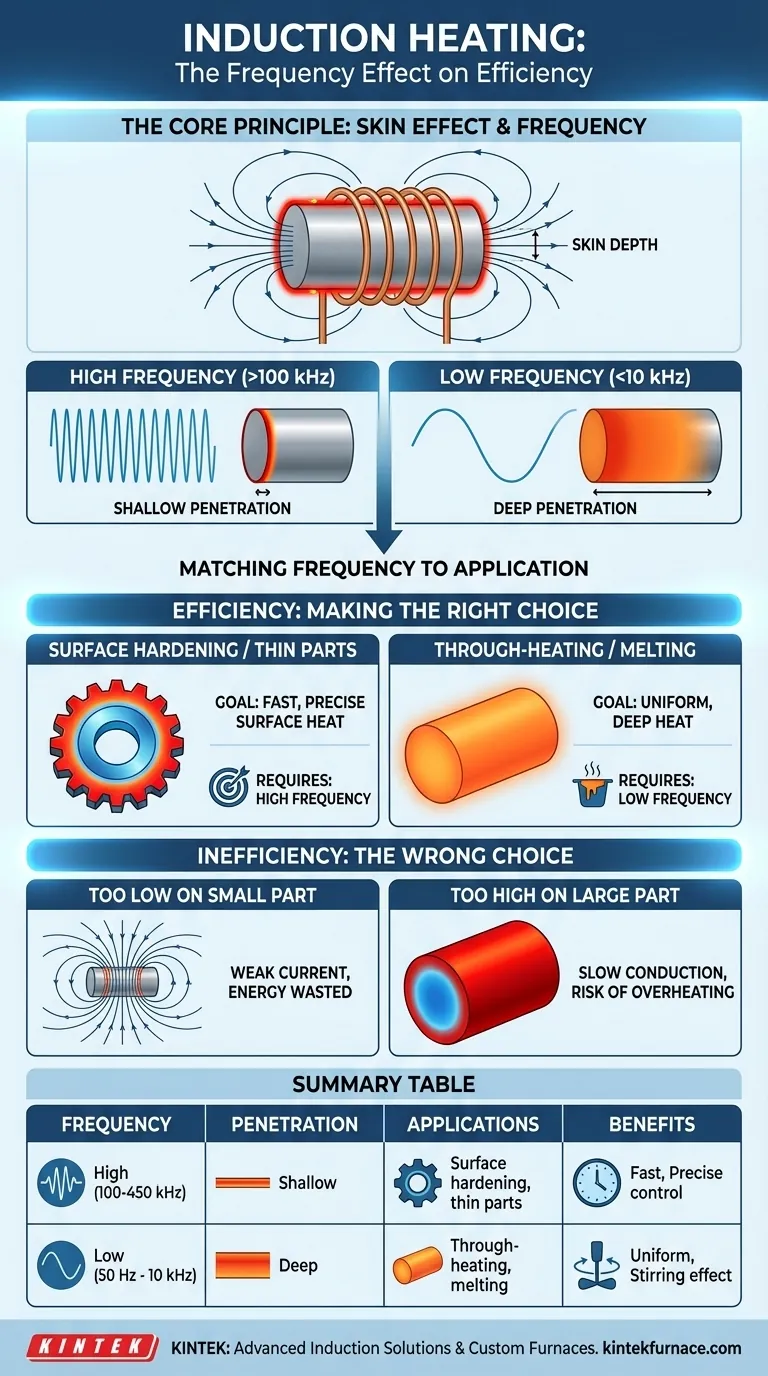
In induction heating, frequency is the single most critical parameter for controlling heating efficiency because it dictates precisely where within a material the heat is generated. Higher frequencies concentrate the heating effect near the surface, while lower frequencies allow the energy to penetrate deeper into the part. Matching the frequency to the material properties and the dimensions of the workpiece is the key to an efficient process.
The core principle is that heating efficiency depends on concentrating the induced electrical currents within the target workpiece. The frequency of the alternating magnetic field determines the "skin depth" of these currents, and for optimal energy transfer, this depth must be correctly scaled to the size of the part you are heating.
