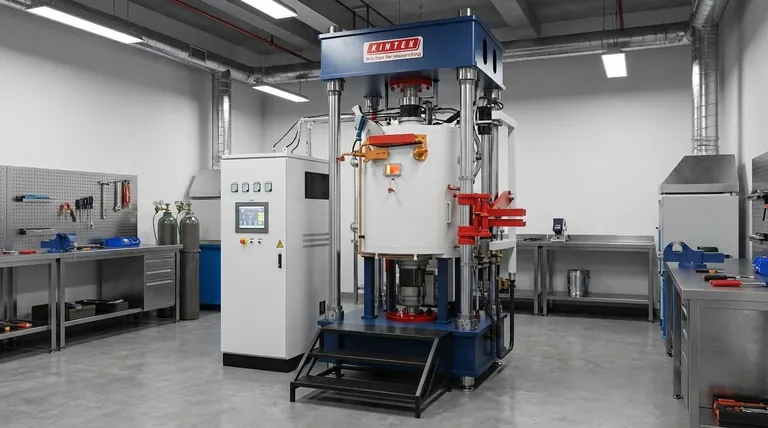
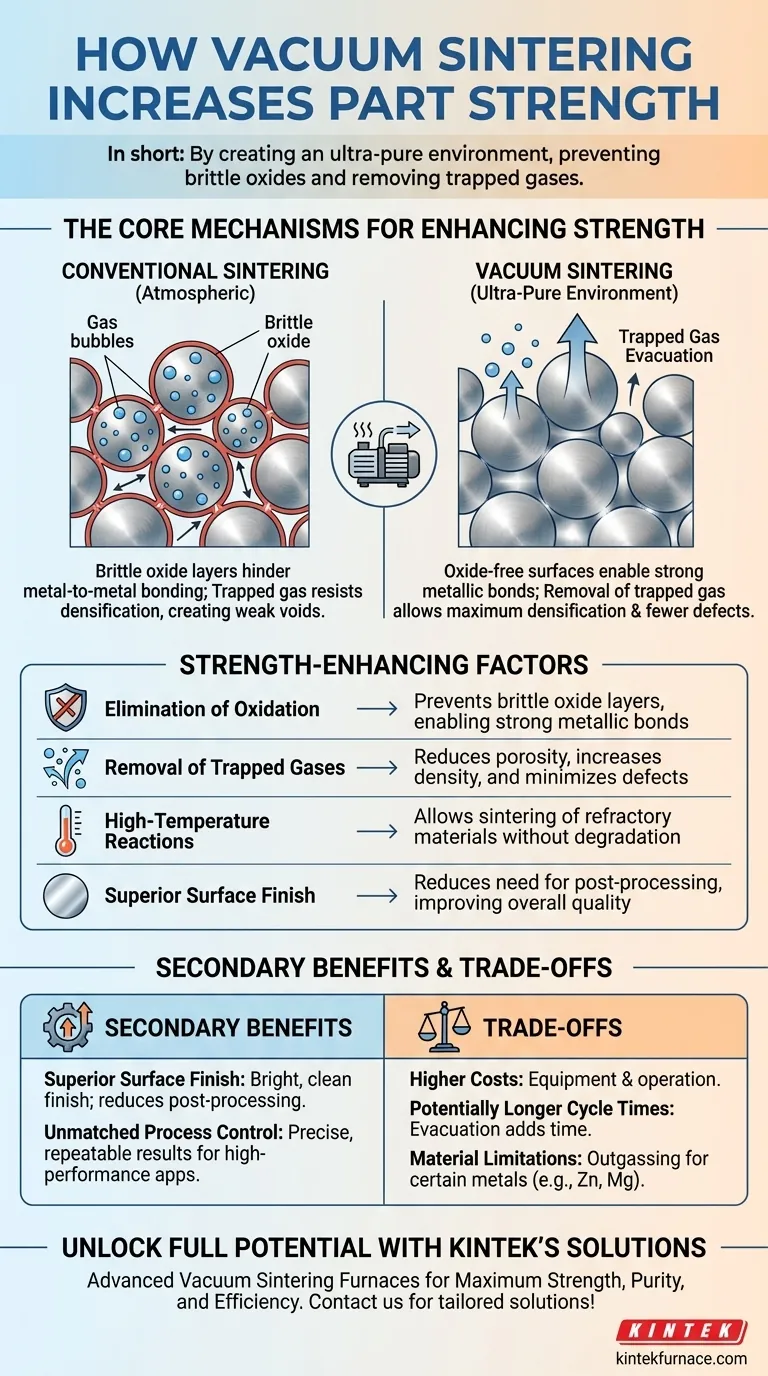
In short, vacuum sintering increases the strength of a part by creating an ultra-pure environment. This environment achieves two critical goals: it prevents the formation of brittle oxides on powder particles and it removes trapped gases from within the part, allowing the material to achieve a significantly higher final density.
