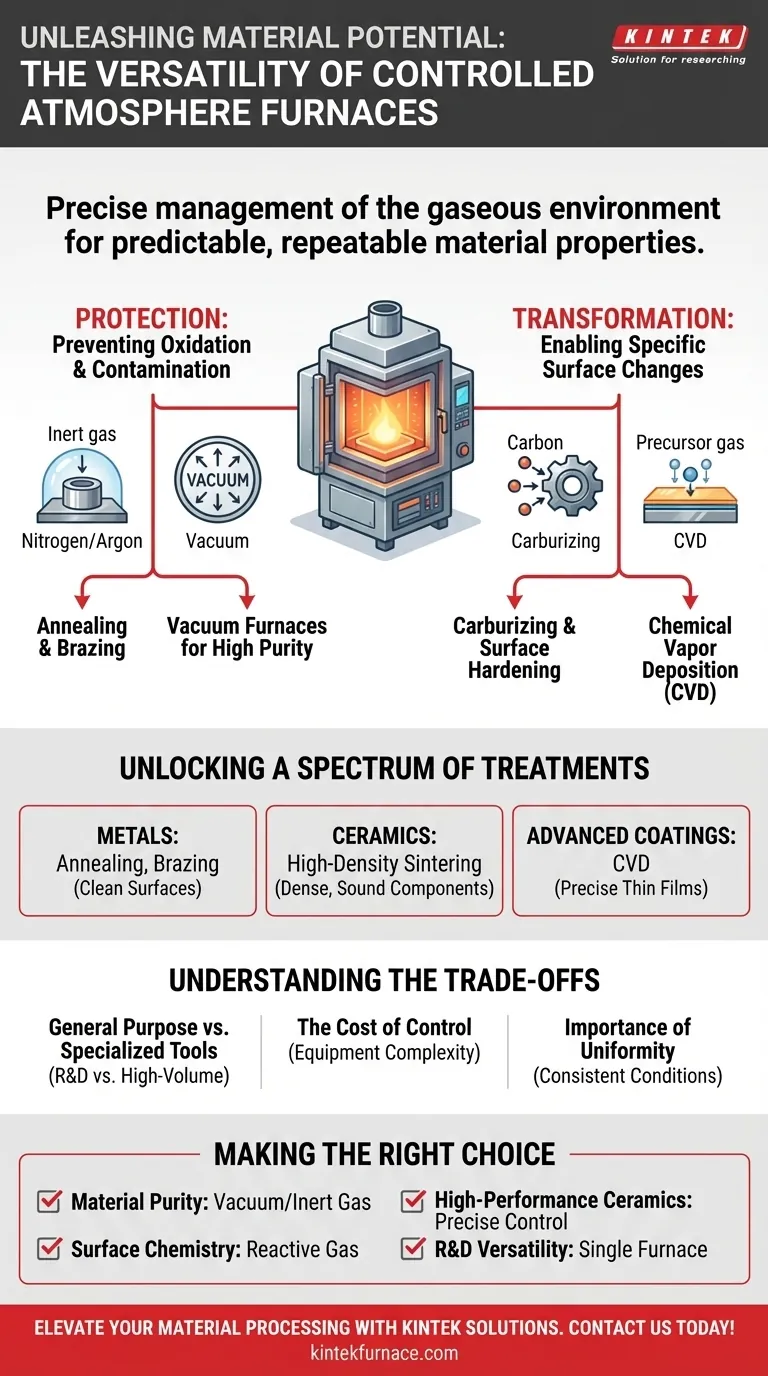
In short, the versatility of a controlled atmosphere furnace comes from its ability to precisely manage the gaseous environment during heat treatment. This control allows a single furnace to execute a wide range of processes—from annealing and brazing to carburizing and sintering—by either protecting the material from unwanted reactions or intentionally causing specific chemical changes to its surface.
The true benefit of this versatility is not just the ability to perform many tasks, but the power to achieve specific, predictable, and repeatable material properties. By mastering the furnace atmosphere, you master the final characteristics of your product.

