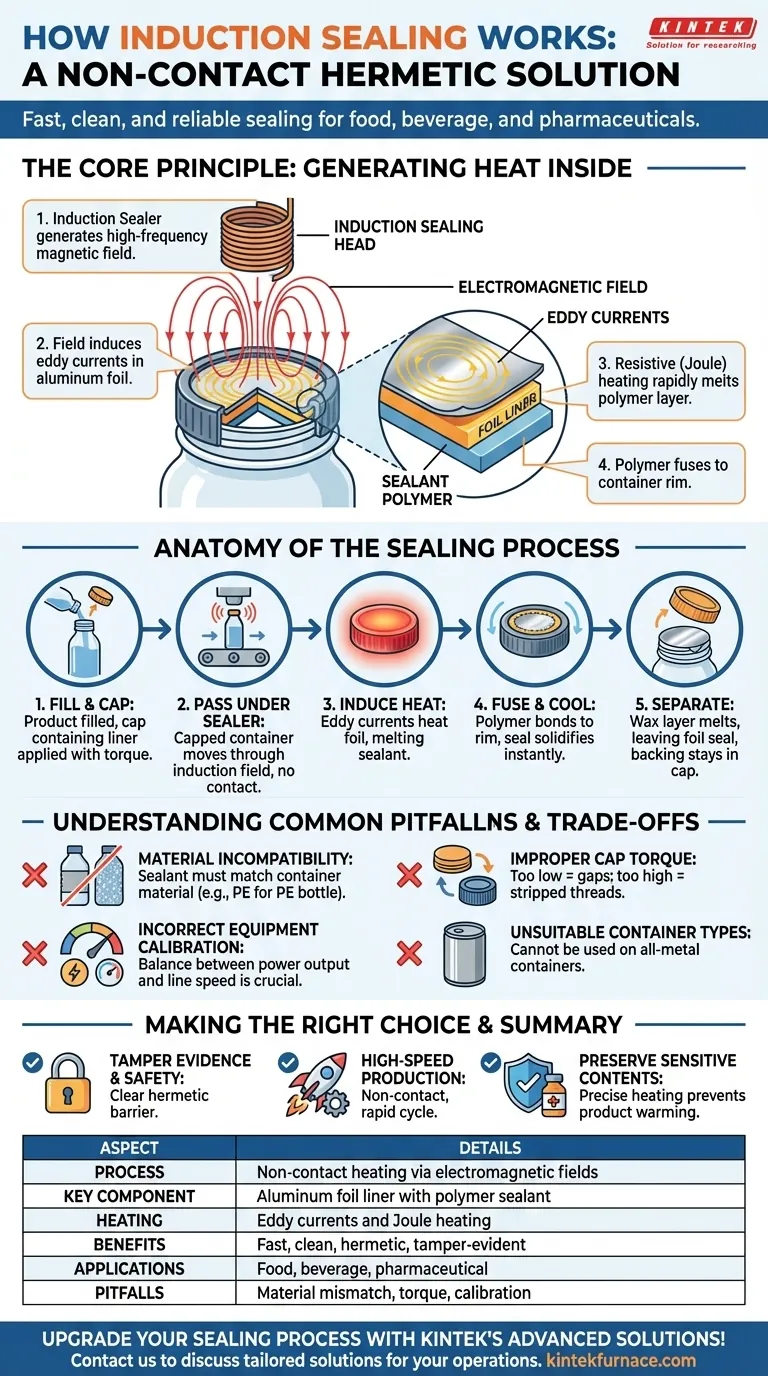
At its core, induction sealing uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic field to heat a foil liner inside a container's cap. This process generates intense heat directly and only within the foil, causing a specialized polymer layer on the liner to melt and fuse to the lip of the container. The result is a fast, clean, and reliable hermetic seal without directly applying heat to the container or its contents.
The critical insight is that induction sealing is a non-contact process. It generates heat inside the cap from a distance, making it exceptionally fast, clean, and precise, which is why it is the gold standard for protecting products in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.

The Core Principle: How Induction Generates Heat
Induction sealing is a clever application of fundamental physics. It's not about convection or conduction from an external heat source; it's about generating heat from within the material itself.
The Electromagnetic Field
An induction sealer's "sealing head" contains a coil that generates a high-frequency alternating magnetic field when power is applied. This field oscillates back and forth millions of times per second.
