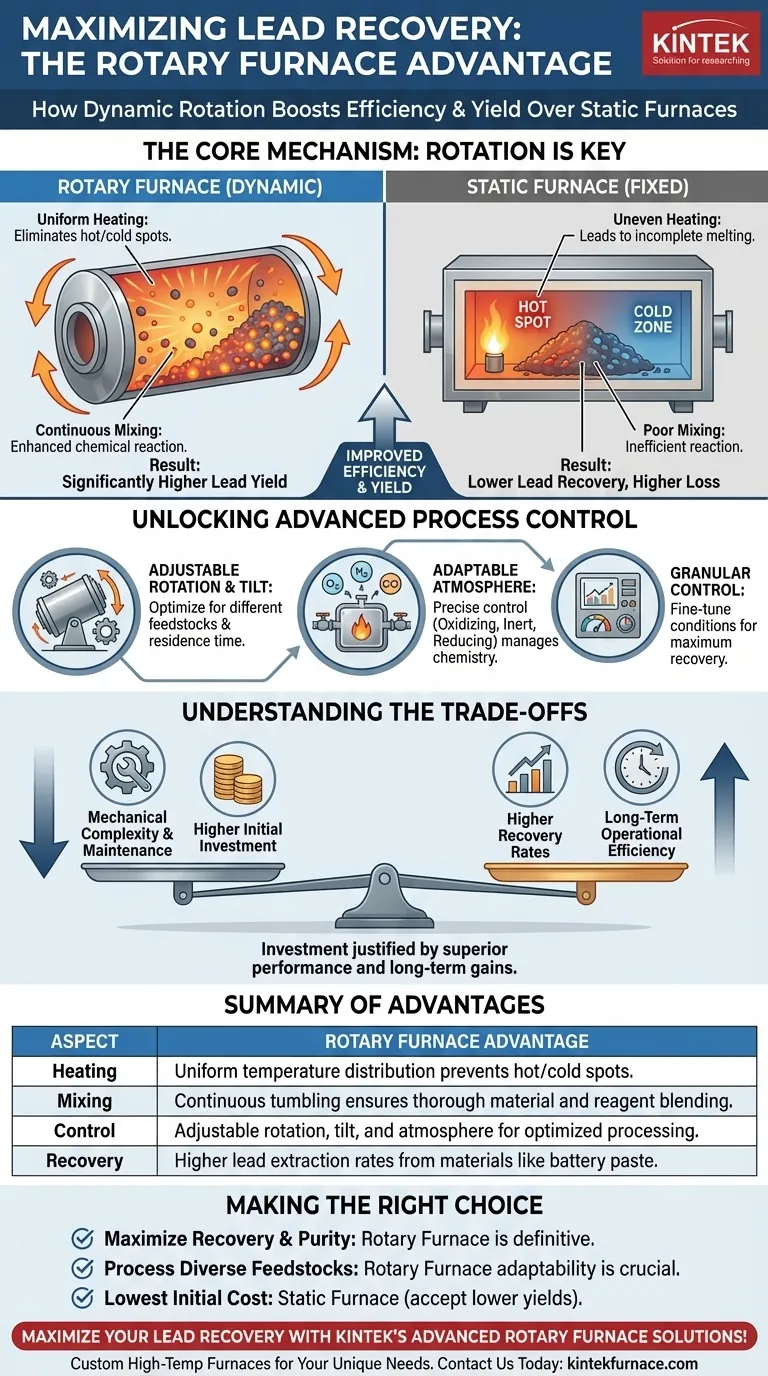
In short, a rotary furnace improves lead recovery by using rotation to ensure materials are heated uniformly and mixed thoroughly. This dynamic process allows a significantly larger percentage of lead to be extracted from raw materials like battery paste and scrap compared to static blast or fixed furnaces, directly boosting operational efficiency and yield.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary furnace is not just its heat, but its motion. By continuously tumbling the material, it solves the chronic problems of uneven heating and poor reactant mixing that limit the performance of traditional, stationary furnaces.

The Core Mechanism: Why Rotation is a Game Changer
To understand why rotary furnaces excel, we must look beyond simply melting the material. Effective lead recovery is a complex process of heat transfer and chemical reaction, both of which are dramatically improved by the furnace's rotational design.
Achieving Superior Temperature Uniformity
In a traditional fixed or blast furnace, heat is applied from a stationary source. This often creates hot spots near the flame and cold spots in dense, unexposed areas of the material load.
Lead trapped in these colder zones may not melt or react properly, resulting in it being lost to the slag. A rotary furnace eliminates this by constantly tumbling the charge, ensuring every particle is regularly exposed to the heat source. This uniform heating is critical for complete processing.
Enhancing Material Mixing and Reaction
Lead recovery relies on chemical reactions, often using fluxes and reducing agents to separate the lead from oxides and other impurities. The tumbling action of a rotary furnace acts as a highly efficient mechanical mixer.
This continuous mixing ensures that fluxes and other reagents are intimately combined with the lead-bearing materials. The result is a faster, more complete chemical reaction, which directly translates to a higher percentage of recovered lead metal.
Unlocking Advanced Process Control
Modern rotary furnaces offer operators a level of control that is simply not possible with older, static designs. This granular control allows for process optimization that further enhances recovery rates.
Precision Through Adjustable Rotation and Tilt
Operators can fine-tune the speed of rotation and the angle of the furnace tilt. A faster rotation can increase mixing for certain materials, while a specific tilt angle can control how long the material stays in the furnace.
This adaptability allows the process to be optimized for different types of feedstock, from fine battery paste to larger pieces of metallic scrap, ensuring ideal conditions for each.
Adaptable Atmosphere Control
The enclosed nature of a rotary furnace allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere. Operators can maintain an oxidizing, inert, or reducing atmosphere as needed.
This is vital for managing the complex chemistry of smelting. For example, a reducing atmosphere can be used to convert lead oxide back to metallic lead, preventing its loss and maximizing the final yield.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, the rotary furnace design is not without its considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging its specific operational characteristics.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating seals, drive system, and tilting mechanism introduce mechanical complexity. These components require a more rigorous maintenance schedule compared to the simpler construction of a static furnace to ensure reliability and prevent leaks.
Higher Initial Investment
The sophisticated engineering, motor, and sealing systems of a rotary furnace typically result in a higher initial capital cost compared to a basic fixed furnace. This investment is justified by the higher recovery rates and long-term operational efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary furnace should be based on your specific operational priorities and feedstock.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lead recovery and achieving high purity: The rotary furnace is the definitive choice due to its unparalleled process control and uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or inconsistent feedstocks: The adaptability of a rotary furnace's rotation speed, tilt, and atmosphere provides a crucial advantage over less flexible systems.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible initial capital cost: A traditional fixed furnace may be an option, but you must accept the trade-off of lower yields and reduced process efficiency.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace's design directly solves the core inefficiencies of static smelting, making it the superior technology for modern, high-yield lead recovery operations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Rotary Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heating | Uniform temperature distribution prevents hot/cold spots |
| Mixing | Continuous tumbling ensures thorough material and reagent blending |
| Control | Adjustable rotation, tilt, and atmosphere for optimized processing |
| Recovery | Higher lead extraction rates from materials like battery paste |
Maximize your lead recovery efficiency with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, boosting yield and operational performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















