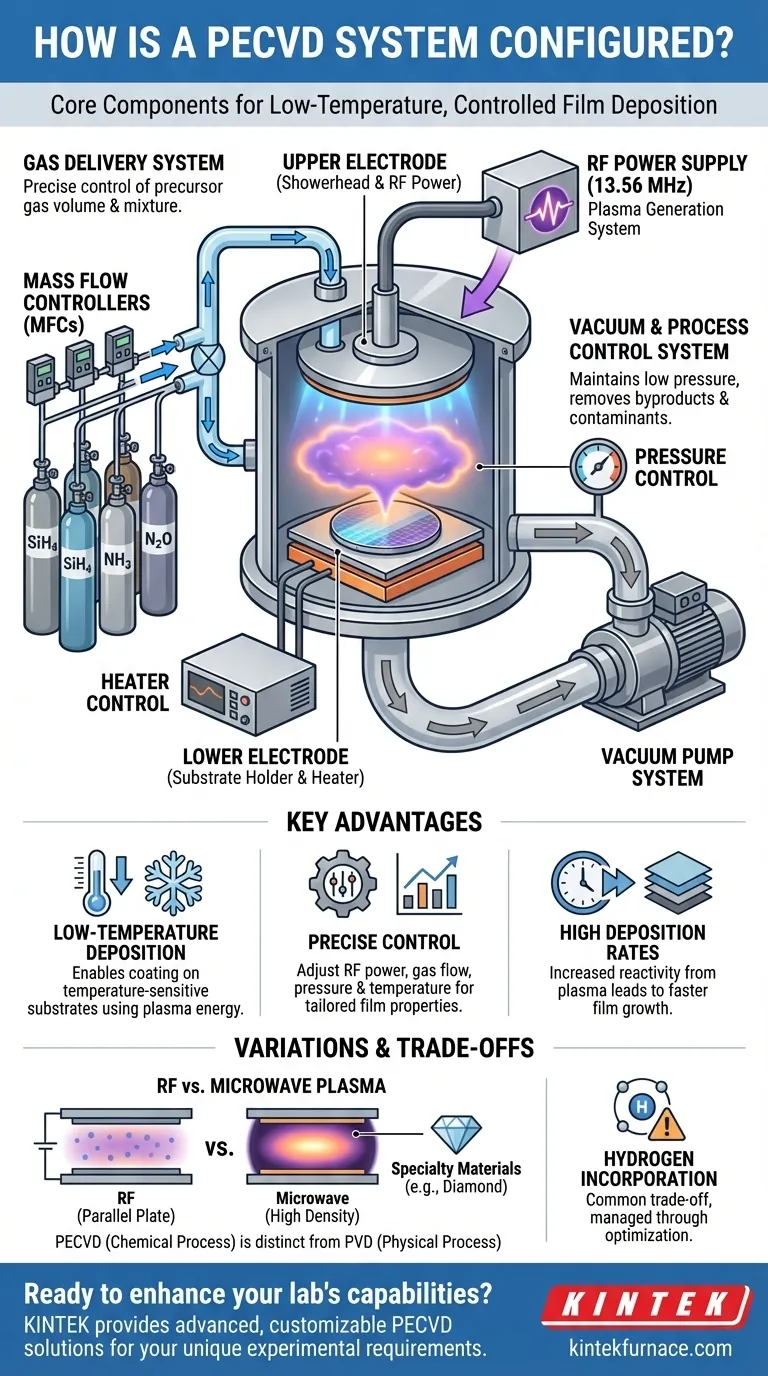
At its core, a Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) system is configured with four primary modules working in concert: a vacuum chamber containing electrodes, a gas delivery system, a radio frequency (RF) or microwave power source, and a vacuum pump system. The power source energizes precursor gases into a plasma, causing a chemical reaction and film deposition on a substrate at temperatures far lower than traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The fundamental purpose of the PECVD configuration is not merely to deposit material, but to precisely control a low-temperature, gas-phase chemical reaction. Each component is designed to manipulate the plasma environment to dictate the final properties of the deposited film.

The Core Components of a PECVD System
Understanding the role of each component reveals how the system achieves its unique capabilities. The configuration is a synergistic design focused on control and uniformity.
The Reaction Chamber
The process occurs within a high-vacuum chamber, often a metal design to minimize contamination. Inside, two parallel electrodes face each other.
