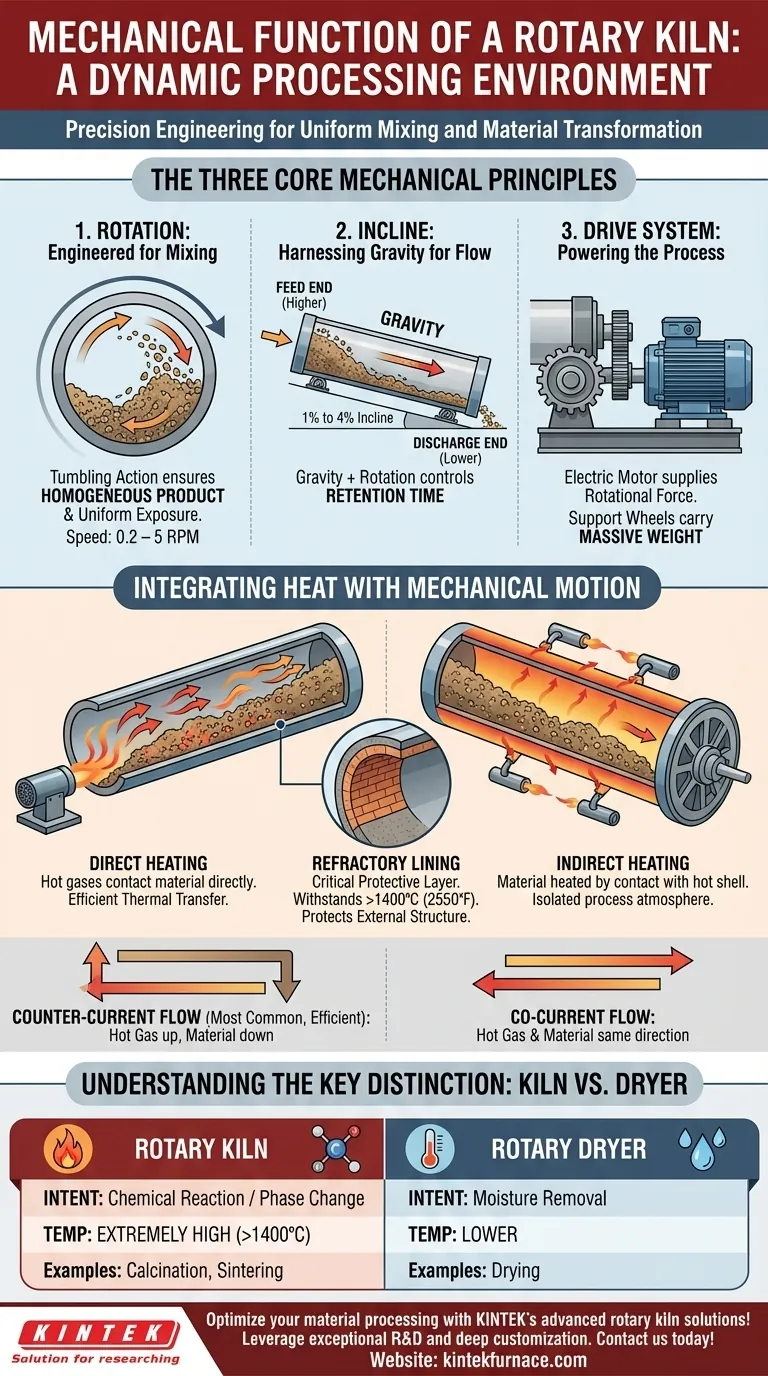
At its core, a rotary kiln is a finely-tuned mechanical system that uses a combination of slow rotation and a slight gravitational incline to process materials. It consists of a large, rotating cylindrical drum mounted on bearings or support wheels. As the drum turns, material fed into the higher end tumbles and mixes as it slowly moves downward toward the discharge end, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to a controlled, high-temperature environment.
A rotary kiln is not merely a heated tube; it is a dynamic processing environment. Its mechanical design—specifically the interplay between rotation and inclination—is deliberately engineered to continuously mix and advance material, guaranteeing uniform heat exposure to trigger a desired chemical reaction or phase change.