The core value of vacuum sintering is not just the heat, but the meticulous control over the atmosphere. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, you enable metal particles to form the strongest possible metallic bonds, creating a final part that is denser, purer, and fundamentally stronger than one sintered in a conventional atmosphere.

The Core Mechanisms for Enhancing Strength
To understand why a vacuum environment is so effective, we need to look at what happens at the microscopic level between individual powder particles during the sintering process.
Eliminating Oxidation
Every metal powder particle, unless handled in a perfectly inert environment, has a microscopic layer of oxide on its surface. During conventional sintering, these oxide layers act as a barrier.
These brittle oxide films prevent the pure metal atoms from diffusing between particles and forming strong, ductile metallic bonds. The resulting connections are weak points within the material.
Vacuum sintering actively removes oxygen and other reactive gases from the furnace. This allows the heat to break down any pre-existing surface oxides and ensures no new ones can form, enabling clean, direct metal-to-metal bonding and maximizing the strength of the final part.
Enhancing Densification by Removing Trapped Gases
The spaces between powder particles, known as pores, are initially filled with air. As the part heats up and begins to shrink, this trapped gas gets compressed.
This compressed gas creates internal pressure within the pores, actively resisting the consolidation of the part. This resistance prevents pores from fully closing, leaving behind voids (porosity) that act as stress concentrators and reduce the material's overall strength and density.
A vacuum furnace removes the air from these pores before the densification stage begins. Without trapped gas to fight against, the pores can collapse much more completely, resulting in a part with higher density and significantly fewer internal defects.
Promoting High-Temperature Reactions
Certain advanced materials, such as refractory metals (tungsten, molybdenum) or specific ceramics, require extremely high sintering temperatures.
Processing these materials in a conventional atmosphere would lead to rapid, catastrophic oxidation. A vacuum or controlled inert atmosphere is the only way to reach the required temperatures without degrading or destroying the material, unlocking their superior performance characteristics.
Beyond Strength: Secondary Benefits of Vacuum
While enhanced strength is a primary driver, the controlled environment of a vacuum furnace delivers several other critical advantages that contribute to a higher-quality final product.
Superior Surface Finish
Because vacuum sintering prevents surface oxidation, parts emerge from the furnace with a bright, clean, and smooth finish. This often reduces or completely eliminates the need for secondary finishing operations like sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or polishing, saving time and cost.
Unmatched Process Control and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces offer precise, programmable control over the entire cycle. This includes the heating rate, holding temperature, vacuum level, and cooling rate (often via rapid gas quenching).
This high degree of control ensures exceptional consistency from batch to batch, a critical requirement for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. As an objective advisor, it is crucial to recognize the limitations of vacuum sintering.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are a significantly larger capital investment than conventional atmospheric furnaces. They also have higher operational costs due to the energy required for the vacuum pumps and the complexity of their maintenance.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The process of evacuating the furnace chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to the overall production cycle. For high-volume, low-cost parts, this can impact throughput compared to continuous atmospheric sintering.
Material Limitations (Outgassing)
Certain metals with a high vapor pressure, such as zinc, magnesium, lead, or cadmium, are not suitable for vacuum sintering. The combination of high heat and low pressure can cause these elements to vaporize out of the alloy, altering the material's composition and properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between vacuum and conventional sintering depends entirely on your material, performance requirements, and economic goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and purity: Use vacuum sintering for reactive materials (like titanium), refractory metals, or any application where achieving the highest possible strength and density is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is complex geometries and net-shape parts: Use vacuum sintering when you need a superior surface finish directly from the furnace to minimize costly post-processing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-sensitive production: Conventional atmospheric sintering is often more economical for non-reactive materials like common iron and steel alloys where good, but not ultimate, properties are sufficient.
By understanding these fundamental principles, you can confidently select the sintering process that best aligns with your specific engineering and business goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Strength |
|---|---|
| Elimination of Oxidation | Prevents brittle oxide layers, enabling strong metallic bonds |
| Removal of Trapped Gases | Reduces porosity, increases density, and minimizes defects |
| High-Temperature Reactions | Allows sintering of refractory materials without degradation |
| Superior Surface Finish | Reduces need for post-processing, improving overall quality |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Sintering Solutions
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive metals, refractory materials, or need superior surface finishes, our vacuum sintering technologies can help you achieve maximum strength, purity, and efficiency.
Ready to enhance your sintering process? Contact us today for a tailored solution that drives your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