The Core Principle: Managing Chemical Reactions
A furnace's atmosphere is not a passive element; it is an active ingredient in the heat treatment process. A controlled atmosphere furnace gives you command over this ingredient, allowing you to dictate the chemical interactions that occur at high temperatures.
Protection: Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many materials, especially metals, will readily react with oxygen in the air at high temperatures, forming oxides on the surface. This can compromise the material's integrity, appearance, and performance.
A controlled atmosphere furnace prevents this by replacing the air with a specific gas. An inert gas like nitrogen or argon creates a protective blanket, shielding the material from unwanted reactions.
For the highest level of protection, a vacuum furnace is used. By removing nearly all atmospheric gases, it creates an ultra-clean environment, which is essential for producing high-purity components free from any contamination.
Transformation: Enabling Specific Surface Changes
Conversely, you can introduce a reactive gas to intentionally alter the material's surface. This is a powerful technique for enhancing specific properties.
The most common example is carburizing, where a carbon-rich atmosphere is used to diffuse carbon atoms into the surface of steel. This creates a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a tougher, more ductile core.
Unlocking a Spectrum of Material Treatments
This dual capability—to protect or to transform—makes the controlled atmosphere furnace a foundational tool across numerous industries and research fields.
For Metals: Annealing and Brazing
Processes like annealing (softening a metal to improve ductility) and brazing (joining two metals with a filler material) require clean surfaces for success. A controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation that would interfere with these processes, ensuring strong, reliable results.
For Ceramics: High-Density Sintering
In the production of advanced ceramics like alumina or silicon carbide, the goal is often to sinter powdered material into a dense, solid object.
The furnace atmosphere is crucial for controlling the sintering process and achieving specific final properties. Precise control prevents unwanted phases from forming and ensures the creation of high-performance, structurally sound ceramic components.
For Advanced Coatings: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Specialized controlled atmosphere furnaces are used for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In this process, precursor gases are introduced into the furnace, where they react and deposit a thin, solid film onto a substrate.
This technique is essential for manufacturing advanced materials, offering precise control over film thickness, uniformity, and composition for applications in electronics and wear-resistant coatings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a controlled atmosphere furnace is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its context is key to leveraging its benefits.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Tools
A highly versatile furnace is excellent for research, development, and multi-process job shops. However, for a single, high-volume process, a furnace optimized specifically for that task (like a dedicated vacuum furnace for medical implants) may offer superior performance or efficiency.
The Cost of Control
The equipment needed to maintain and monitor a specific atmosphere—gas lines, sensors, vacuum pumps—adds complexity and operational cost compared to a simple furnace that operates in ambient air. The benefits of control must justify this investment.
The Importance of Uniformity
Atmosphere control is only effective if it's consistent throughout the processing chamber. Features like rotating furnace tubes or advanced thermal management systems are critical for ensuring every part of the material is exposed to the same conditions, guaranteeing uniform results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of atmosphere depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing any reaction: A vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere is your best tool to eliminate contamination.
- If your primary focus is altering a material's surface chemistry: A reactive atmosphere, as used in carburizing, is necessary to achieve the desired transformation.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance ceramics: Precise atmospheric and thermal control during sintering is critical for achieving high density and specific properties.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The furnace's versatility allows for experimentation across a wide range of materials and processes without needing multiple specialized units.
Ultimately, the versatility of a controlled atmosphere furnace empowers you to move beyond simple heating and actively engineer the final properties of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Application | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Protection from oxidation | Annealing, Brazing | Inert gas or vacuum environment |
| Surface transformation | Carburizing, CVD | Reactive gas control |
| High-density sintering | Ceramics production | Precise atmosphere and thermal management |
| Versatility for R&D | Multi-process labs | Single furnace for diverse treatments |
Ready to elevate your material processing with tailored furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your processes and deliver predictable, repeatable results for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage



















