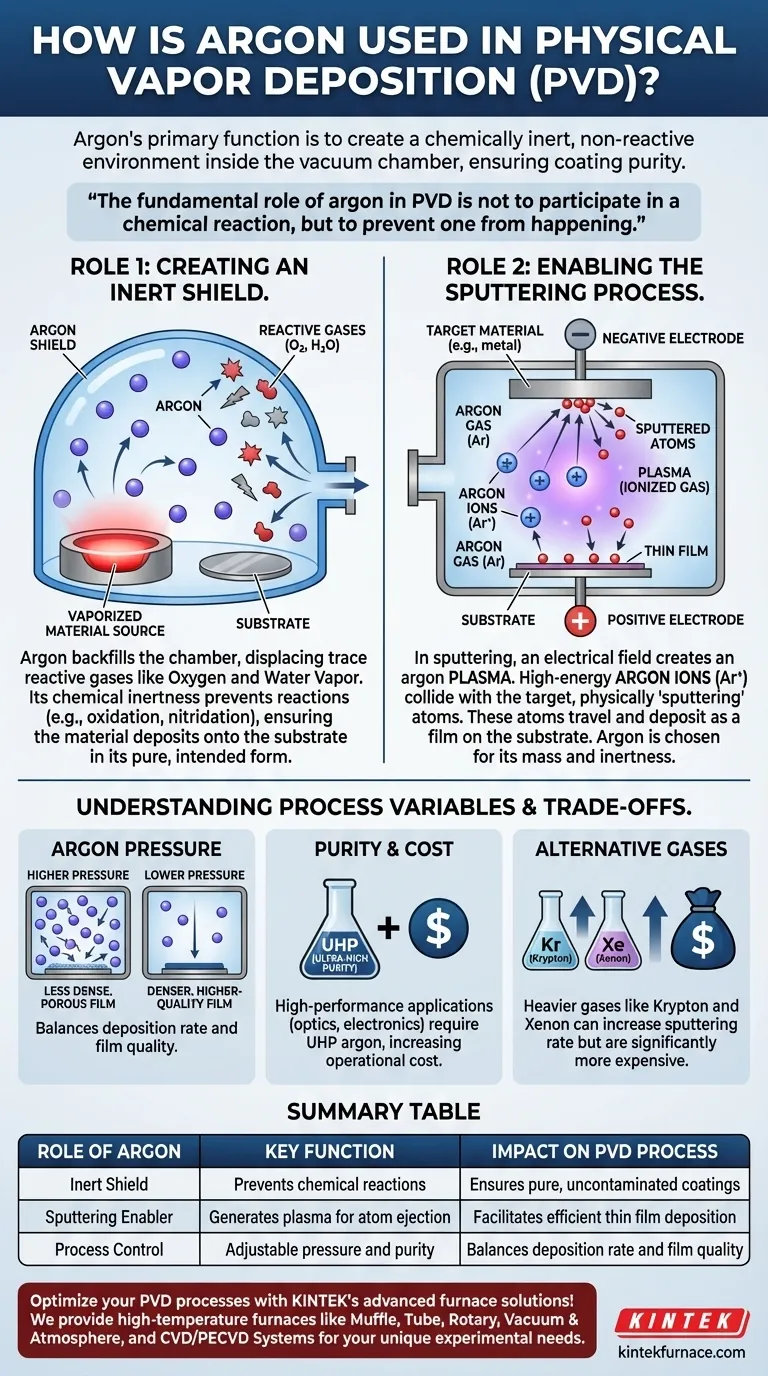
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), argon's primary function is to create a chemically inert, non-reactive environment inside the vacuum chamber. This prevents the hot, vaporized coating material from reacting with residual gases like oxygen or water vapor. By shielding the material during its transit from the source to the substrate, argon ensures the final coating is pure and free from contamination.
