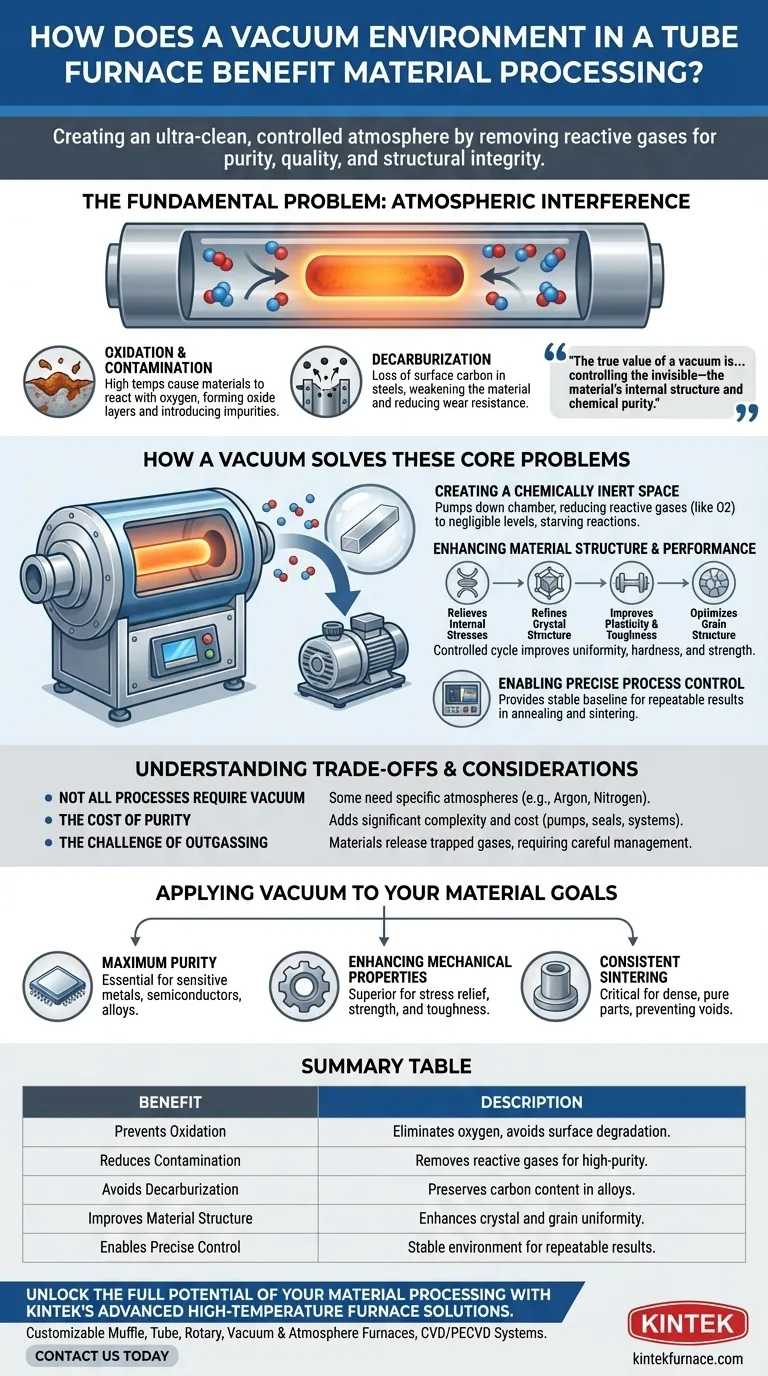
In material processing, a vacuum environment within a tube furnace serves one critical purpose: to create an ultra-clean, controlled atmosphere by removing reactive gases. At the high temperatures required for processes like annealing and sintering, this prevents unwanted chemical reactions such as oxidation and contamination, ensuring the purity, quality, and structural integrity of the final material.
The true value of a vacuum is not just preventing what's visible, like corrosion, but controlling the invisible—the material's internal structure and chemical purity. By eliminating atmospheric interference, you gain precise control over the final properties of the material, from its hardness to its crystal lattice.