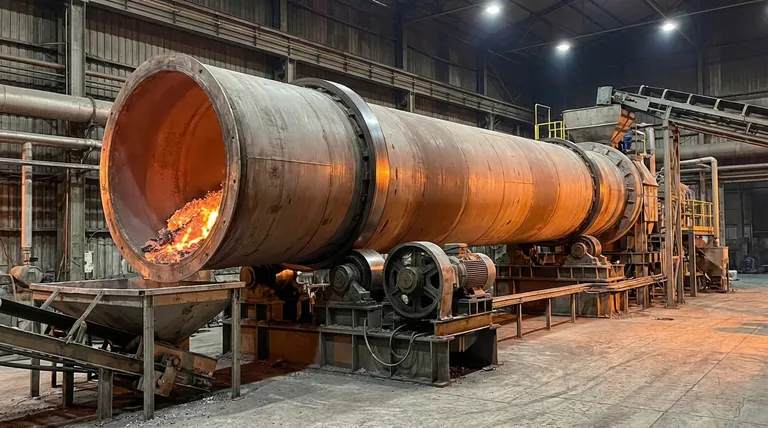

The Core Mechanical Principles
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln is rooted in three fundamental mechanical actions working in concert: rotation, incline, and the drive system that enables them.
The Rotating Drum: Engineered for Mixing
The slow, constant rotation of the kiln's cylindrical body is its most critical mechanical feature. This movement, typically between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (rpm), forces the material inside to cascade, or tumble.
This tumbling action is essential for achieving a homogeneous product. It continuously exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source, preventing hot spots and ensuring the entire batch is processed evenly.
The Incline: Harnessing Gravity for Controlled Flow
A rotary kiln is always installed at a slight angle, typically between 1% and 4% from horizontal. This incline is a simple but brilliant mechanical control.
As the drum rotates, gravity pulls the tumbling material from the higher feed end toward the lower discharge end. The steepness of this slope, combined with the rotation speed, precisely dictates the retention time—how long the material spends inside the kiln.
The Drive System: Powering the Process
The entire system is powered by a robust drive train. An electric motor provides the rotational force, which is transferred to the kiln body.
The massive weight of the drum is supported by bearings or a series of support wheels. This heavy-duty assembly is designed for continuous operation under extreme thermal and mechanical stress.
Integrating Heat with Mechanical Motion
The mechanical design of the kiln exists to support its primary thermal purpose. The way heat is introduced and managed is intrinsically linked to the kiln's physical structure.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A kiln can be heated in one of two ways. In a direct-fired kiln, hot gases from a burner flow directly through the inside of the drum, making contact with the material.
In an indirect-fired kiln, the drum is heated from the outside. The material inside is heated by contact with the hot shell wall, keeping it isolated from the combustion gases. This is crucial when the process atmosphere must be tightly controlled.
Counter-Current vs. Co-Current Flow
In direct-fired kilns, the direction of gas flow is a key design choice. The most common and thermally efficient method is counter-current flow. Here, the burner is at the discharge end, and hot gases flow up the kiln against the downward movement of the material.
Less common is co-current flow, where the hot gas enters at the feed end and moves in the same direction as the material.
The Refractory Lining: A Critical Protective Layer
The inside of the kiln's metal shell is lined with a refractory lining. This layer of heat-resistant brick or castable material is a critical mechanical component.
It protects the external steel structure from the extreme internal temperatures, which can often exceed 1400°C (2550°F), preventing structural failure.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Kiln vs. Dryer
While they appear mechanically similar, a rotary kiln and a rotary dryer serve fundamentally different purposes, which dictates their design and operation.
The Role of Temperature
The primary differentiator is temperature. Rotary dryers operate at lower temperatures with the sole goal of removing moisture from a material.
Rotary kilns, by contrast, use extremely high temperatures to cause a chemical reaction or phase change. This includes processes like calcination, sintering, or thermal desorption, which fundamentally alter the material's properties.
The Difference in Intent
Think of it this way: a dryer changes a material's state by removing water. A kiln changes its chemical identity. This difference in intent drives all other design considerations, from the type of refractory lining to the required heat input and retention time.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Understanding these mechanical principles is key to selecting and operating the right equipment for your industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is inducing a chemical reaction or phase change: You require a rotary kiln, as its high-temperature design and controlled retention time are essential for driving these transformations.
- If your primary focus is simply removing moisture: A lower-temperature rotary dryer is the more appropriate and energy-efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency: A counter-current heating design is generally the superior mechanical configuration for a direct-fired kiln.
By grasping these fundamental concepts, you can see the rotary kiln not as a brute-force heater, but as a precise instrument of material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Mechanical Component | Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Drum | Mixes and tumbles material | 0.2-5 rpm for uniform exposure |
| Incline | Controls material flow via gravity | 1-4% slope for retention time |
| Drive System | Powers rotation | Electric motor with support wheels |
| Heating Method | Applies heat for processing | Direct or indirect firing options |
| Refractory Lining | Protects structure from high heat | Withstands >1400°C temperatures |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your industrial goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