The fundamental role of argon in PVD is not to participate in a chemical reaction, but to prevent one from happening. It acts as an inert shield, protecting the purity of the coating material and, in many cases, serving as the physical means to generate the material vapor itself.

The Dual Roles of Argon in PVD
Argon is the workhorse gas of PVD for two distinct but equally critical reasons. It serves as both a protective blanket and, in the most common PVD method, a physical projectile.
Role 1: Creating an Inert Shield
The PVD process occurs in a high vacuum at elevated temperatures, conditions that make materials highly susceptible to chemical reactions.
Even trace amounts of reactive gases can have a significant negative impact. For instance, oxygen can form oxides and nitrogen can form nitrides on the vaporized material, altering its intended properties.
By backfilling the vacuum chamber with high-purity argon, these residual reactive gases are displaced. Argon's chemical inertness means it will not react with the coating material, ensuring it deposits onto the substrate in its pure, intended form.
Role 2: Enabling the Sputtering Process
Beyond providing a protective atmosphere, argon is the key enabler of sputter deposition, a primary type of PVD.
In sputtering, an electrical field is applied within the argon-filled chamber, which strips electrons from the argon atoms and creates a plasma—a glowing, ionized gas.
These newly formed, positively charged argon ions are then accelerated by a strong electric field, causing them to collide with the source material, known as the "target."
The force of these collisions is strong enough to physically knock atoms off the target, "sputtering" them into the vapor phase. These sputtered atoms then travel through the chamber and deposit as a thin film on the substrate. Argon is used because it has sufficient mass to eject target atoms effectively but remains chemically inert throughout the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Variables
While argon is essential, its use involves critical process-control decisions that directly impact the final product. Mismanaging these variables can lead to poor quality coatings.
The Impact of Argon Pressure
The pressure of the argon gas inside the chamber is a key control parameter. It represents a trade-off between deposition rate and film quality.
A higher argon pressure increases the chance of collisions between the sputtered atoms and argon gas. This can scatter the coating material, reducing its energy and potentially leading to a less dense, more porous film.
A lower argon pressure allows the sputtered atoms to travel more directly to the substrate with higher energy. This generally results in a denser, higher-quality film but can sometimes lead to lower deposition rates or instability in the plasma.
Purity and Cost
For high-performance applications like semiconductor manufacturing or optical lenses, the purity of the argon is non-negotiable. Even minuscule impurities in the gas supply can introduce defects into the coating.
This requirement for ultra-high purity (UHP) argon can represent a significant operational cost, creating a balance between process requirements and budget.
Alternative Inert Gases
While argon is the most common choice due to its balance of performance and cost, other noble gases like krypton (Kr) and xenon (Xe) are sometimes used.
These heavier gases can increase the sputtering rate (sputter yield) for certain materials. However, they are substantially more expensive than argon, limiting their use to specialized applications where the increased efficiency justifies the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the argon environment is fundamental to achieving your desired coating properties. Your specific goal will determine which aspects of its use you need to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is high-purity coatings (e.g., optics, electronics): The inertness and purity of the argon gas are its most critical features to prevent chemical contamination.
- If your primary focus is deposition speed (e.g., decorative or wear coatings): The argon pressure becomes a key variable to optimize, balancing deposition rate against the desired film density and adhesion.
- If your primary focus is sputtering a difficult material: Consider that heavier inert gases like krypton can be used to increase sputter yield, but this comes at a significant cost increase over argon.
Ultimately, mastering the use of argon is fundamental to controlling the quality, consistency, and performance of any PVD coating.
Summary Table:
| Role of Argon | Key Function | Impact on PVD Process |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Shield | Prevents chemical reactions | Ensures pure, uncontaminated coatings |
| Sputtering Enabler | Generates plasma for atom ejection | Facilitates efficient thin film deposition |
| Process Control | Adjustable pressure and purity | Balances deposition rate and film quality |
Optimize your PVD processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance coating purity and efficiency in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















