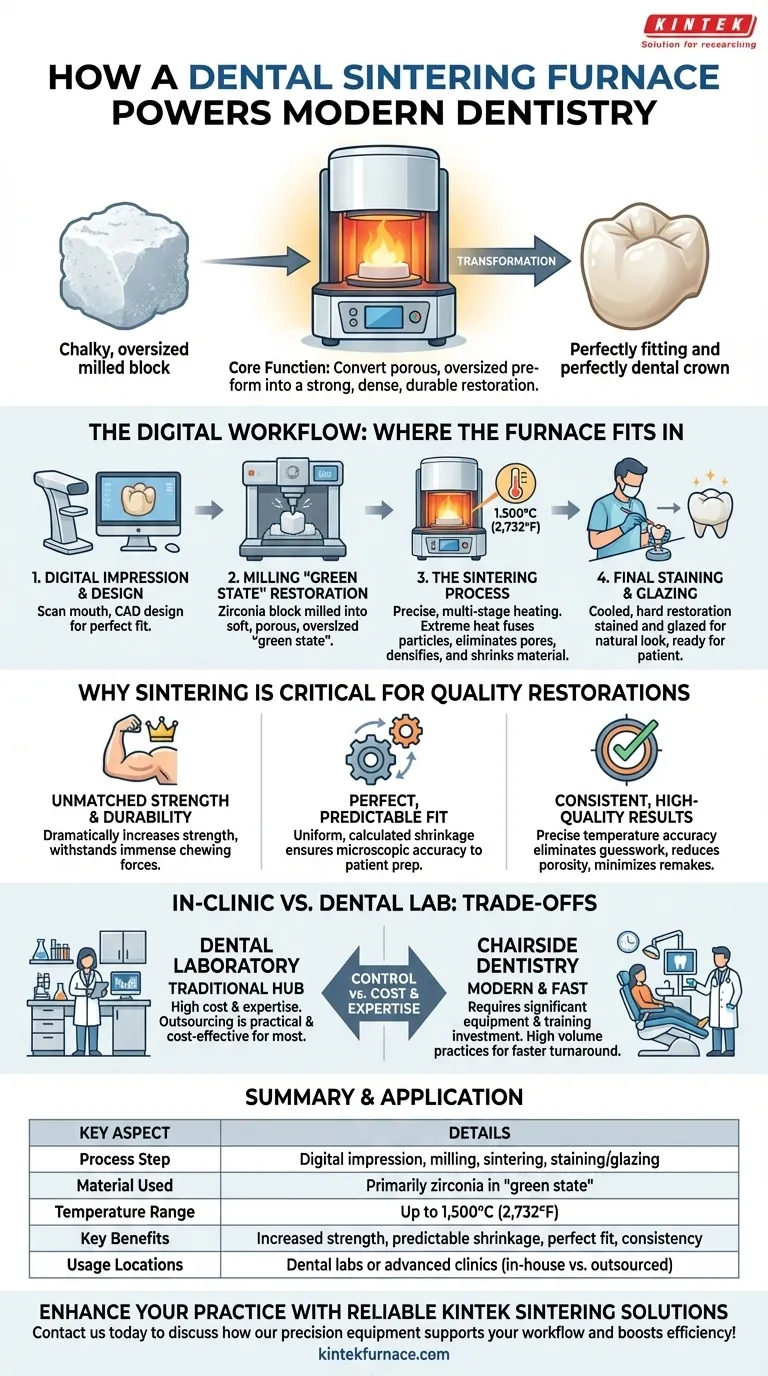
In modern dentistry, a ceramic block sintering furnace is not used directly on a patient, but rather in a dental laboratory or advanced clinic to fabricate the final restoration. After a digital impression is taken and the restoration is milled from a block of ceramic material like zirconia, the furnace uses precisely controlled high temperatures to transform this chalky, fragile piece into an incredibly strong, dense, and perfectly fitting final crown, bridge, or implant.
The core function of a sintering furnace is to convert a porous, oversized ceramic pre-form into a solid, durable, and dimensionally accurate dental restoration. It is the critical step that provides the necessary strength and longevity for modern ceramic dental work.