The upper electrode is typically powered to generate the plasma and often incorporates a "showerhead" design. This is a critical feature that distributes the precursor gases evenly across the chamber, ensuring the deposited film has uniform thickness and properties.
The lower electrode holds the substrate (the wafer or sample) and is frequently heated. This provides thermal energy to the surface to promote film adhesion and influence its final structure.
The Gas Delivery System
This system provides the chemical building blocks for the film. It typically consists of a multi-line gas pod, with each line dedicated to a specific precursor or reactant gas.
Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) are used on each line to precisely regulate the volume of gas entering the chamber. This granular control over the gas mixture is essential for depositing complex materials like silicon oxynitride or for tuning film properties like refractive index and stress.
The Plasma Generation System
This is the engine of the PECVD process. An RF power supply (often at 13.56 MHz) is connected to the upper electrode, creating an oscillating electromagnetic field.
This field energizes the low-pressure gas in the chamber, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a plasma—a reactive soup of ions, electrons, radicals, and neutral species. These highly reactive radicals are the primary agents of film deposition.
The Vacuum and Process Control System
A vacuum pump system serves two purposes: it first removes air and contaminants from the chamber to create a clean, controlled environment. During the process, it continuously removes reaction byproducts.
This system, along with the MFCs, also maintains the chamber at a specific low pressure (e.g., 6-500 Torr). The pressure level is a critical parameter that directly impacts plasma density and, consequently, the deposition rate and quality of the film.
How the Configuration Enables Key Advantages
The specific arrangement of PECVD components directly translates into its primary benefits, setting it apart from other deposition techniques like PVD or standard CVD.
Low-Temperature Deposition
The use of RF energy to create a reactive plasma is the key to low-temperature processing. The system breaks down precursor gases using electromagnetic energy rather than purely thermal energy. This allows for the deposition of high-quality films on temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or fully processed semiconductor devices.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
The sophisticated control modules are central to PECVD's versatility. By adjusting RF power, gas flow rates, chamber pressure, and substrate temperature, an operator can directly influence the film's stoichiometry, density, stress, and electrical characteristics. Modern systems with parameter-ramping software allow these variables to be changed dynamically during deposition.
High Deposition Rates
The plasma significantly increases the reactivity of the precursor gases. This leads to deposition rates that are often much faster than those achievable with low-pressure CVD (LPCVD) at similar temperatures, improving throughput for manufacturing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, the PECVD configuration is not universal. Its design comes with specific trade-offs and variations tailored for different materials.
PECVD vs. PVD
A PECVD system is fundamentally different from Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). PECVD is a chemical process where new material is synthesized from precursor gases. PVD is a physical process that transports material from a solid target to the substrate via sputtering or evaporation. This dictates the entirely different hardware for the power source, gas requirements, and chamber internals.
Microwave vs. RF Plasma
While RF-powered parallel-plate reactors are common for depositing dielectric films like silicon dioxide and silicon nitride, some applications demand a different approach. Microwave PECVD systems use microwave energy to generate a much denser plasma, which is necessary for growing highly crystalline materials like synthetic diamond, carbon nanotubes, and nanowires. These are specialized, not general-purpose, configurations.
Inherent Chemical Byproducts
Because PECVD relies on chemical precursors (e.g., silane, SiH₄, for silicon films), a common trade-off is the incorporation of hydrogen into the deposited film. This can be undesirable for certain electronic applications and must be managed through process optimization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal PECVD configuration depends entirely on the material you intend to deposit and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is depositing common dielectric films (SiO₂, SiN): A standard parallel-plate, RF-powered PECVD system is the industry-standard tool for this task.
- If your primary focus is growing specialty crystalline materials (diamond, CNTs): You will require a specialized microwave plasma (MW-PECVD) system designed for higher plasma densities and temperatures.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize a system with a wide operational range for pressure and power, multiple MFC-controlled gas lines, and advanced process control software.
Ultimately, the configuration of a PECVD system is engineered to give you precise control over plasma chemistry for low-temperature film growth.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Reaction Chamber | Houses electrodes and substrate for uniform film deposition |
| Gas Delivery System | Provides and controls precursor gases via mass flow controllers |
| Plasma Generation System | Energizes gases with RF or microwave power to create plasma |
| Vacuum and Control System | Maintains low pressure, removes byproducts, and regulates process parameters |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tailored PECVD system? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including PECVD systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for low-temperature, high-quality film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition



