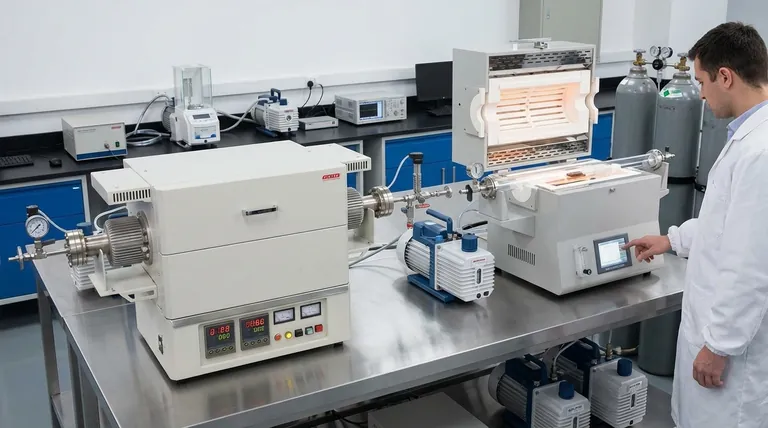

The Fundamental Problem: Atmospheric Interference
At room temperature, the air around us seems relatively harmless. However, when heated to hundreds or thousands of degrees inside a furnace, common gases like oxygen, water vapor, and nitrogen become highly reactive agents that can irreversibly damage a material.
The Threat of Oxidation and Contamination
Oxidation is the most common form of damage. At high temperatures, most materials will readily react with oxygen, forming an oxide layer on their surface. This is not just cosmetic; it alters the material's fundamental properties and introduces impurities.
This process is a form of contamination, where elements from the atmosphere bond with and degrade the sample. This compromises the material's purity, which is critical for high-performance applications in electronics, aerospace, and medical fields.
The Challenge of Decarburization
For steels and other carbon-based alloys, another significant risk is decarburization. This is the loss of carbon from the surface of the metal when heated in the presence of oxygen.
Because carbon is a key alloying element that determines hardness and strength, its loss weakens the material's surface, reducing wear resistance and fatigue life.
How a Vacuum Solves These Core Problems
A vacuum furnace directly counteracts atmospheric interference by physically removing the air and other gases from the processing chamber. This creates a chemically inert space where the material can be treated without fear of unwanted reactions.
Creating a Chemically Inert Space
By pumping down the chamber to a low pressure, the concentration of reactive gases like oxygen is reduced to negligible levels. This effectively starves potential chemical reactions of the "fuel" they need to occur.
The result is a pristine processing environment that preserves the chemical composition and purity of the material throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Enhancing Material Structure and Performance
Beyond just preventing damage, a vacuum environment is crucial for actively improving material properties. During vacuum annealing, for instance, the controlled heating and cooling cycle in a clean environment does several things:
- Relieves internal stresses built up during manufacturing.
- Refines the crystal structure for better uniformity.
- Improves plasticity and toughness, making the material less brittle.
- Optimizes grain structure, which can increase hardness and strength.
Enabling Precise Process Control
A vacuum provides a perfectly stable and predictable baseline. Without the variable of atmospheric gases, engineers gain precise control over the entire heat treatment process.
This consistency is essential for repeatable results in sensitive processes like sintering, where powdered materials are heated to fuse into a solid, dense object. A vacuum ensures the final product is free of internal voids or impurities caused by trapped gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a vacuum environment is not a universal solution. Its application depends on the specific material and the desired outcome.
Not All Processes Require a Vacuum
Some heat treatments intentionally use a specific atmosphere. For example, a process might require a pure argon environment to prevent reactions or a nitrogen-rich atmosphere for nitriding steel. A vacuum is simply one tool for atmospheric control.
The Cost of Purity
Integrating vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems adds significant complexity and cost to a furnace setup. The level of vacuum required also impacts expense—achieving a "high vacuum" is more demanding than a "rough vacuum."
The Challenge of Outgassing
Materials themselves can be a source of contamination. When heated in a vacuum, trapped gases within the sample can be released in a process called outgassing. This can compromise the vacuum level and requires careful management through proper pumping procedures and furnace design.
Applying Vacuum to Your Material Goals
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the specific properties you need to achieve in your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: A vacuum is essential for processing sensitive metals, semiconductors, or alloys where even trace amounts of oxidation would cause failure.
- If your primary focus is enhancing mechanical properties: Vacuum annealing is the superior method for relieving stress and improving the strength and toughness of metals and alloys without surface degradation.
- If your primary focus is consistent sintering: A vacuum environment is critical for creating dense, pure ceramic or metal parts by preventing trapped gases that cause porosity and defects.
Ultimately, using a vacuum gives you definitive control over the processing environment, allowing you to engineer materials to their highest potential.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Eliminates oxygen to avoid surface degradation and impurity formation. |
| Reduces Contamination | Removes reactive gases for high-purity material processing. |
| Avoids Decarburization | Preserves carbon content in alloys to maintain hardness and strength. |
| Improves Material Structure | Enhances crystal and grain structure for better uniformity and toughness. |
| Enables Precise Control | Provides stable environment for repeatable results in annealing and sintering. |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're aiming for maximum purity, enhanced mechanical properties, or consistent sintering, our expertise ensures precise control and superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity
- What is the significance of porcelain furnaces in academic and scientific research? Unlock Innovation with Precise High-Temperature Control



















