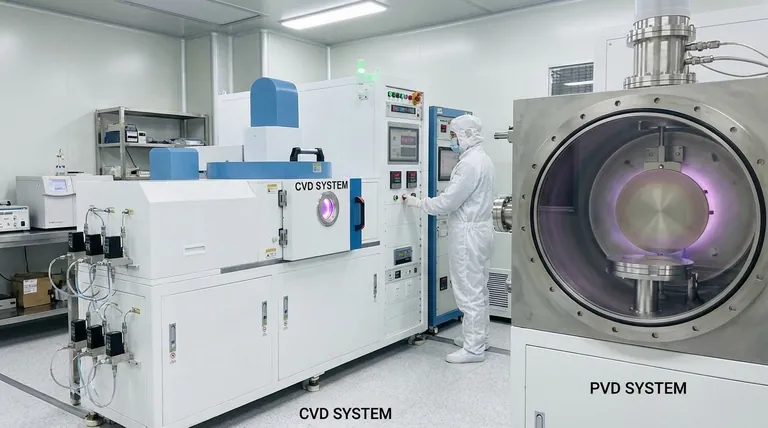
Crucially, the starting material state dictates the entire deposition process. In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the source material is introduced into the process chamber as a gas. In contrast, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) begins with the source material in a solid state, which is then converted into a vapor.
The fundamental distinction is not just the starting state of the material, but the nature of the process itself. PVD is a physical transfer of material from a solid target to a substrate, while CVD is a chemical reaction of precursor gases that creates a new solid film on the substrate.
The Fundamental Process Distinction
Understanding the initial state of the material—solid versus gas—is the key to grasping the core difference in how these two powerful coating technologies work. One is a physical state change, while the other is a chemical transformation.
PVD: A Physical Transformation
In a PVD process, a solid target material is the source for the coating. This solid is physically converted into a vapor inside a vacuum chamber.
This vaporization is typically achieved through high-energy methods like sputtering (bombarding the target with ions) or thermal evaporation (heating the material until it vaporizes).
The resulting vapor then travels through the chamber and condenses onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin film. The chemical composition of the deposited film is essentially the same as the solid target it came from.
CVD: A Chemical Reaction
In a CVD process, there is no solid target. Instead, one or more reactive gases, known as precursors, are introduced into the chamber.
These gases are heated and flow over the substrate. The elevated temperature at the substrate's surface provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction or decomposition of the precursor gases.
This reaction forms a new, solid material directly on the substrate's surface, molecule by molecule. The resulting film is a chemical product of the precursor gases, not a direct transfer of a source material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The difference between a physical transfer (PVD) and a chemical reaction (CVD) creates distinct advantages and disadvantages for each method.
Complexity and Control
PVD is a conceptually simpler process, primarily governed by physical parameters like vaporization rate, chamber pressure, and temperature.
CVD is inherently more complex. It requires precise control over gas concentrations, flow rates, and temperature gradients to manage the chemical reactions and ensure the desired film quality.
Conformality and Coverage
Because CVD uses free-flowing gases, it can deposit highly conformal coatings. This means it can uniformly coat intricate, complex shapes and even internal surfaces, as the gas can reach anywhere within the chamber.
PVD is a line-of-sight process. The vaporized material travels in a relatively straight line from the target to the substrate, making it difficult to evenly coat complex geometries or the backside of an object.
Purity and Applications
CVD can produce exceptionally high-purity and high-performance films. Since the material is built atom-by-atom from precursor gases, it allows for incredible control over the final structure. This is why CVD is essential in the semiconductor industry for producing pristine thin films.
PVD is highly versatile and generally involves fewer hazardous chemical precursors, but achieving the same level of atomic-level perfection as CVD can be more challenging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use PVD or CVD should be based on the specific requirements of your application, from geometry to material properties.
- If your primary focus is coating complex shapes uniformly or achieving the highest material purity: CVD is often the superior choice due to its chemical reaction mechanism and non-line-of-sight nature.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity, lower operating temperatures, or coating relatively flat, line-of-sight surfaces: PVD provides a more direct, often more cost-effective, and robust physical deposition route.
Ultimately, knowing whether to start with a solid or a gas is the first step in selecting the right tool for engineering a surface.
Summary Table:
| Process | Starting Material State | Key Mechanism | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | Gas | Chemical reaction of precursors | Semiconductor films, conformal coatings |
| PVD | Solid | Physical vaporization (e.g., sputtering) | Flat surfaces, tool coatings |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right high-temperature furnace for your CVD or PVD applications? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