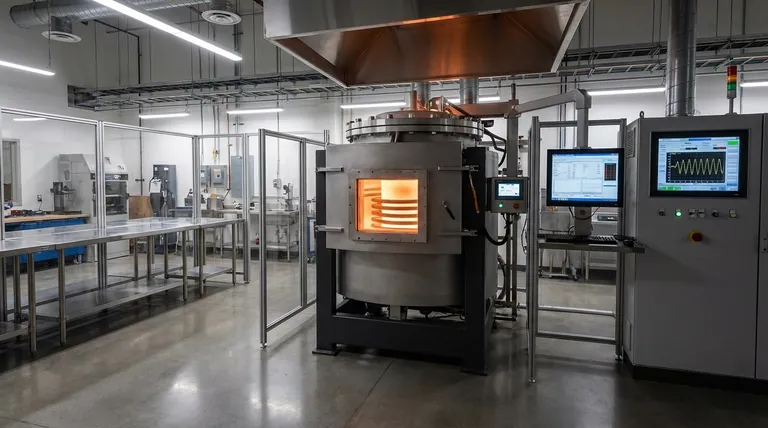

The Core Principle: Frequency and the Skin Effect
To understand efficiency, you must first understand the physics of how induction heating works. The process relies on a phenomenon known as the "skin effect."
What is the Skin Effect?
An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When you place a conductive workpiece (like steel) inside this field, it induces electrical currents within the part, known as eddy currents.
These eddy currents are not uniform. They are strongest at the surface of the workpiece and their density decreases exponentially toward the center. This concentration of current on the "skin" of the material is the skin effect. The resistance of the metal to the flow of these currents is what generates precise, instantaneous heat.
How Frequency Controls Penetration Depth
The frequency of the alternating current in the coil directly controls how deep this "skin" of eddy currents is. The relationship is simple and inverse:
- High Frequency (e.g., 100 kHz - 450 kHz) creates a very thin skin, concentrating the current and heating effect in a shallow layer near the surface.
- Low Frequency (e.g., 50 Hz - 10 kHz) creates a much thicker skin, allowing the current and heating to penetrate deep into the core of the material.
The term for this is penetration depth or reference depth. It is the depth at which the induced current has fallen to about 37% of its value at the surface. Approximately 86% of the total heat is generated within this single layer of depth.
Matching Frequency to Your Application
The goal is to select a frequency that places the heat exactly where you need it for your specific process. An efficient process is one where the generated heat aligns with the thermal goal.
For Surface Hardening and Thin Parts
For applications like surface hardening gears or bearings, the objective is to heat only the outer surface to a high temperature very quickly, leaving the core cool and ductile.
This requires high frequencies. A shallow penetration depth ensures that energy is focused exclusively on the surface, minimizing the time needed for the heat to soak into the core and maximizing speed and control.
For Through-Heating and Melting
For applications like heating a large billet for forging or melting a full crucible of metal, the goal is to heat the entire volume of the material as uniformly as possible.
This requires low to medium frequencies. A deeper penetration depth ensures that energy is generated throughout a significant portion of the part's cross-section. This promotes more uniform heating and, in the case of melting, helps create an electromagnetic stirring effect that improves melt consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inefficiencies
Choosing the wrong frequency leads directly to wasted energy and poor results. The relationship between part size and penetration depth is critical. A widely used rule of thumb is that the part's diameter should be at least four to eight times the penetration depth for good efficiency.
The Problem with a Frequency That's Too Low
If you use a low frequency on a very small part, the penetration depth can be larger than the part itself.
In this scenario, the magnetic field passes through the part with very little resistance, inducing only weak eddy currents. Most of the energy from the coil is not "captured" by the workpiece, resulting in extremely poor efficiency and slow heating.
The Problem with a Frequency That's Too High
If you use a high frequency on a very large part intended for through-heating, you create intense heat only at the surface.
You are then forced to rely on slow thermal conduction to carry that heat to the core of the part. This is highly inefficient, wastes energy into the surrounding environment, and risks overheating, melting, or damaging the surface long before the core reaches the target temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct frequency is a function of your material, your part geometry, and your ultimate process objective.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or heating thin materials: Choose high to very high frequencies (100 kHz and above) to create a shallow heating depth.
- If your primary focus is through-heating large parts for forging or forming: Choose low frequencies (typically below 10 kHz) to ensure deep and uniform heat penetration.
- If your primary focus is melting metal in a furnace: Use a low to medium frequency that is scaled to the furnace diameter to promote deep penetration and beneficial electromagnetic stirring.
Ultimately, mastering frequency selection transforms induction from a simple heating method into a precise and highly efficient manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Penetration Depth | Ideal Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (100 kHz - 450 kHz) | Shallow | Surface hardening, thin parts | Fast surface heating, precise control |
| Low (50 Hz - 10 kHz) | Deep | Through-heating, melting large parts | Uniform heating, electromagnetic stirring |
Struggling with inefficient heating in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including induction systems tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise frequency matching and optimal efficiency for your unique experiments. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