The Foil Liner's Role
The seal itself is a multi-layered disc, or "liner," that sits inside the cap. A critical layer of this liner is aluminum foil, which is an excellent electrical conductor.
Generating Eddy Currents
When the capped container passes through the electromagnetic field, the field induces powerful electrical currents within the aluminum foil layer. These circulating currents are known as eddy currents.
Resistive Heating
As these eddy currents swirl through the foil, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy into heat—a principle known as Joule heating—causing the foil's temperature to rise dramatically in just a few seconds.
Activating the Sealant Layer
The final layer of the liner, facing the container, is a heat-seal polymer. The intense heat from the foil melts this polymer layer, causing it to flow and fuse onto the rim of the container. As it cools, it creates a strong, permanent, and airtight bond.
Anatomy of the Sealing Process
The elegance of induction sealing lies in its integration into a high-speed packaging line. The process is seamless for the operator.
The Cap and Liner System
Typically, container manufacturers receive their caps with the induction liners already inserted. The liner is held in place by friction or a light wax bond.
The Step-by-Step Sealing Cycle
- Fill and Cap: The container is filled with the product, and the cap containing the induction liner is screwed on with proper torque.
- Pass Under the Sealer: The capped container moves along a conveyor belt and passes under the induction sealing head. No physical contact occurs.
- Induce Heat: For a brief moment, the electromagnetic field is active, inducing eddy currents and heating the foil liner.
- Fuse and Cool: The heat melts the sealant polymer, which bonds to the container rim. The container moves past the sealer and the seal cools and solidifies almost instantly.
- Separate: The heat also melts a wax layer that holds the foil to a pulpboard or foam backing. When the consumer opens the container, the foil seal remains on the container, while the backing stays inside the cap to enable resealing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, induction sealing requires proper setup and compatible materials to function correctly. Ignoring these details is the most common source of failure.
Material Incompatibility
The sealant polymer on the liner must be compatible with the container material. A liner designed for a polyethylene (PE) bottle will not create a strong bond with a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle. This is the most critical matching requirement.
Improper Cap Torque
The cap must be screwed on tight enough to ensure the liner sits flat and firm against the container rim. If the torque is too low, gaps will lead to a weak or non-existent seal. If it's too high, you can strip the threads and compromise the entire closure.
Incorrect Equipment Calibration
The system requires a balance between the power output of the sealer and the speed of the conveyor line. Too much power or too slow a speed can overheat and burn the liner, while too little power or too fast a speed will result in an incomplete, weak seal.
Unsuitable Container Types
Induction sealing is designed for plastic or glass containers with non-metallic caps. It cannot be used on containers made entirely of metal, as the metal body would interfere with and absorb the electromagnetic field, preventing the liner from heating properly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating induction sealing depends on balancing your specific priorities for product integrity, safety, and production efficiency.
- If your primary focus is tamper evidence and safety: Induction sealing is the definitive choice, providing a clear, hermetic barrier that must be physically broken to access the product.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, automated production: The non-contact, rapid heating cycle makes induction sealing perfectly suited for high-volume manufacturing lines with minimal maintenance.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive contents: Induction's precise heating of only the foil—without warming the product—is ideal for heat-sensitive pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and foods.
Ultimately, induction sealing provides a superior and robust method for ensuring your product's integrity from the factory to the end user.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Non-contact heating via electromagnetic fields |
| Key Component | Aluminum foil liner with polymer sealant |
| Heating Mechanism | Eddy currents and Joule heating in the foil |
| Benefits | Fast, clean, hermetic seals, tamper evidence |
| Applications | Food, beverage, pharmaceutical industries |
| Common Pitfalls | Material incompatibility, improper torque, calibration issues |
Upgrade Your Sealing Process with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions!
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, food, or other industries needing reliable sealing or thermal processing, we can help enhance your efficiency and product integrity.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Stainless Steel KF ISO Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- Why is a segmented PID control system necessary for lithium battery vacuum drying? Ensure Precision & Safety
- What are the advantages of electric current-assisted TLP bonding? Maximize Efficiency for Inconel 718 Joining
- What are the stages of a vacuum furnace pumping system and how do they function? Learn the Sequential Process for High-Vacuum Efficiency
- Why is sealing critical in vacuum or protective atmosphere furnaces? Ensure Quality and Consistency in High-Temp Processing
- What materials are used for the heating elements in a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs



