The Digital Workflow: Where the Furnace Fits In
The sintering furnace is a key component in the digital dentistry workflow. It represents the crucial transition from a digitally designed object to a physically viable medical device.
Step 1: Digital Impression and Design
The process begins with a digital scan of the patient's mouth. This data is used in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to design a perfectly fitting restoration.
Step 2: Milling the "Green State" Restoration
A block of ceramic material, most commonly zirconia, is placed in a milling machine. The machine carves the restoration based on the digital design.
This initial, milled piece is known as being in its "green state" or "chalky state." It is soft, porous, and intentionally oversized to account for the shrinkage that will occur during sintering.
Step 3: The Sintering Process
The green-state restoration is placed into the furnace. The furnace then executes a precise, multi-stage heating program, often lasting several hours.
During this cycle, the temperature is raised to extreme levels (up to 1,500°C or 2,732°F). This intense heat causes the ceramic particles to fuse together, eliminating the pores and densifying the material.
Step 4: Final Staining and Glazing
After cooling, the now fully-sintered, incredibly hard restoration is stained and glazed to match the patient's natural tooth color. It may undergo a final, shorter firing in the furnace to set the glaze, giving it a natural, glossy appearance before being permanently secured in the patient's mouth.
Why Sintering is Critical for Quality Restorations
The sintering process is not just about hardening the material; it is about guaranteeing the clinical success of the restoration through predictable and controlled transformation.
Achieving Unmatched Strength and Durability
The primary benefit is a dramatic increase in strength. Sintering transforms weak, chalky zirconia into one of the strongest and most durable materials used in dentistry, capable of withstanding immense chewing forces.
Ensuring a Perfect, Predictable Fit
The controlled heating and cooling cycles ensure that the restoration shrinks uniformly and predictably. This shrinkage is calculated in the initial design phase, so the final, sintered piece fits the patient's preparation with microscopic accuracy.
Producing Consistent, High-Quality Results
Modern furnaces provide unparalleled temperature accuracy. This precision eliminates guesswork, reduces porosity, and prevents internal stresses, resulting in consistently strong, reliable restorations and minimizing the need for remakes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: In-Clinic vs. Dental Lab
While the technology is essential, where it is located involves a significant trade-off between control and cost.
The Dental Laboratory: The Traditional Hub
Historically, sintering furnaces are found in dedicated dental laboratories. The high cost of the equipment and the technical expertise required to operate and maintain it made outsourcing the most practical model for dental clinics.
The Rise of "Chairside" Dentistry
Some modern, high-volume dental clinics have invested in in-house milling and sintering systems. This "chairside" approach offers faster turnaround times, sometimes allowing for same-day crowns.
The Expertise and Cost Factor
The primary barrier to in-clinic adoption is the significant investment in equipment and training. The furnace requires specific programming for different materials, and improper use can ruin the restoration. For most practices, leveraging the expertise of a specialized lab remains the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
How to Apply This to Your Practice
Your decision to use in-house or outsourced sintering depends entirely on your clinical goals, patient volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum control and the fastest possible turnaround: Investing in a complete chairside system with a sintering furnace may be a justifiable path for a high-volume practice.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and consistent, high-quality results without a large capital outlay: Partnering with a trusted dental laboratory remains the industry standard and the most practical approach for the vast majority of clinics.
Ultimately, the dental sintering furnace is the unsung hero that enables the creation of strong, aesthetic, and perfectly fitting ceramic restorations that define modern dentistry.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process Step | Digital impression, milling, sintering, staining/glazing |
| Material Used | Primarily zirconia in 'green state' |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1,500°C (2,732°F) |
| Key Benefits | Increased strength, predictable shrinkage, perfect fit, consistency |
| Usage Locations | Dental labs or advanced clinics (in-house vs. outsourced) |
Ready to enhance your dental practice with reliable sintering solutions? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnaces tailored for dental laboratories and clinics. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Achieve consistent, high-quality restorations with our precision equipment—contact us today to discuss how we can support your workflow and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations



















