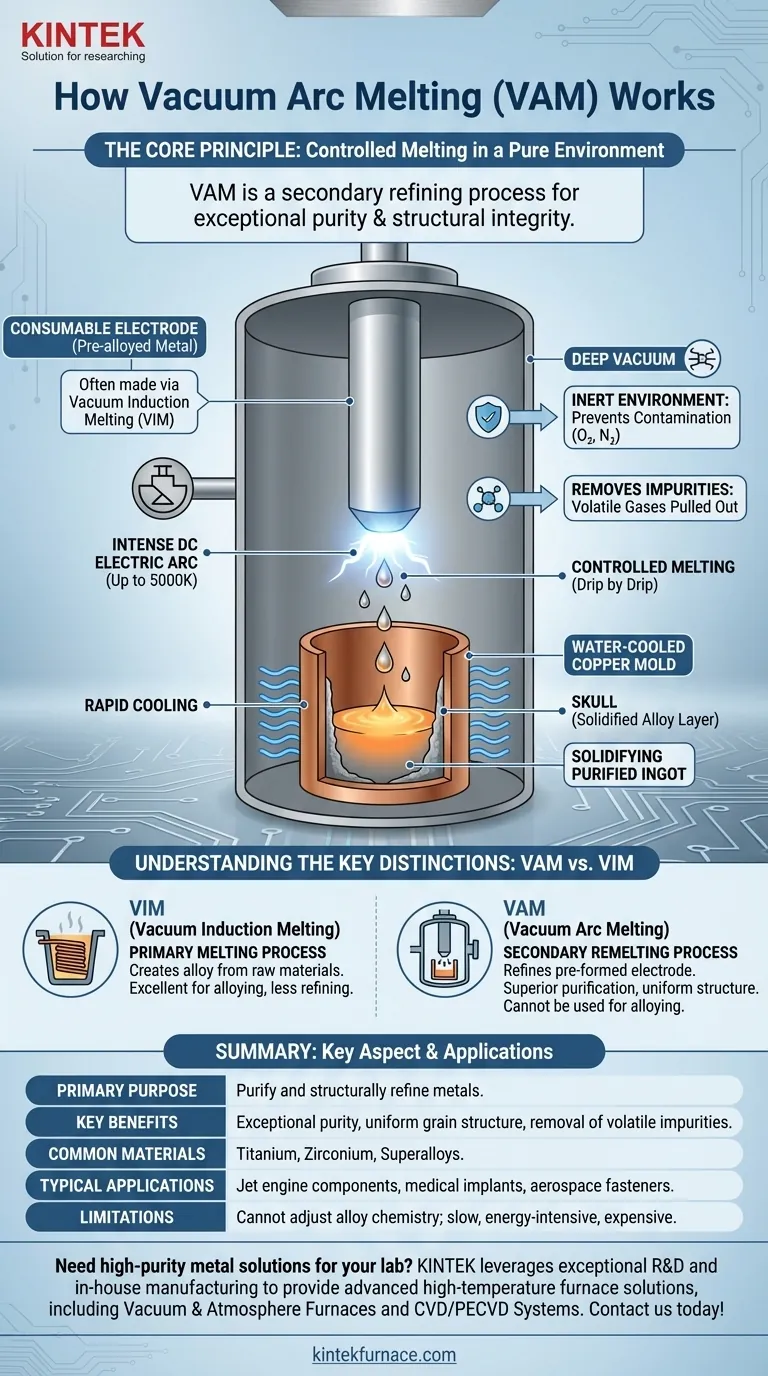
Vacuum Arc Melting is a secondary refining process used to produce metals and alloys with exceptional purity and structural integrity. It functions by striking a high-energy electric arc inside a vacuum chamber, which melts a specially prepared metal cylinder (a consumable electrode) drip by drip into a water-cooled copper mold, forming a highly purified, solidified ingot.
The primary purpose of Vacuum Arc Melting (VAM) is not simply to melt metal, but to purify and structurally refine it. It is a critical secondary step for creating high-performance materials that are free from the contaminants and defects introduced during initial production.
