In essence, the scalability of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces allows a single, proven process to transition seamlessly from initial laboratory research to full-scale industrial manufacturing. This is achieved through system designs that maintain critical process parameters—like temperature, pressure, and gas composition—even as the substrate size or batch quantity increases. This ensures the material properties perfected in a small-scale lab setting can be reliably reproduced at a massive commercial scale.
The core value of CVD furnace scalability is not just about producing more, but about preserving the integrity and quality of the final material as production volume grows. It bridges the gap between scientific discovery and industrial application.

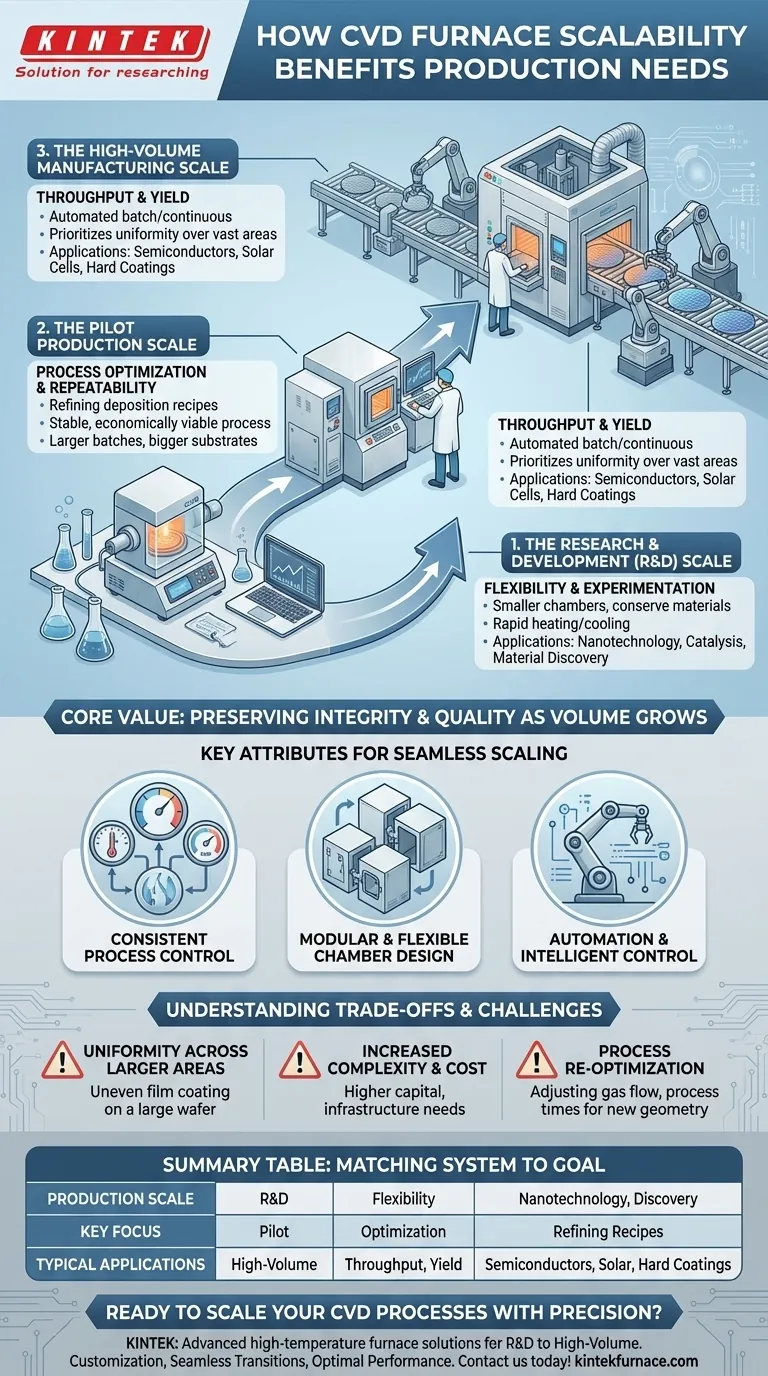
From Lab Bench to Factory Floor: The Spectrum of Scalability
A key strength of CVD technology is its adaptability to different stages of a product lifecycle. The furnace design and operation can be tailored for vastly different throughput requirements without fundamentally altering the deposition chemistry.