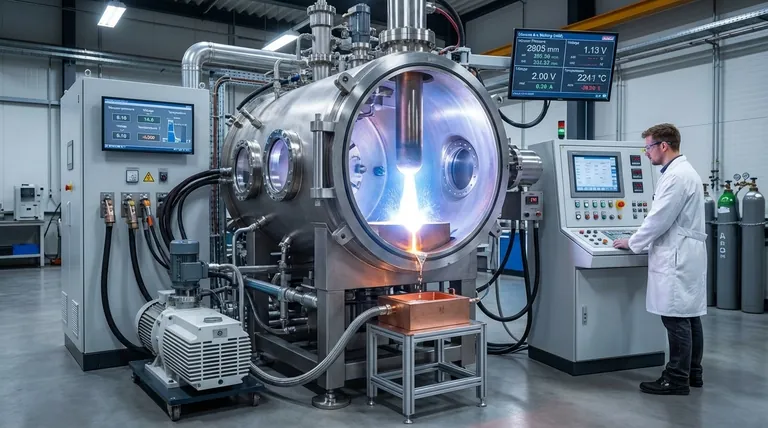

The Core Principle: Controlled Melting in a Pure Environment
The fundamental challenge VAM solves is melting reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, or high-performance superalloys. When melted in open air, these materials readily react with oxygen and nitrogen, which compromises their mechanical properties.
The Consumable Electrode
The process does not start with raw scrap or ore. It begins with a large, cylindrical consumable electrode made of the alloy to be refined.
This electrode is often created in a prior step, typically through Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM), where the initial alloying and primary melting occurs.
The Electric Arc as a Heat Source
An intense DC electric arc is struck between the bottom of the hanging electrode and a small amount of starter material in the base of the mold.
This arc generates extreme, localized temperatures (up to 5000 K), which melts the very tip of the electrode in a controlled manner. As the metal melts, it falls as droplets from the electrode into the pool below.
The Water-Cooled Copper Mold
The droplets collect in a water-cooled copper mold. Because copper has very high thermal conductivity, it rapidly pulls heat away from the molten metal pool.
This rapid cooling causes the metal to solidify from the outside-in. A thin, solid layer of the alloy itself, known as a "skull," forms against the mold wall, acting as a perfect, non-reactive crucible that prevents any contamination from the copper mold.
The Role of the Vacuum
The entire process occurs under a deep vacuum, which serves two critical functions.
First, it provides an inert environment, preventing contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen.
Second, the vacuum actively removes volatile impurities. Gaseous impurities (like hydrogen) and elements with high vapor pressure are literally pulled out of the molten pool, further purifying the metal as it solidifies.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
VAM is often confused with other vacuum furnace processes. Understanding its specific role is crucial for material specification. The most common point of confusion is with Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM).
VAM vs. Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
VIM is a primary melting process. It uses electromagnetic induction to melt raw materials together in a crucible to create an alloy of a specific chemistry. It is excellent for alloying but offers less refining capability.
VAM is a secondary remelting process. It takes an already-formed electrode (often made via VIM) and refines it. It offers minimal ability to adjust alloy chemistry but provides superior purification and a more uniform, defect-free grain structure. Many high-performance alloys are specified as "VIM-VAR" (Vacuum Arc Remelted), indicating this two-step process.
Limitations of VAM
The primary limitation of VAM is that it cannot be used for alloying. The composition of the final ingot is fixed by the composition of the starting electrode.
Furthermore, it is a slow, energy-intensive, and expensive process reserved for materials where ultimate performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
When to Specify Vacuum Arc Melting
Choosing the right melting process depends entirely on your material performance requirements and your starting materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific alloy from raw metals: Your starting point is Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) to achieve the target chemical composition in a clean environment.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and structural integrity: For applications like jet engine turbine disks, medical implants, or critical aerospace fasteners, VAM is the essential second step to refine a pre-alloyed electrode.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible material quality: Specify a dual VIM-VAR process. This ensures the alloy chemistry is correct (from VIM) and that the final product is exceptionally pure and structurally sound (from VAM).
By understanding VAM as a specialized refining tool, you can accurately specify the processing needed to meet your material's most demanding performance targets.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Secondary refining via electric arc melting in vacuum |
| Primary Purpose | Purify and structurally refine metals, removing contaminants |
| Common Materials | Titanium, zirconium, superalloys |
| Key Benefits | Exceptional purity, uniform grain structure, removal of volatile impurities |
| Limitations | Cannot be used for alloying; slow, energy-intensive, and expensive |
| Typical Applications | Jet engine components, medical implants, aerospace fasteners |
Need high-purity metal solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for metals like titanium and superalloys. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