The Research & Development (R&D) Scale
At this initial stage, furnaces are designed for maximum flexibility. They typically feature smaller chambers to conserve expensive precursor materials and enable rapid heating and cooling cycles.
The goal here is experimentation. Researchers can quickly test new material combinations, process parameters, and substrate types, making these systems ideal for novel material discovery and academic work in fields like nanotechnology and catalysis.
The Pilot Production Scale
This is the intermediate step between the lab and full production. Pilot-scale furnaces are larger and focus on process optimization and repeatability.
Engineers use these systems to refine the deposition recipe for consistency across slightly larger batches or bigger substrates. The focus shifts from discovery to establishing a stable, reliable, and economically viable process before committing to major capital investment.
The High-Volume Manufacturing Scale
At the industrial level, scalability means maximizing throughput and yield. These CVD systems are often large, automated batch furnaces or continuous processing tools integrated directly into a production line.
Here, the design prioritizes uniformity over vast areas, high deposition rates, and minimal downtime. This scale is essential for industries like semiconductor fabrication, solar cell manufacturing, and applying hard coatings to cutting tools, where cost per unit is a critical driver.
Key Attributes That Enable Seamless Scaling
True scalability is not an accident; it is an engineered outcome built on several core principles of CVD system design.
Consistent Process Control
The ability to scale a process relies on maintaining precise control over the deposition environment. Advanced CVD systems ensure that temperature uniformity, pressure stability, and gas flow dynamics are managed with extreme precision, regardless of chamber size.
Modular and Flexible Chamber Design
Modern furnaces are often built with a modular approach. A process developed in a single-wafer R&D chamber can be transferred to a large-scale batch furnace that holds dozens or hundreds of wafers. This design philosophy ensures the core physics and chemistry of the deposition remain consistent.
Automation and Intelligent Control
In high-volume manufacturing, automation is non-negotiable for scalability. Automated wafer handling, recipe execution, and data logging eliminate human variability, ensuring every batch is processed under identical conditions. This guarantees the high yield and quality required for commercial products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, scaling a CVD process is not without its engineering challenges. Recognizing these trade-offs is crucial for successful implementation.
Uniformity Across Larger Areas
As the substrate size or batch load increases, maintaining perfect uniformity in film thickness and composition becomes significantly more difficult. Gas flow patterns and temperature gradients can emerge in larger chambers, requiring sophisticated engineering solutions to mitigate.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Larger, automated systems carry a higher capital cost and are more complex to operate and maintain. The infrastructure required for gas delivery, vacuum pumping, and safety systems also scales, representing a significant investment.
Process Re-optimization
Simply "making the chamber bigger" rarely works. A process validated in an R&D tool almost always requires re-optimization for a production tool. Gas flow rates, process times, and temperature profiles may need to be adjusted to achieve the same results in a different geometry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal CVD system is defined by your ultimate goal. By matching the furnace's capabilities to your production needs, you can ensure an efficient and effective outcome.
- If your primary focus is novel material discovery or academic research: Prioritize a flexible, small-scale R&D system that allows for rapid experimentation with minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor fabrication or optical coatings: Select a system renowned for its exceptional purity and uniformity, even if it means lower throughput with single-substrate processing.
- If your primary focus is industrial hard coatings or solar cell production: Invest in a large-batch or continuous processing system where automation, deposition rate, and cost-per-unit are the most critical metrics.
By understanding how scalability impacts process integrity, you can strategically select a CVD system that aligns perfectly with your technical and commercial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Production Scale | Key Focus | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| R&D Scale | Flexibility and rapid experimentation | Nanotechnology, catalysis, material discovery |
| Pilot Production Scale | Process optimization and repeatability | Refining deposition recipes for larger batches |
| High-Volume Manufacturing Scale | Throughput, yield, and cost efficiency | Semiconductor fabrication, solar cells, hard coatings |
Ready to scale your CVD processes with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're in R&D, pilot production, or high-volume manufacturing, we ensure seamless transitions and optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how our scalable solutions can benefit your laboratory or industrial application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















